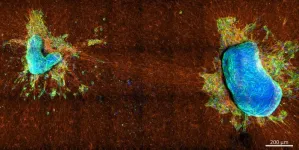
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 7, 2024 – Understanding how cancerous cells spread from a primary tumor is important for any number of reasons, including determining the aggressiveness of the disease itself. The movement of cells into the extracellular matrix (ECM) of neighboring tissue is an essential step in cancer progression that directly correlates to the onset of metastasis.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, a team of researchers from Germany and Spain used a breast cancer cell line panel and primary tumor explants from breast and cervical cancer patients to examine two different cellular contractility modes: one that generates collective tissue surface tension that keeps cell clusters compact and another, more directional, contractility that enables cells to pull themselves into the ECM.
“We focused on two parameters, namely the ability of the cells to pull on the ECM fibers and generate traction forces and on their ability to pull on each other, thereby generating a high tissue surface tension,” said author Eliane Blauth. “We linked each property to different contractile mechanisms and asked how they are connected to cancer cell escape and tumor aggressiveness.”
The team found that more aggressive cells pull more strongly on the ECM than on themselves while noninvasive cells pull more strongly on themselves than on the ECM – and that the different pulling behaviors are attributed to different structures of actin cytoskeleton inside the cells. Invasive cells use predominantly actin stress fibers — thick actin bundles that span the cell — to generate forces on their surroundings, while noninvasive cells generate forces through their actin cortex, a thin network directly under the cell membrane.
The study showed it is not the overall magnitude of these contractility modes but the interplay between them that determines a cell’s potential for escape. Experiments with only moderately invasive cells demonstrated the total force these cells generate on the ECM fibers is comparable to that of noninvasive cells, yet they can still detach and invade the ECM, which is not possible for noninvasive cells.
“The noninvasive cells still have a high cortical contractility, keeping them together, while the moderately invasive cells have a nearly disappearing cortical contractility,” said Blauth. “So not much is holding them back even though they pull much weaker on the ECM fibers.”
The team’s measurements with patient-derived vital tumor explants confirmed their findings from the cell line experiments. Here, the number of cells with a high cortical contractility decreased during tumor progression.
“This further indicates that the ability of the cells to pull on each other and hold themselves clustered together becomes weaker as the tumor grows, potentially increasing metastasis risk.”
###
The article “Different contractility modes control cell escape from multicellular spheroids and tumor explants” is authored by Eliane Blauth, Steffen Grosser, Frank Sauer, Mario Merkel, Hans Kubitschke, Enrico Warmt, Erik W. Morawetz, Philip Friedrich, Benjamin Wolf, Susanne Briest, Grit Gesine Ruth Hiller, Lars-Christian Horn, Bahriye Aktas, and Josef A. Käs. The article will appear in APL Bioengineering on May 7, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0188186). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0188186.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
###
END
Study sheds light on cancer cell ‘tug-of-war’
How cancer cells tug against each other determines whether they can migrate elsewhere in the body.
2024-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Social determinants of health and the availability of cancer clinical trials in the US
2024-05-07
About The Study: Substantial geographic disparities in cancer clinical trials availability exist throughout the United States, with the most socially vulnerable counties being far less likely to have any trial and having only a fraction of trials available, a disparity that has worsened over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rishi Robert Sekar, M.D., M.S., email rsekar@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10162)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Multilevel characteristics of cumulative symptom burden in young survivors of childhood cancer
2024-05-07
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that symptoms are prevalent years after young childhood cancer survivors’ initial cancer diagnosis, and interventions to reduce caregiver anxiety and neighborhood adversity and improve resilience may alleviate symptom burden.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, I-Chan Huang, Ph.D., email i-chan.huang@stjude.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10145)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
2024-05-07
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more adaptable and efficient hearing devices ranging from hearing aids to smartphones.
In the 1940s, an engineering model was developed to explain how humans can locate a sound source based on differences of just a few tens of millionths of a second in when the sound reaches each ear.
