(Press-News.org) Electric bicycle rebates have exploded in popularity in North America as transportation planners try to get people out of their cars and into healthier, more climate-friendly alternatives. However, there is limited understanding of the full impacts of these incentives.
Are new cycling habits sustainable? Who benefits most from these incentives? And are they worth the cost?
Researchers at UBC’s Research on Active Transportation (REACT) Lab have some answers. They surveyed participants in an e-bike incentive program offered by the District of Saanich, B.C. and found that most new e-bike users continued to regularly use their bikes as a substitute for car travel, even a year after purchase. Low-income households reduced their car trips and decreased carbon emissions the most. And incentives are a cost-effective way of reducing carbon emissions.
Reduced car travel
The Saanich program, available in 2021 and 2022, offered three different rebates to offset the cost of new e-bikes, depending on one’s income. The basic rebate amounted to $350, while the lowest-income households could receive up to $1,600.
Results showed a significant surge in e-bike adoption, with 93 per cent of users being new to e-bikes, and 60 per cent new to cycling altogether.
One year after purchase, users continued to be satisfied with their e-bikes, integrating them into their routines for three to four days a week. They reduced weekly car travel by an average of 48 kilometres per week, a reduction of 30-40 per cent.
“The incentive not only encouraged people to switch to e-bikes, it also resulted in remarkable changes in travel behaviour that persisted long after the purchase,” said Dr. Alex Bigazzi, principal investigator and associate professor of civil engineering at UBC who leads REACT.
The incentives had the greatest impact on lower-income groups. Among those who received the $1,600 incentive, eight out of 10 would not have purchased an e-bike without it, compared to just two out of 10 who received the $350 incentive.
Lower carbon emissions
With less driving, users reduced their travel-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by an average of 16 kilograms of CO2 per week, one year after buying their e-bikes. Notably, those who received the biggest incentives reduced car use and carbon emissions the most.
“The larger incentives aimed at lower-income families did a great job getting new riders in the saddle and gave them a lower-cost alternative to using their cars,” Dr. Bigazzi said.
More cost-effective than EV rebates
A common criticism of e-bike incentives is their high cost relative to their climate benefits, but the Saanich program was competitive with other transportation subsidies in Canada at a cost of approximately $190 to $720 per tonne of GHG emissions.
“This suggests that e-bike incentives are more cost-effective in reducing emissions compared to electric car incentives, and that’s without including a range of cycling-related benefits such as increased physical activity, reduced local air pollutants and decreased travel costs,” Dr. Bigazzi said.
The REACT Lab has partnered with the Province of B.C. and other researchers to study the provincewide e-bike incentive program. The broader scope will allow researchers to look at factors including variations in climate and terrain and the availability of safe cycling routes, to better understand their influences.
Interview language(s): English
Images: Dropbox
END
E-bike incentives prove to be worth the investment
UBC study finds rebate program significantly reduced car travel and carbon emissions
2024-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
2024-04-30
With the help of a form of machine learning called deep reinforcement learning (DRL), the EPFL robot notably learned to transition from trotting to pronking – a leaping, arch-backed gait used by animals like springbok and gazelles – to navigate a challenging terrain with gaps ranging from 14-30cm. The study, led by the BioRobotics Laboratory in EPFL’s School of Engineering, offers new insights into why and how such gait transitions occur in animals.
“Previous research has introduced energy efficiency and musculoskeletal injury avoidance as the two main explanations ...
Lundquist investigator Dr. Ashraf Ibrahim is the lead author in the landmark study on pioneering oral fungal infection treatment showing promise in preclinical trials
2024-04-30
A novel oral amphotericin B (MAT2203) developed by Matinas BioPharma for treatment of invasive mucormycosis (IM) and other deadly invasive fungal infections, has demonstrated encouraging results in a series of preclinical studies. The groundbreaking research, led by Lundquist Institute (TLI) Investigator Ashraf Ibrahim, PhD, has been published in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
The studies focused on MAT2203, an oral lipid nanocrystal formulation of amphotericin B, which has previously demonstrated safety and effectiveness in the clinical treatment of various fungal infections. The research aimed ...
