Terahertz flexible multiplexing chip enabled by synthetic topological phase transitions
2024-05-08
(Press-News.org)
This study is led by Prof. Xu (State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University), Prof. Yu (College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University), Prof. Han (Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Technology, Tianjin University and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing, School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Guilin University of Electronic Technology), and Prof. Sun (State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University and State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, Department of Precision Instrument, Tsinghua University).
The terahertz band is a gap band between microwave and infrared, and has shown great application potential in many cutting-edge information fields such as 6G communications. Terahertz silicon-based photonics has many advantages such as high transmission efficiency and is an effective platform for realizing terahertz devices. However, how to implement devices with richer functions in the terahertz band or expand device control capabilities is still a hot research topic in terahertz integrated photonics.
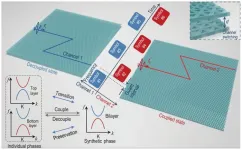
In this study, the author proposed a chip design method based on topological interlayer coupling regulation. This method uses the interlayer coupling strength of the bilayer valley photonic crystal to regulate the Hamiltonian of the bilayer topological photonic system:
H = HT + HB + HTB
Where HT and HB represent the Hamiltonian of the top and bottom photonic lattice respectively, while HTB is used to describe the Hamiltonian generated due to interlayer coupling. By regulating the distance between layers, the system can be effectively controlled to be in a coupled state or a decoupled state, and the interlayer coupling Hamiltonian HTB can be adjusted to control the topological phase transitions of the photonic system. Due to the bulk-edge correspondence, the topological edge states before and after the phase transition can be distributed in different spatial paths. Through modular topological phase design, the author realized the flexible multiplexing chip shown in Figure 1.
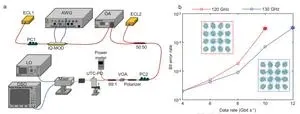
In order to verify the potential application value of the technical solution in next-generation communications, the research team conducted relevant tests on the terahertz communication performance of the chip (Figure 2.a). The multiplexing chip achieves 10 Gbps and 12 Gbps 16-QAM signal transmission on two switchable channels of 120 GHz and 130 GHz respectively, with available bandwidths of 2.5 GHz and 3 GHz respectively (Figure 2.b).
This work enriches the methods of terahertz on-chip channel manipulation, further promotes the application of topological photonics in advanced communication systems and devices, and may inspire more novel physical mechanisms and phenomena in bilayer and multi-layer topological systems.
See the article:
Design of the topological photonic lattices, Simulation results, and measured S-parameters.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwae116
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-08
Hypertension is among the leading cardiovascular diseases. Despite extensive research, evidence concerning the relationship between long-term exposure to ambient particulate matter and hypertension remains limited and inconsistent, particularly with regard to submicron particulate matter (PM1). While randomized controlled trials are considered the gold standard for causal inference, environmental epidemiological studies typically rely on observational data. Traditional approaches in observational studies are less effective than randomized controlled trials in fully controlling for confounding factors to achieve results with causal interpretability. With the advancement of causal ...
2024-05-08
Recently, Science Bulletin published a research conducted by Prof. Pingqing Fu and Dr. Libin Wu from Tianjin University, Peng Wang from Fudan University, and their Chinese and foreign collaborators. They explored the source of ammonium in PM2.5 at different heights of the atmospheric boundary layer in Beijing, and found that combustion-related ammonia is very important to ammonium in PM2.5 during haze pollution in winter.
Air pollution and treatment in Beijing have been widely concerned by both the scientific community and the public. Although its PM2.5 has decreased significantly in the past few years, there is still haze pollution in Beijing, especially in winter. The chemical compositions ...
2024-05-08
The researchers conducted a study over four days, including overnight stays, with 18 subjects at :envihab, the DLR medical research centre in Cologne. At a simulated altitude of 2500 meters above sea level, the influence of hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) on various hemodynamic and metabolic parameters was investigated. The central venous pressure via a catheter and the blood flow in the lungs using real-time magnetic resonance imaging were evaluated. The results showed that neither the pulmonarypressure nor the blood flow changed significantly. All patients able to tolerate a longer stay at altitude of 24 to 30 hours without complications.
