(Press-News.org) Liver disease, due to viral infections, alcohol abuse, obesity, or cancer, accounts for 1 in every 25 deaths worldwide. A liver transplant can be life saving for people with end-stage liver disease. However, the procedure has limitations related to donor shortage, a technically challenging and invasive surgical procedure, and the requirement for lifelong immunosuppressive medication in the transplant recipients. An alternative to whole organ transplantation is the less invasive injection of dissociated human liver cells, but donor shortage is still an issue. Utilizing interspecies blastocyst complementation to obtain transplantable human liver cells or whole organs in sufficient quantity in a different animal species was one way to overcome these barriers.
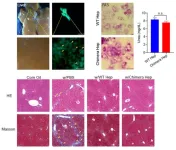
One important question is whether liver cells grown in a different species would be fully functional. To find out, Wei Li and colleagues from the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing injected mouse embryonic stem cells into early rat embryos. Mouse-rat chimeras born from these engineered embryos contained mouse cells in most parts of the body including the livers. The percentage of live mouse liver cells enriched was up to 20.6% from chimeric livers. Encouragingly, mouse liver cells grown in mouse-rat chimeras had normal appearance and mature function in a panel of lab-based tests. Moreover, mouse liver cells from mouse-rat chimeras could be transplanted into mice with liver damage and had a similar therapeutic effect as normal mouse liver cells in relieving chronic liver fibrosis. This data, recently published in the journal Stem Cell Reports, provides proof of principle that functional liver cells can be grown in a different species…and could represent a solution to transplant shortage. Future work is needed to develop efficient techniques to grow human liver cells in large animals such as pigs, and to investigate whether these human liver cells are fully functional.
END
New stem cell research may have implications for liver transplantation
2024-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New cells could be key to treating obesity
2024-05-09
Understanding how fat tissue forms and functions is crucial for addressing obesity and related metabolic diseases. However, adipose tissue, or body fat, behaves differently based on its location in the body.
Take, for example, the omentum: a large, apron-like fatty tissue hanging from the stomach that covers organs within the peritoneum, such as the stomach and intestines. It not only stores fat but also plays roles in immune regulation and tissue regeneration.
Omental adipose tissue is associated with ...
Supercharging immune cells to battle blood cancer: Breakthrough in cancer immunotherapy
2024-05-09
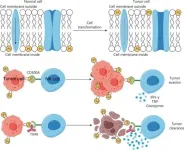
A new study reveals a groundbreaking approach to immunotherapy, demonstrating that blocking the interaction between the CD300A receptor and phosphatidylserine (PS) significantly enhances the ability of human natural killer (NK) cells to lyse hematologic malignancies (HMs).
Cancer has a profound impact on human life, and immune checkpoint therapy (ICT) has made remarkable strides in cancer treatment. However, ICT faces challenges such as low overall response rates and the emergence of immune-related adverse events. To overcome these hurdles, researchers are exploring new immune checkpoints. CD300A, a type-I transmembrane protein with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory ...
Liberals and conservatives differ on climate change beliefs—but are relatively united in taking action
2024-05-09
The division between liberals and conservatives on both climate-change beliefs and related policy support is long-standing. However, the results of a newly released global experiment show that despite these differences, the two camps actually align when it comes to taking certain actions to combat climate change.
The study, led by researchers at New York University, finds that when given the opportunity, liberals and conservatives take action to address climate change at roughly the same levels—and that ...
Biogeographical evidence shows trickster animal folklore limited by environmental factors
2024-05-09
Humans have the capacity to imagine civilizations and creatures that have never existed, and our language reflects that ability. It would therefore be understandable if the stories we tell ourselves stretched beyond the bounds of local ecology. However, research has shown that many cultural artifacts and ideas are strongly affected by environmental factors.
Researchers in Japan wanted to know if the biogeography of a region could constrain motifs in animal folklore. To do this, they studied the distribution of animal trickster folklore against the distribution of the animal the folklore ...
Researchers harness blurred light to 3D print high quality optical components
2024-05-09
WASHINGTON — Canadian researchers have developed a new 3D printing method called blurred tomography that can rapidly produce microlenses with commercial-level optical quality. The new method may make it easier and faster to design and fabricate a variety of optical devices.
“We purposely added optical blurring to the beams of light used for this 3D printing method to manufacture precision optical components,” said Daniel Webber from the National Research Council of Canada. “This enables production of optically smooth surfaces.”
In Optica, Optica Publishing Group’s journal for high-impact research, these researchers demonstrate the new method by using ...
Older adults with aggressive blood cancer are responsive to treatment and show prolonged survival
2024-05-09
(WASHINGTON, May 9, 2024) – Standard of care treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is safe and effective for adults over 80, according to a study published in Blood Neoplasia. For roughly a quarter of patients, this treatment can durably prolong survival.
AML is an aggressive and often deadly form of blood cancer that can be difficult to treat. For older adults with AML, the conventional treatment consists of a medication called venetoclax combined with a hypomethylating agent (HMA), also known as VEN-HMA. AML treatment is often intensive and can significantly suppress the immune system ...
Redesigning healthcare: Integrating social care into a safety net health system
2024-05-09
INDIANAPOLIS -- Neighborhoods of high need are where investment in social care offers the best opportunities to improve health. Screening for social determinants of health is comparatively easy, but building the infrastructure to meet needs occurring outside the formal healthcare system is quite difficult. Few health systems have achieved more than even partial integration of social care into routine patient care.
In a case study of pioneering social care provided by Eskenazi Health, a safety net health system located in Indianapolis, ...
Discovery made into which children will outgrow their peanut allergy
2024-05-09
Australian researchers have discovered how changes in antibody levels over time can predict which children are likely to outgrow their peanut allergy.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) in Melbourne and published in Allergy, found two thirds of children with a peanut allergy remain allergic by the age of 10. But for those who did naturally outgrow their allergy, the majority achieved this by six years old.
The study was the first to use antibodies as biomarkers to identify persistent or a resolved ...
Princeton physicists reveal the microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
2024-05-09
By Tom Garlinghouse for the Princeton University Department of Physics
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions that give rise to magnetism have been understood for around a century, since the early days of quantum mechanics. But there are many different forms of magnetism in nature, and scientists are still discovering the mechanisms that drive them.
Now, physicists ...
Oikopleura who? Species identity crisis in the genome community
2024-05-09
When two animals look the same, eat the same, behave the same way, and live in similar environments, one might expect that they belong to the same species.
However, a tiny zooplankton skimming the ocean surfaces of microscopic food particles challenges this assumption. Researchers from Osaka University, University of Barcelona and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have analyzed the genome of Oikopleura dioica from the Seto Inland Sea, the Mediterranean, and the Pacific Ocean around the Okinawa Islands, and in doing so, they have raised numerous questions about speciation and the role of gene location in ...