(Press-News.org) Four proposed state-of-the art image search engines for automating search and retrieval of digital histopathology slides were found to be of inadequate performance for routine clinical care, new research suggests.
The performance of the artificial intelligence algorithms to power the histopathology image databases was worse than expected, with some having less than 50% accuracy, which is not suitable for clinical practice, said Dr. Helen Shang, a third-year internal medicine resident and incoming hematology-oncology fellow at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
“Currently, there are many AI algorithms being developed for medical tasks but there are fewer efforts directed on rigorous, external validations,” said Shang, who co-led the study with Dr. Mohammad Sadegh Nasr of the University of Texas at Arlington. “The field has also yet to standardize how AI algorithms should be best tested prior to clinical adoption.”
The paper is published in the peer-reviewed journal NEJM AI.
As it now stands, pathologists manually search and retrieve histopathology images, which is very time consuming. As result, there has been growing interest in developing automated search and retrieval systems for the digitized cancer images.
The researchers designed a series of experiments to evaluate the accuracy of search engine results on tissue and subtype retrieval tasks on real-world UCLA cases and larger, unseen datasets. The four engines examined are Yottixel, SISH, RetCCL, HSHR. Each takes a different approach toward indexing, database generation, ranking and retrieval of images.
Overall, the researchers found inconsistent results across the four algorithms – for instance, Yottixel performed best on breast tissue, while RetCCL had the highest performance on brain tissue. They also found that a group of pathologists found search engine results to be of low to average quality with several visible errors.
The researchers are devising new guidelines to standardize the clinical validation of AI tools, Shang said. They are also developing new algorithms that leverage a variety of different data types to develop more reliable and accurate predictions.
“Our studies show that despite amazing progress in artificial intelligence over the past decade, significant improvements are still needed prior to widespread uptake in medicine,” Shang said. “These improvements are essential in order to avoid doing patients harm while maximizing the benefits of artificial intelligence to society.”
The study’s additional authors are Dr. Chace Moleta and Dr. Jitin Makker of UCLA, and, Jai Prakash Veerla, Jillur Rahman Saurav, Amir Hajighasemi, Parisa Boodaghi Malidarreh, Manfred Huber, and Jacob Luber, Ph.D of the University of Texas at Arlington.
The study was funded by the University of Texas System Rising STARs Award and the CPRIT First Time Faculty Award.
END
Four state-of-the-art, artificial intelligence search engines for histopathology images may not be ready for clinical use
2024-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Young adults reduced drinking during and after pandemic
2024-05-02
A new study examined the drinking levels and patterns of young adults before, during and after the pandemic. The researchers found alcohol use and alcohol-related problems substantially decreased in heavy-drinking young adults during the pandemic, and these decreases were still evident as the pandemic began to wane. The results are available in the May 2 issue of the journal Nature Mental Health.
“The pandemic gave us a unique opportunity to see how wide-spread mitigation measures like social distancing and bar/restaurant closures may have affected alcohol consumption,” said lead ...
Random robots are more reliable
2024-05-02
Northwestern University engineers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm designed specifically for smart robotics. By helping robots rapidly and reliably learn complex skills, the new method could significantly improve the practicality — and safety — of robots for a range of applications, including self-driving cars, delivery drones, household assistants and automation.
Called Maximum Diffusion Reinforcement Learning (MaxDiff RL), the algorithm’s success lies in its ability to encourage robots to explore their environments as randomly as possible in order to gain a diverse set of ...
Why do male chicks play more than females? Study finds answers in distant ancestor
2024-05-02
Play is widespread, but far from ubiquitous, across the animal kingdom. Especially common in mammals, play is also known to occur in taxa as diverse as birds, fish, octopuses, and even insects. But what is its function, given that natural selection never selects fun for its own sake? One prominent hypothesis is that play is beneficial to individuals because it allows them to practice skills needed later in life.
Now, a study in Frontiers in Ethology has shown that male baby chickens play far more than females. This result is of interest given that domestic ...