Oxygenation ...
2024-05-08
The Australian brook lamprey (Mordacia praecox) is part of a group of primitive jawless fish. It’s up to 15 cm long, with rows of sharp teeth. Surprisingly, it doesn’t use these teeth to suck blood like most lamprey species – it’s non-parasitic.
As larvae, the Australian brook lamprey lives buried in the bottom of streams for around three years, filter-feeding. Its adult phase is about one year long, in which it doesn’t feed at all. Prior to this study – funded in part by the Australian Government through the National Environmental Science Program’s (NESP) Resilient Landscapes Hub – the species was widely believed to only live in a few streams ...
2024-05-08
A unique $3.7m plant lab will put researchers on the frontline in the fight against climate change and create crops for “tomorrow’s atmosphere today”.
The new flagship facility at the University of Essex will allow scientists to adapt plants for a hotter drier planet as food security is increasingly threatened.
It boasts a cutting-edge commercially standard vertical farm, an indoor field that replicates real environments anywhere in the globe, and suites that imitate a warming world – with researchers able to raise CO2 concentration and temperature levels at will.
Computer ...
2024-05-08
Scientists at the University of Surrey are developing a new way to power low-orbit spacecraft using – literally – thin air.
Surrey Space Centre aims to enable extremely low-altitude spacecraft orbits in the upper atmosphere, thanks to funding from the UK Space Agency.
This new spacecraft concept could offer new capabilities in Earth observation, climate monitoring and satellite communications.
Dr Andrea Lucca Fabris, principal investigator from Surrey Space Centre and an electric propulsion specialist, said:
“There are benefits to flying in very low altitude orbits, like being able to operate Earth observation at much ...
2024-05-08
The author of a disaster novel couldn't have dreamed it up any better: On a Friday, the thirteenth of all days, the potentially dangerous asteroid (99942) Apophis will come extremely close to humanity. On 13 April 2029, there will only be around 30,000 kilometres between the cosmic rock and Earth. It will then be possible to see Apophis with the naked eye as a point of light in the evening sky, even from Würzburg.
What makes the asteroid so dangerous: its average diameter is an impressive 340 metres. If it were to hit the Earth, the ...
2024-05-08
Research warns of hazardous health risks from flavoured vapes
Research predicts the potential formation of 127 acutely toxic chemicals in flavoured vapes
Findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive regulation of vaping products
Wednesday, 8 May 2024: New research has uncovered the potentially harmful substances that are produced when e-liquids in vaping devices are heated for inhalation. The study, published in Scientific Reports, highlights the urgent need for public health policies concerning flavoured vapes.
The research team at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dublin, used artificial ...
2024-05-08
Three Florida Atlantic University researchers at the forefront of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) research have each received a $350,000 grant from the Florida Department of Health’s “Ed and Ethel Moore Alzheimer’s Disease Research Program.”
The Ed and Ethel Moore Alzheimer’s Disease Research Program was established to improve the health of Floridians by stimulating research into the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, care management and cure of AD.
Florida has the second highest incidence of AD in the nation with 580,000 people ages 65 and ...
2024-05-08
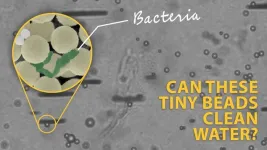
When old food packaging, discarded children’s toys and other mismanaged plastic waste break down into microplastics, they become even harder to clean up from oceans and waterways. These tiny bits of plastic also attract bacteria, including those that cause disease. In a study in ACS Nano, researchers describe swarms of microscale robots (microrobots) that captured bits of plastic and bacteria from water. Afterward, the bots were decontaminated and reused. Watch a video of them swarming.
The size ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Terahertz flexible multiplexing chip enabled by synthetic topological phase transitions