(Press-News.org) Chromosomal 22q11.2 deletions increase risk for meningomyelocele, one of the most severe and common forms of spina bifida, researchers report. According to the findings, this risk is mediated by the loss of Crkl, one of several neural tube expressed genes located on the 22q11.2 deletion interval, and this risk is only partially alleviated by folate supplementation. Meningomyelocele (MM) is a severe type of neural tube defect, which often requires pre- or post-natal surgical repair and can result in a variety of physical and developmental difficulties. Although the incidence of the condition has declined in recent decades, largely due to folic acid (FA) fortification, MM remains a particular challenge in some areas of the world. The causes of MM remain largely unknown, and the risk attributable to common genetic variants remains unexplored. To better understand the genetic architecture of MM, Keng Vong and colleagues established the Spina Bifida Sequencing Consortium to identify the genetic mutations present in a child with MM that are not present in the parents. They found that previously unrecognized de novo or inherited chromosomal 22q11.2 deletions (22q11.2del) were the most common recurrent genetic condition, suggesting that patients with MM were 22.98 times more likely to harbor 22q11.2del compared to the general population. Moreover, in a separate study of a cohort of individuals with 22q11.2 deletion, Vong et al. discovered that the risk of MM was roughly 12- to 15-fold greater than expected. Using a mouse model, the authors investigated candidate genes driving MM risk and found that loss of Crkl was enough to alter neural tube development and at least partially mediated by maternal folic acid.
END
Chromosomal 22q11.2 deletion confers risk for severe spina bifida
2024-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Circadian clocks in the brain and muscles coordinate to support daily muscle function
2024-05-02
Molecular circadian clocks in the brain and muscle tissue cooperate to keep muscles healthy and functioning daily, according to a new study in mice. The findings could provide valuable insight into understanding the roles of circadian disruption in age-associated health issues and potential strategies to protect muscle function in aging individuals. A circadian molecular clock network is crucial for daily physiology and maintaining health. It’s thought that this network – which extends throughout all cells in the body – is hierarchically organized and coordinated by the brain’s suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which receives daily light cues and synchronizes ...
*FREE* The effectiveness of early childhood education programs is scientifically uncertain
2024-05-02
Early care and education (ECE) programs – like Pre-Kindergarten (Pre-K) and Head Start – are widely regarded as effective public investments for reducing income- and race-based achievement gaps and helping children succeed in school with impacts extending well into adulthood. However, in a Policy Forum, Margaret Burchinal and colleagues present recent evidence suggesting that preschool impacts are not unequivocally positive and the science on the overall outcomes of these programs remains unsettled. According to Burchinal et al., more rigorous research is needed to understand how to design early education programs that produce long-term positive ...
Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
2024-05-02
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in the opposite direction, making it difficult to measure the position and momentum of the atom precisely. This recoil can have big implications for quantum sensing, which detects minute changes in parameters, for example, using changes in gravitational waves to determine the shape of the Earth or even detect dark matter.
In a new paper published in the Science, JILA and NIST Fellows Ana Maria Rey and James Thompson, ...
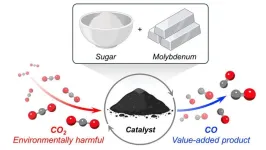
Sugar-based catalyst upcycles carbon dioxide
2024-05-02
A new catalyst made from an inexpensive, abundant metal and common table sugar has the power to destroy carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.
In a new Northwestern University study, the catalyst successfully converted CO2 into carbon monoxide (CO), an important building block to produce a variety of useful chemicals. When the reaction occurs in the presence of hydrogen, for example, CO2 and hydrogen transform into synthesis gas (or syngas), a highly valuable precursor to producing fuels that can potentially replace gasoline.
With recent advances in carbon capture technologies, post-combustion carbon capture is ...
Deeper understanding of malaria parasite sexual development unlocks opportunities to block disease spread
2024-05-02
For the first time, the developmental stages of the deadliest human malaria parasite have been mapped in high resolution, allowing researchers to understand this ever-adapting adversary in more detail than previously possible.
The study, published today (2 May) in Science, details the critical developmental stages of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, using single-cell RNA sequencing. This gives detailed information on the life stages of this parasite as it matures, changing from an asexual state to a sexual state, which is necessary before the parasite can be transmitted to mosquitoes.
The research from ...
Breaking ground: Investigating the long-term effects of early childhood education
2024-05-02
EMBARGOED TO 2:00 P.M. ET May 2, 2024
Contact: Patricia Lamiell; patricia.lamiell@tc.columbia.edu or Ari Morgan; teacherscollege@skdknick.com
Breaking Ground: Investigating the Long-Term Effects of
Early Childhood Education
New review from Teachers College, Columbia University, University of Virginia, University of California-Irvine, and University of Delaware Reveals Varied Impact of Preschool Programs on Long-Term School Success.
EDITOR’S NOTE: The EMBARGOED ...
Synchronization between the central circadian clock and the circadian clocks of tissues preserves their functioning and prevents ageing
2024-05-02
Barcelona, 2 May 2024 - Discovered in the 1970s, circadian clocks are essential for the regulation of biological time in most cells in the human body. These internal mechanisms adjust biological processes to a 24-hour cycle, allowing the synchronisation of cellular functions with daily variations in the environment. Circadian rhythms, which are coordinated by a central clock in the brain that communicates with clocks in different peripheral tissues, influence many functions, from our sleep patterns to our ability to metabolise food.
A team led by Dr. Salvador Aznar Benitah, an ICREA researcher ...
Physicists arrange atoms in extremely close proximity
2024-05-02
Proximity is key for many quantum phenomena, as interactions between atoms are stronger when the particles are close. In many quantum simulators, scientists arrange atoms as close together as possible to explore exotic states of matter and build new quantum materials.
They typically do this by cooling the atoms to a stand-still, then using laser light to position the particles as close as 500 nanometers apart — a limit that is set by the wavelength of light. Now, MIT physicists have developed a technique that allows them to arrange atoms in much closer proximity, down to a mere 50 nanometers. For context, a red blood cell ...
Scientists track ‘doubling’ in origin of cancer cells
2024-05-02
Working with human breast and lung cells, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have charted a molecular pathway that can lure cells down a hazardous path of duplicating their genome too many times, a hallmark of cancer cells.
The findings, published May 3 in Science, reveal what goes wrong when a group of molecules and enzymes trigger and regulate what’s known as the “cell cycle,” the repetitive process of making new cells out of the cells’ genetic material.
The findings could be used to develop therapies that interrupt snags in the cell cycle, ...
Human activity is causing toxic thallium to enter the Baltic sea, according to new study
2024-05-02
Woods Hole, Mass. (May 2, 2024) -- Human activities account for a substantial amount - anywhere from 20% to more than 60% - of toxic thallium that has entered the Baltic Sea over the past 80 years, according to new research by scientists affiliated with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and other institutions.
Currently, the amount of thallium (element symbol TI), which is considered the most toxic metal for mammals, remains low in Baltic seawater. However, the research suggests that the amount of thallium could increase due to further anthropogenic, or human induced, activities, or due to natural or human re-oxygenation of the Baltic that could make the sea ...