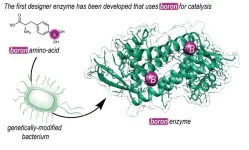
(Press-News.org) Boronic acid has been used in organic chemistry for decades, even though it is not present in any organism. ‘It gives rise to different chemical reactions than those we find in nature,’ explains Gerard Roelfes, Professor of Biomolecular Chemistry & Catalysis at the University of Groningen. His group created an enzyme with boronic acid at its reactive centre and then used directed evolution to make it more selective and to improve its catalytic power. Furthermore, enzymatic reactions are more sustainable than classical chemical reactions, as they take place at low temperatures and without toxic solvents. The study was presented online in the journal Nature on 8 May.
The application of boron in organic chemistry dates back some seventy years and was awarded a Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1979. In recent years, the interest in boron as a catalyst has grown, but as yet, its use in the chemical industry is limited. Roelfes: ‘So far, boron catalysis is too slow and it is not very suitable for enantioselective reactions.’ These types of reactions are used to create chiral molecules, which can exist in two versions that are mirror images of each other, like a left and a right hand. In many drugs, both ‘hands’ can have a different effect. It is, therefore, important to selectively produce the proper ‘hand’, especially for the pharmaceutical industry.
Expanded genetic code
‘To make this possible, we set out to introduce boron into an enzyme. Our group has a long history of designing enzymes that don’t exist in nature.’ The Roelfes group used an expanded genetic code to introduce a non-natural amino acid that contains a reactive boronic acid group into an enzyme. ‘Using this technique, we can determine at the DNA level where we place the amino acid in a protein.’
Once they made an enzyme with boronic acid at its reactive centre, they could use directed evolution to increase its efficiency, resulting in faster catalysis. ‘Furthermore, by placing the boronic acid in the chiral context of an enzyme, we were able to achieve highly enantioselective catalysis.’ The reaction that is described in the journal Nature is a ‘proof of principle’ and shows the way to harnessing the catalytic power of boron in enzymes.
Biocatalysis
Using enzymes to create organic compounds is important for the pharmaceutical industry. ‘In their push towards greener and more sustainable ways of producing drugs, they are looking at biocatalysis to replace conventional chemical reactions.’ At the University of Groningen, concerted efforts are being made towards this goal. ‘We have a number of research groups at the Faculty of Science and Engineering engaged in this kind of work, using different approaches to create biocatalytic solutions for the chemical industry.’ In this context, Roelfes and his team will continue to develop their boronic acid enzymes and create other such new-to-nature enzymes.
Reference: Lars Longwitz, Reuben B. Leveson-Gower, Henriëtte J. Rozeboom, Andy-Mark W. H. Thunnissen & Gerard Roelfes: Boron catalysis in a designer enzyme. Nature, online 8 May 2024.
END
University of Groningen chemists produce new-to-nature enzyme containing boron
2024-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study led by ORNL informs climate resilience strategies in urban, rural areas
2024-05-08
Local decision-makers looking for ways to reduce the impact of heat waves on their communities have a valuable new capability at their disposal: a new study on vegetation resilience.
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory completed a study of how well vegetation survived extreme heat events in both urban and rural communities across the country in recent years. The analysis informs pathways for climate mitigation, including ways to reduce the effect of urban heat islands.
Vegetation such as trees provide a valuable cooling effect, shading surfaces and deflecting solar radiation while releasing ...
Save the Date: American College of Surgeons Clinical Congress in San Francisco, October 19-22
2024-05-08
CHICAGO – The American College of Surgeons (ACS) Clinical Congress 2024 will take place Saturday, October 19, through Tuesday, October 22, in San Francisco and will feature opportunities for members of the media to learn about the latest evidence-based practices and research in surgery and healthcare.
This year’s Clinical Congress will once again be a hybrid event, allowing reporters to cover the conference onsite or virtually.
Clinical Congress is one of the world’s largest educational meetings for surgeons, ...
