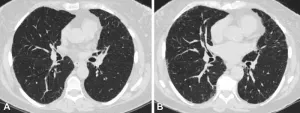
(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Smokers who have small abnormalities on their CT scans that grow over time have a greater likelihood of experiencing acute respiratory disease events, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Quantitative interstitial abnormalities (QIA) are subtle abnormalities on chest CTs that do not meet the diagnostic criteria for advanced pulmonary diseases but are nonetheless associated with decreased lung function and capacity, increased respiratory symptoms and death.
“QIA includes features like reticulation and ground-glass opacities as well as subtle density changes with important clinical implications,” said Bina Choi, M.D., associate physician in the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and postdoctoral fellow at the Applied Chest Imaging Laboratory, Harvard Medical School in Boston. “In some patients, QIA may be a precursor to advanced diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis or emphysema.”
Acute respiratory disease events are episodes of increased cough, phlegm or shortness of breath that last at least two days and require treatment with steroids or antibiotics. Severe acute respiratory disease episodes require an emergency room visit or hospitalization.
“We wanted to determine whether progression in QIA on chest CT is associated with acute respiratory disease events in individuals with a history of smoking,” Dr. Choi said. “While many acute respiratory disease events are likely related to airway disease and COPD, some may instead be associated with QIA especially in people without obstruction or emphysema.”
Dr. Choi’s team performed a secondary analysis of the CT scans of 3,972 participants (mean age 60.7; 2,120 women) in the COPDGene® Study, one of the largest studies ever to investigate the underlying genetic factors of COPD. The study included individuals with a 10-pack-year or greater smoking history recruited from multiple centers between November 2007 and July 2017.
QIA was measured with machine learning-based tools as a percentage of lung volume on a CT scan. QIA progression was assessed using the participants’ QIA measurements at baseline and five-year follow-up CT exams.
Statistical analyses revealed that participants in the highest quartile of QIA progression had more frequent acute respiratory disease and severe acute respiratory disease events than those in the lowest quartile.
“We found that progression in QIA is independently associated with these acute respiratory disease events both intercurrent and subsequent to progression,” she said.
Dr. Choi said the results suggest that QIA progression may represent changes in lung tissue processes that have both short- and long-term impacts on patient symptoms and the worsening of those symptoms.
“Severe acute respiratory disease events may be a sign of disease activity and a source of morbidity at the earliest stages of lung tissue injury,” she said. “Some people with QIA progression may merit more aggressive monitoring and earlier intervention.”
###
“Association of Acute Respiratory Disease Events with Quantitative Interstitial Abnormality Progression at CT in Individuals with a History of Smoking.” Collaborating with Dr. Choi were Alejandro A. Diaz, M.D., M.P.H., Ruben San José Estépar, M.S., Nicholas Enzer, B.S., Victor Castro, B.A., MeiLan K. Han, M.D., M.S., George R. Washko, M.D., M.M.Sc., Raúl San José Estépar, Ph.D., and Samuel Y. Ash, M.D., M.P.H., for the COPDGene Study
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on chest CT, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts.
Pole-top fires pose significant challenges to power providers and communities worldwide. In March, pole-top fires cut power from 40,000 homes and businesses in Perth.
The 2020 Royal Commission into National Natural Disaster Arrangements found that power outages experienced by 280,000 customers from various energy providers during Black Summer fires were mainly triggered by events involving insulators ...
A team of astronomers and citizen scientists has discovered a planet in the habitable zone of an unusual star system, including two stars and potentially another exoplanet.
The planet hunters spotted the Neptune-like planet as it crossed in front of its host star, temporarily dimming the star’s light in a way akin to a solar eclipse on Earth. This ‘transit method’ usually identifies planets with tight orbits, as they are more likely to follow paths that put them between Earth and their host star and, when following such paths, move into light-blocking positions more frequently. That’s why this newly discovered planet is ...
WASHINGTON, DC (April 30, 2024)—Tambourine Philanthropies (Tambourine), in partnership with the Milken Institute Science Philanthropy Accelerator for Research and Collaboration (SPARC), is pleased to announce the recipients of its ALS Breakthrough Research Fund. Tambourine has committed over $5 million total to eight teams around the world for basic and discovery-focused research aiming to change how we understand and treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Tambourine launched the ALS Breakthrough Research ...
Electric bicycle rebates have exploded in popularity in North America as transportation planners try to get people out of their cars and into healthier, more climate-friendly alternatives. However, there is limited understanding of the full impacts of these incentives.
Are new cycling habits sustainable? Who benefits most from these incentives? And are they worth the cost?
Researchers at UBC’s Research on Active Transportation (REACT) Lab have some answers. They surveyed participants in an e-bike incentive program offered by the District of ...
With the help of a form of machine learning called deep reinforcement learning (DRL), the EPFL robot notably learned to transition from trotting to pronking – a leaping, arch-backed gait used by animals like springbok and gazelles – to navigate a challenging terrain with gaps ranging from 14-30cm. The study, led by the BioRobotics Laboratory in EPFL’s School of Engineering, offers new insights into why and how such gait transitions occur in animals.
“Previous research has introduced energy efficiency and musculoskeletal injury avoidance as the two main explanations ...
A novel oral amphotericin B (MAT2203) developed by Matinas BioPharma for treatment of invasive mucormycosis (IM) and other deadly invasive fungal infections, has demonstrated encouraging results in a series of preclinical studies. The groundbreaking research, led by Lundquist Institute (TLI) Investigator Ashraf Ibrahim, PhD, has been published in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
The studies focused on MAT2203, an oral lipid nanocrystal formulation of amphotericin B, which has previously demonstrated safety and effectiveness in the clinical treatment of various fungal infections. The research aimed ...
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have the potential to make life easier for people with motor or speech disorders, allowing them to manipulate prosthetic limbs and employ computers, among other uses. In addition, healthy and impaired people alike could enjoy BCI-based gaming. Non-invasive BCIs that work by analyzing brain waves recorded through electroencephalography are currently limited by inconsistent performance. Bin He and colleagues used deep-learning decoders to improve a BCI’s performance responding to ...
Background and objectives
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder with unclear molecular mechanisms. Noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), have been identified as critical regulators of gene expression. This study aimed to investigate the triple network of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA, known as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), and to identify essential lncRNAs that regulate PD-related gene expression through their target miRNAs. The study also identified a common triple network between COVID-19 and PD that may contribute to exacerbating PD symptoms.
Methods
A bioinformatics approach was employed to construct ...
The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) has developed a clinical tool to help health care professionals incorporate a food as medicine approach into their practice by assessing and tracking the proportion of whole, unrefined plant-based foods and water intake in their patients’ dietary patterns.
The ACLM Diet Screener, a 27-item diet assessment tool available free on ACLM’s website, was designed to guide clinical conversations around diet and support nutrition prescriptions, while also being brief enough for use during routine ...
Québec, April 30, 2024 - Cranberry extracts appear to improve intestinal microbiota and help prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The study of Université Laval and the Institute of Nutrition and Functional Foods (INAF) reported beneficial effects after only four days of use.
Cranberries and berries are associated with multiple health benefits, mainly attributed to their high content of polyphenols, in the form of tannins. They also contain high concentrations of oligosaccharides, small fibres that are thought to contribute to their bioactivity.
The research team, led by Yves Desjardins, professor ...