(Press-News.org) Many parents ponder why one of their children seems more emotionally troubled than the others. A new study in the United Kingdom reveals a possible basis for those differences.
Adolescents who view their households as more unstructured, disorganized, or hectic than their siblings develop more mental health and behavioral problems in early adulthood, according to the study. The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
In research tracking thousands of twins born in the mid-1990s, Sophie von Stumm, a psychology professor at the University of York, found that teenagers who perceived their homes as more disorganized, unstructured, or fast-paced than their siblings suffered more anxiety and depression and engaged in more substance use and problem behavior. If future research confirms those findings, she said, psychologists could develop interventions that modify adolescents’ perceptions of their home environments.
von Stumm said she’s long been curious about why people who share an experience come away with vastly different perceptions and interpretations of what happened. For her study, she used data from 4,732 same-sex twin pairs from the Twins Early Development Study (TEDS), an ongoing examination of twins born in the mid-1990s in England and Wales. She excluded data from opposite-sex twin pairs to rule out potential gender-based differences in perceptions.
At ages 9, 12, 14, and 16, the twins and their parents rated the level of routine, noise, and general confusion in the home.
“Some households are more chaotic than others: There’s always a TV or radio playing, different people come and go every day, and there are no routines, like regular bedtimes or mealtimes,” von Stumm explained.
In reviewing responses from the twins at age 16, she observed that siblings could have significantly different views about the atmosphere in their home. One sibling might view the household as far more noisy and fast-paced than the other.
“You’d think the siblings grew up in different families,” von Stumm said. “That’s how subjective their perceptions are.”
At age 23, the twins completed a questionnaire designed to measure their educational attainment, employment status, income, substance use, sexual risk-taking, conflicts with the law, mental health, and behavioral tendencies. Those who had, at age 16, reported experiencing greater household chaos than their twin siblings scored higher on depression, anxiety, antisocial behavior, and other mental health problems. The results were consistent across both identical and fraternal twin pairs.
“Siblings who perceived the household as more chaotic than their brothers or sisters reported poorer mental health outcomes in young adulthood,” von Stumm said. “This association was evident from adolescence onwards, confirming theories that the onset of mental health issues likely is during teenage years.”
von Stumm said she next plans to explore the precise age and reasons that siblings start to differ in their perceptions of household chaos.
“It is possible that children who experience more adverse events in early life than their siblings, like suffering an injury or being excluded from school, develop a heightened sensitivity to household chaos that then has long-term effects on their mental health,” she said. “Because many common adverse early-life events, such as parental conflict or separation, affect all children of a family, we don’t know yet if there are specific ones that can cause poor long-term mental health.”
The article, “Adolescents’ perceptions of household chaos predict their adult mental health: A twin difference longitudinal cohort study,” is available here.
The Association for Psychological Science is the scientific home of thousands of leading psychological science researchers, practitioners, teachers, and students from around the world. APS is dedicated to advancing scientific psychology across disciplinary and geographic borders and committed to disseminating psychological science to the public, incentivizing global collaboration among researchers, catalyzing the further development of psychological science, and promoting the application of psychological science to public policy.
END
Teens who view their homes as more chaotic than their siblings have poorer mental health in adulthood
2024-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insight into genesis of spina bifida
2024-05-08
A group of researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine led an investigation that offers new insight into the causes of spina bifida, the most common structural disorder of the human nervous system.
Work of the group, led by Keng Ioi Vong, Ph.D., and Sangmoon Lee, M.D. Ph.D., both from the laboratory of Joseph G. Gleeson, M.D., at the UC San Diego School of Medicine Department of Neurosciences and the Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine, reveals the first link between spina bifida and a common chromosomal microdeletion ...
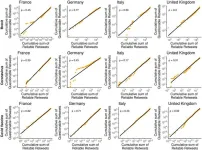
The spread of misinformation varies by topic and by country in Europe
2024-05-08
The eventual prevalence of a piece of misinformation may depend on its topic and the country in which it spreads, with notable differences between the UK, Germany, France and Italy, according to a study published May 8, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fabiana Zollo from the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Italy, and colleagues. This finding suggests that policies to combat misinformation and polarization may need to be context-specific in order to be effective, the authors say.