Deep-learning decoding for a noninvasive brain-computer interface
2024-04-30
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have the potential to make life easier for people with motor or speech disorders, allowing them to manipulate prosthetic limbs and employ computers, among other uses. In addition, healthy and impaired people alike could enjoy BCI-based gaming. Non-invasive BCIs that work by analyzing brain waves recorded through electroencephalography are currently limited by inconsistent performance. Bin He and colleagues used deep-learning decoders to improve a BCI’s performance responding to ...
Elucidating the role of a shared lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in exacerbating Parkinson’s disease symptoms in the context of COVID-19 infection
2024-04-30
Background and objectives
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder with unclear molecular mechanisms. Noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), have been identified as critical regulators of gene expression. This study aimed to investigate the triple network of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA, known as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), and to identify essential lncRNAs that regulate PD-related gene expression through their target miRNAs. The study also identified a common triple network between COVID-19 and PD that may contribute to exacerbating PD symptoms.
Methods
A bioinformatics approach was employed to construct ...
American College of Lifestyle Medicine announces unique screening tool for clinicians to efficiently assess patient dietary patterns
2024-04-30
The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) has developed a clinical tool to help health care professionals incorporate a food as medicine approach into their practice by assessing and tracking the proportion of whole, unrefined plant-based foods and water intake in their patients’ dietary patterns.
The ACLM Diet Screener, a 27-item diet assessment tool available free on ACLM’s website, was designed to guide clinical conversations around diet and support nutrition prescriptions, while also being brief enough for use during routine ...
Cranberry extracts could boost microbiota and counter cardiometabolic diseases
2024-04-30
Québec, April 30, 2024 - Cranberry extracts appear to improve intestinal microbiota and help prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The study of Université Laval and the Institute of Nutrition and Functional Foods (INAF) reported beneficial effects after only four days of use.
Cranberries and berries are associated with multiple health benefits, mainly attributed to their high content of polyphenols, in the form of tannins. They also contain high concentrations of oligosaccharides, small fibres that are thought to contribute to their bioactivity.
The research team, led by Yves Desjardins, professor ...
Discovery of uranium-contaminated soil purification material without secondary environmental pollution
2024-04-30
Nuclear energy has long been regarded as a next-generation energy source, and major countries around the world are competing to secure cutting-edge technologies by leveraging the high economic efficiency and sustainability of nuclear power. However, uranium, which is essential for nuclear power generation, has serious implications for both soil ecosystems and human health. Despite being a key radioactive material, uranium poses significant health risks due to its chemical toxicity to the kidneys, bones, and cells. As a result, both the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the World Health Organization recommend allowing and advocating for uranium concentrations in wastewater ...
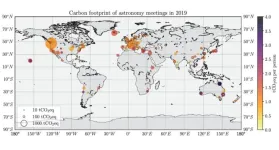
The carbon emissions of academic astronomy
2024-04-30
The carbon emissions associated with air travel to professional conferences make up a sizable fraction of the emissions produced by academia. Andrea Gokus and colleagues estimated the CO2-equivalent emissions for conference travel to all 362 open meetings in the field of astronomy in 2019. The total is an estimated 42,500 tCO2e, or about one ton per participant per meeting. According to the authors, networking and discussing new scientific developments at meetings is important for advancing the field, but adjustments can be made to reduce the hefty carbon cost. Holding meetings virtually ...
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis articles reveal the importance of phytocompounds and metabolomics analysis
2024-04-30
IBD is a common chronic gastrointestinal disorder and current treatment strategies can cause adverse effects. Thus, there is a need to identify alternative compounds to treat IBD. Similarly, the dose-related toxicity and efficacy of anticancer drugs needs to be monitored accurately to improve the treatment outcomes. Moreover, over the years, plant-based therapeutic compounds and traditional Chinese medicine formulas have gained attention for their enhanced healing effects and are promising for various treatment regimens.
The recent issue of the JPA, published ...
Great strides in the development of high refractive index polymers for optoelectronics
2024-04-30
Optoelectronic devices have found their way into many aspects of our daily lives, from OLED displays to photodetectors, security systems, and environmental monitoring. In all the applications, these devices utilize high refractive index polymers (HRIPs) to control light.
In general, the optical properties of transparent HRIPs enable efficient light transmission and manipulation, allowing optoelectronics devices to guide and control the flow of light to improve their performance. However, there are no low-cost options for HRIPs that can guarantee good optical performance while being transparent and environmentally ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] E-bike incentives prove to be worth the investmentUBC study finds rebate program significantly reduced car travel and carbon emissions