Gerry Rubin receives the 2024 Gruber Neuroscience Prize
2024-05-08
Janelia Senior Group Leader Gerry Rubin and Cori Bargmann of The Rockefeller University have been jointly awarded the 2024 Gruber Neuroscience Prize for their pioneering work in elucidating the organization of neural circuits in behavior and developing new genetic tools to advance the field of neuroscience.
The Gruber Neuroscience Prize, established in 2004, honors scientists for major discoveries that have advanced the understanding of the nervous system. The prize is part of the Gruber International Prize Program, hosted by the Gruber Foundation, which honors individuals in the fields of ...
Pore pressure diffusion led to microseismicity at Illinois basin carbon sequestration site
2024-05-08
Pore pressure diffusion generated by carbon dioxide injected underground at a carbon storage site in the Illinois Basin is the likely cause of hundreds of microearthquakes that took place at the site between 2011 and 2012, according to a new analysis.
The modeling study published in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America indicates that pressure diffusion along existing faults into the basement rock could have destabilized the faults where the microseismicity—ranging from Mw -2 to 1—occurred, said Ruben Juanes of MIT and colleagues.
There are some similarities between CO2 injection and wastewater injection from oil and gas operations, although globally the ...
New study finds AI-generated empathy has its limits
2024-05-08
ITHACA, N.Y. – Conversational agents (CAs) such as Alexa and Siri are designed to answer questions, offer suggestions – and even display empathy. However, new research finds they do poorly compared to humans when interpreting and exploring a user’s experience.
CAs are powered by large language models (LLMs) that ingest massive amounts of human-produced data, and thus can be prone to the same biases as the humans from which the information comes.
Researchers from Cornell University, Olin College and Stanford University tested this theory ...
NASA’s Webb hints at possible atmosphere surrounding rocky exoplanet
2024-05-08
Researchers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope may have detected atmospheric gases surrounding 55 Cancri e, a hot rocky exoplanet 41 light-years from Earth. This is the best evidence to date for the existence of any rocky planet atmosphere outside our solar system.
Renyu Hu from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, is lead author on a paper published today in Nature. “Webb is pushing the frontiers of exoplanet characterization to rocky planets,” Hu said. “It is truly ...
A tailored vaccine could one day treat eczema in children -- new research
2024-05-08
New research from a multi-disciplinary team at Trinity College Dublin suggests a “tailored vaccine” might hold the key to treating bacteria-driven flares of eczema in children.
The team has taken several leaps forward in understanding how the immune response works in cases of eczema driven by the common, troublesome Staphylococcus aureus bacterium, and in doing so they have identified new cellular targets for a vaccine.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, affects up to one in four children in Ireland. Common symptoms include itchy, dry skin, and – when bacteria are involved – weeping wounds that can ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for May 8, 2024
2024-05-08
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer insights into expanding the use of FGFR inhibitors, maintaining radiation therapy as standard of care for locally recurrent endometrial cancer, an antibody-drug ...
The interference of many atoms, and a new approach to boson sampling
2024-05-08
In daily life, when two objects are “indistinguishable,” it’s due to an imperfect state of knowledge. As a street magician scrambles the cups and balls, you could, in principle, keep track of which ball is which as they are passed between the cups. However, at the smallest scales in nature, even the magician cannot tell one ball from another. True indistinguishability of this type can fundamentally alter how the balls behave.
For example, in a classic experiment by Hong, Ou and Mandel, two identical photons (balls) striking opposite sides of a half-reflective mirror are always ...
AI and holography bring 3D augmented reality to regular glasses
2024-05-08
Researchers in the emerging field of spatial computing have developed a prototype augmented reality headset that uses holographic imaging to overlay full-color, 3D moving images on the lenses of what would appear to be an ordinary pair of glasses. Unlike the bulky headsets of present-day augmented reality systems, the new approach delivers a visually satisfying 3D viewing experience in a compact, comfortable, and attractive form factor suitable for all-day wear.
“Our headset appears to the outside world just like an everyday pair of glasses, but what the wearer sees through the lenses is an enriched world overlaid with vibrant, full-color 3D computed imagery,” said Gordon ...