Researchers analyzed ...
Pacific Oyster density has increased up to 32-fold across a decade in some California waters, and coincides with summer seawater temperature increases of 2-4°C
2024-05-08
Pacific Oyster density has increased up to 32-fold across a decade in some California waters, and coincides with summer seawater temperature increases of 2-4°C
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302935
Article Title: Intra-decadal increase in globally-spread Magallana gigas in southern California estuaries
Author Countries: USA
Funding: “Funding was provided by CSU Fullerton and via subcontracts with Merkel & Associates, Inc. and Port of San Diego to DCZ. Funders had no involvement in the study design or data collection process.” The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
The EU could mitigate climate change equivalent to 13% of its agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by planting cover crops on bare soil before maize
2024-05-08
The EU could mitigate climate change equivalent to 13% of its agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by planting cover crops on bare soil before maize
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302139
Article Title: Cover crops support the climate change mitigation potential of agroecosystems
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research within the Project "CATCHY", project number: 031B1060C. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
Strengthening CAR-T therapy to work against solid tumors
2024-05-08
May 8, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Researchers at the National Cancer Institute-designated Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center (MECCC) have shown that a breakthrough therapy for treating blood cancers can be adapted to treat solid tumors—an advance that could transform cancer treatment. The promising findings, reported today in Science Advances, involve CAR-T cell therapy, which supercharges the immune system to identify and attack cancer cells.
“CAR-T cell therapy has revolutionized ...
Exercise, new drug class recommended for management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
2024-05-08
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) today released a new clinical guideline for effectively managing individuals diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). The guideline reiterates the importance of collaborative decision-making with patients who have HCM and provides updated recommendations for the most effective treatment pathways for adult and pediatric patients.
HCM is an inherited cardiac condition most often caused by a gene mutation that makes the heart muscle too thick (hypertrophy), which impairs its ability to adequately pump blood throughout ...
Study: Heavy snowfall and rain may contribute to some earthquakes
2024-05-08
When scientists look for an earthquake’s cause, their search often starts underground. As centuries of seismic studies have made clear, it’s the collision of tectonic plates and the movement of subsurface faults and fissures that primarily trigger a temblor.
But MIT scientists have now found that certain weather events may also play a role in setting off some quakes.
In a study appearing today in Science Advances, the researchers report that episodes of heavy snowfall and rain likely contributed to ...
USC study reveals role of iron in allergic asthma and points to potential new therapies
2024-05-08
New USC research shows that iron serves as a gas pedal driving certain immune cells that cause inflammation in the lungs during an allergic asthma attack – and blocking or limiting iron may reduce the severity of symptoms.
During an attack, immune cells known as group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) can become overactive, causing excessive inflammation and a tightening of the airways, making it difficult to breath. However, the underlying biology is poorly understood.
Now, researchers from the Keck School ...
SARS-CoV-2 and type 1 diabetes in children: new study aims to explore the relationship
2024-05-08
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that leads to disrupted glucose metabolism. It requires lifelong insulin therapy. The Global Platform for the Prevention of Autoimmune Diabetes (GPPAD) collaborates within a European network to develop new methods to prevent this condition which is, to date incurable. AVAnT1A is GPPAD's third intervention study. It will investigate whether vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in the first year of life can protect children who have an increased genetic risk for type 1 diabetes from developing the condition. The study is supported by funding from The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley ...
ECOG-ACRIN adds another trial to the ComboMATCH precision oncology study platform
2024-05-08
Another ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) treatment trial is open as part of the ComboMATCH precision medicine study platform. ComboMATCH-E5 is evaluating treatment for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated advanced solid tumors with two different targeted drugs given together. The two drugs include the KRAS G12C inhibitor sotorasib and panitumumab, a human monoclonal antibody antagonist specific to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Each drug is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as single-agent therapy for particular cancer types.
"Given the preclinical data demonstrating EGFR over-dependency ...