When good bacteria go bad - New links between bacteremia and probiotic use
2024-05-02
Osaka, Japan – Probiotics offer a range of health benefits, but their adverse effects can occasionally lead to bacteremia, wherein bacteria circulate in the bloodstream throughout the body. In Japan, Clostridium butyricum (C. butyricum) MIYAIRI 588 is commonly used, yet the prevalence and characteristics of bacteremia caused by this strain, as well as its bacteriological and genetic profile, remain unknown.
A research team from the Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, found an association between bacteremia and probiotics from a study of the genetic materials of bacteria in hospitalized patients with bacteremia.
From September 2011 to February 2023, ...
MCG scientists identify new treatment target for leading cause of blindness
2024-05-02
Medical College of Georgia scientists report that a gene previously implicated in the development of atherosclerotic lesions in coronary arteries could be key to understanding why many people don’t benefit from the most used therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness.
AMD is a condition characterized by abnormal blood vessel growth in the back of the eye. It is highly prevalent in the elderly and people with diabetes, obesity, and many other chronic metabolic diseases. Excessive vascular growth damages the macula, the part of the eye that translates light into image signals.
Anti-VEGF therapy, which blocks vascular ...
Promising new treatment strategy for deadly flu-related brain disorders
2024-05-02
Osaka, Japan – It might start simply, with a cough or sneeze…but in some cases, the flu virus can make its way to your brain, causing serious symptoms or even death through a disease known as influenza-associated encephalopathy (IAE).
Now, in a study published in Acta Neuropathologica, researchers have revealed that IAE may be caused by the virus entering the brain through a specific cell type, and have identified possible treatment strategies.
Although IAE is increasingly common, surprisingly little is known about ...
Scientists’ new approach in fight against counterfeit alcohol spirits
2024-05-02
In the shadowy world of counterfeit alcoholic spirit production, where profits soar and brands are exploited, the true extent of this illegal market remains shrouded.
Now scientists from the International Centre for Brewing and Distilling (ICBD) at Heriot-Watt University, in Edinburgh, Scotland, working alongside Dr John Edwards of Process NMR Associates, based in New York, are compiling a database to test, compare and log counterfeit spirits.
The research has featured in a paper, titled, Worldwide Illicit and Counterfeit ...
Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
2024-05-02
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements.
The energy capacity and charge-recharge cycling (cyclability) of lithium-iron-oxide, a cost-effective cathode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, is improved by adding small amounts of abundant elements. The development, achieved by researchers at Hokkaido University, Tohoku University, and Nagoya Institute of Technology, is reported in the journal ACS Materials Letters.
Lithium-ion batteries have become indispensable in modern life, used in a multitude ...
Artificial intelligence enhances monitoring of threatened marbled murrelet
2024-05-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Artificial intelligence analysis of data gathered by acoustic recording devices is a promising new tool for monitoring the marbled murrelet and other secretive, hard-to-study species, research by Oregon State University and the U.S. Forest Service has shown.
The threatened marbled murrelet is an iconic Pacific Northwest seabird that’s closely related to puffins and murres, but unlike those birds, murrelets raise their young as far as 60 miles inland in mature and old-growth forests.
“There are very few species like it,” said co-author Matt Betts of the OSU College of Forestry. “And there’s no ...
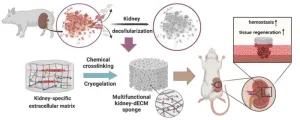
The solution to kidney bleeding and recovery lies within a hemostasis sponge, using the inherent capabilities of the kidneys
2024-05-02
Professor Dong-Woo Cho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering along with Jae Yun Kim, a PhD candidate, from the School of Interdisciplinary Bioscience and Bioengineering and Tugce Sen, a PhD student, from Department of Mechanical Engineering at POSTECH, teamed up with Professor Jae Yeon Lee from Daegu Haany University's Department of Companion Animal Health. Together, they crafted a material aimed at swiftly staunching kidney bleeding and facilitating wound recovery. Their research featured in the online edition of Biomaterials, an ...