This model worked on the theory that we must ...
It flickers, then it tips – study identifies early warning signals for the end of the African humid period
2024-05-07
The transition from the African Humid Period (AHP) to dry conditions in North Africa is the clearest example of climate tipping points in recent geological history. They occur when small perturbations trigger a large, non-linear response in the system and shift the climate to a different future state, usually with dramatic consequences for the biosphere. That was also the case in North Africa, where the grasslands, forests, and lakes favored by humans disappeared, causing them to retreat to areas like the mountains, oases, and the Nile Delta. This ...
Aquatic weed among ‘world’s worst’ expands in Northeastern US
2024-05-07
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 7 May 2024 – An article in the latest issue of Invasive Plant Science and Management provides new insights on a northern hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) subspecies (lithuanica) and its establishment outside the Connecticut River. Considered among the “world’s worst” aquatic weeds, northern hydrilla hinders recreational activities by forming dense canopies. If unchecked, it has the potential to displace native species and host a bacterium that produces ...
Emergency department packed to the gills? Someday, AI may help
2024-05-07
UCSF-led study finds artificial intelligence is as good as a physician at prioritizing which patients need to be seen first.
Emergency departments nationwide are overcrowded and overtaxed, but a new study suggests artificial intelligence (AI) could one day help prioritize which patients need treatment most urgently.
Using anonymized records of 251,000 adult emergency department (ED) visits, researchers at UC San Francisco evaluated how well an AI model was able to extract symptoms from patients’ ...
Asthma education is key to reducing deaths worldwide, say respiratory health associations
2024-05-07
NEW YORK, NY - May 7, 2024 – On World Asthma Day 2024 the message is clear: "Asthma Education Empowers." The Forum of International Respiratory Societies (FIRS), of which the American Thoracic Society is a founding member, stresses the crucial role of education in empowering people with asthma to manage their condition effectively and to know when to seek medical assistance.
FIRS also urges health care professionals to enhance their awareness of the preventable morbidity and mortality from asthma and of the published evidence on effective asthma management, so they are equipped to provide reliable information and optimal treatment for their patients.
Asthma ...
60% of women with disabilities view cannabis as a ‘harmless’ drug
2024-05-07
A growing number of states and territories in the United States have legalized medical and recreational cannabis use. As such, recreational cannabis has been associated with a lower perception of risk of harm in the general U.S. population.
However, in women of childbearing age, evidence has shown that cannabis use may increase the risk of adverse reproductive and perinatal health outcomes. Furthermore, research on the perception of risk from using cannabis among vulnerable populations such as those with disabilities is lacking.
Using data from the 2021 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, researchers from Florida ...
Years after his death, late scientist's work could yield new cancer treatments
2024-05-07
Some of the final work of a late University of Virginia School of Medicine scientist has opened the door for life-saving new treatments for solid cancer tumors, including breast cancer, lung cancer and melanoma.
Prior to his sudden death in 2016, John Herr, PhD, had been collaborating with UVA Cancer Center’s Craig L. Slingluff Jr., MD, to investigate the possibility that a discovery from Herr’s lab could help treat cancer.
Eight years of research has borne that idea out: Herr’s research into the SAS1B protein could lead to “broad and profound” new treatments ...
SwRI evaluates reliability of pressure relief valves for liquid natural gas tanks in train derailment scenarios
2024-05-07
SAN ANTONIO — May 7, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has helped determine the viability of pressure relief valves for liquid natural gas tanks in the event of a train derailment for the Federal Rail Administration (FRA). The report from the FRA shows that a study conducted by SwRI demonstrates that the pressure relief valves work as designed to prevent overpressurization and explosion if a derailment occurs.
“The pressure relief valves on tanks that transport liquid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
[Press-News.org] Study sheds light on cancer cell ‘tug-of-war’How cancer cells tug against each other determines whether they can migrate elsewhere in the body.