(Press-News.org) Areas at risk for malaria transmission in Africa may decline more than previously expected because of climate change in the 21st century, suggests an ensemble of environmental and hydrologic models. The combined models predicted that the total area of suitable malaria transmission will start to decline in Africa after 2025 through 2100, including in West Africa and as far east as South Sudan. The new study’s approach captures hydrologic features that are typically missed with standard predictive models of malaria transmission, offering a more nuanced view that could inform malaria control efforts in a warming world. Most of the burden of malaria falls on people living in low- and middle-income countries in Africa, where health infrastructure is incomplete and malaria control programs have stalled over recent years. Because it is spread by mosquitoes, malaria is also one of the most prominent climate-sensitive diseases. For example, changes in rainfall could expand or restrict the geographic range of mosquitoes and the availability of standing water that they need to breed, particularly in Africa where the climate is already rapidly shifting. However, most attempts to predict the impact of climate change on malaria have only represented surface water using precipitation, ignoring other important hydrologic features such as river inflow. Instead of relying on one model, Mark Smith and colleagues apply an ensemble of global hydrological and climate models to predict malaria transmission in Africa on a continental scale. They incorporated hydrologic metrics such as surface runoff and evaporation, paying special focus to densely populated areas near large-scale river networks such as the Nile. Compared to precipitation-based models, the ensemble method predicted these changes in area will be more widespread and more sensitive to differing future scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions. “As [new] data sources become increasingly available, we will benefit from their explicit incorporation in projections of hydrological processes to explain physically realistic malaria transmission risk at scales that can inform national operational malaria control strategies,” Smith et al. conclude.
END
Climate models predict larger than expected decline in African malaria transmission areas
2024-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Indian ocean temperature anomalies predict global dengue trends
2024-05-09
Sea surface temperature anomalies in the Indian Ocean predict the magnitude of global dengue epidemics, according to a new study. The findings suggest that the climate indicator could enhance the forecasting and planning for outbreak responses. Dengue – a mosquito-borne flavivirus disease – affects nearly half the world’s population. Currently, there are no specific drugs or vaccines for the disease, and outbreaks can have serious public health and economic impacts. As a result, the ability to predict the risk of outbreaks and prepare accordingly is crucial for many regions where ...
Cubic millimeter fragment of human brain reconstructed at nanoscale resolution
2024-05-09
Using more than 1.4 petabytes of electron microscopy (EM) imaging data, researchers have generated a nanoscale-resolution reconstruction of a millimeter-scale fragment of human cerebral cortex, providing an unprecedented view into the structural organization of brain tissue at the supracellular, cellular, and subcellular levels. The human brain is a vastly complex organ and, to date, little is known about its cellular microstructure, including the synaptic and neural circuits it supports. Disruption of these circuits is known to play a role in myriad brain disorders. Yet studying human brain ...
What makes a public health campaign successful?
2024-05-09
The highest performing countries across public health outcomes share many drivers that contribute to their success. That’s the conclusion of a new study published May 9 in the open-access journal PLOS Global Public Health by Dr. Nadia Akseer, an Epidemiologist-Biostatistician at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and co-author of the study and colleagues in the Exemplars in Global Health (EGH) program.
In recent years, the EGH program has begun to identify and study positive outliers when it comes to global health programs around the world, with an aim of uncovering not only which health interventions work, ...
Manganese sprinkled with iridium: a quantum leap in green hydrogen production
2024-05-09
As the world is transitioning from a fossil fuel-based energy economy, many are betting on hydrogen to become the dominant energy currency. But producing “green” hydrogen without using fossil fuels is not yet possible on the scale we need because it requires iridium, a metal that is extremely rare. In a study published May 10 in Science, researchers led by Ryuhei Nakamura at the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) in Japan report a new method that reduces the amount of iridium needed for the reaction by 95%, without altering the rate of hydrogen production. This breakthrough could revolutionize our ability to produce ecologically ...
Topological Phonos: Where vibrations find their twist
2024-05-09
An international team of researchers has discovered that the quantum particles responsible for the vibrations of materials—which influence their stability and various other properties—can be classified through topology. Phonons, the collective vibrational modes of atoms within a crystal lattice, generate disturbances that propagate like waves through neighboring atoms. These phonons are vital for many properties of solid-state systems, including thermal and electrical conductivity, neutron scattering, and quantum phases like charge density waves and superconductivity.
The spectrum of phonons—essentially ...
A fragment of human brain, mapped
2024-05-09
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue may not sound like much. But considering that tiny square contains 57,000 cells, 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses, all amounting to 1,400 terabytes of data, Harvard and Google researchers have just accomplished something enormous.
A Harvard team led by Jeff Lichtman, the Jeremy R. Knowles Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology and newly appointed dean of science, has co-created with Google researchers the largest synaptic-resolution, 3D reconstruction of a piece of human brain to date, showing in vivid detail each cell and its web of neural connections in a piece of human ...
Quantum breakthrough sheds light on perplexing high-temperature superconductors
2024-05-09
Superfast levitating trains, long-range lossless power transmission, faster MRI machines — all these fantastical technological advances could be in our grasp if we could just make a material that transmits electricity without resistance — or ‘superconducts’ — at around room temperature.
In a paper published in the May 10 issue of Science, researchers report a breakthrough in our understanding of the origins of superconductivity at relatively high (though still frigid) temperatures. The findings concern a class of superconductors that has puzzled scientists since 1986, called ‘cuprates.’
“There was tremendous excitement when ...
Vilcek Foundation appoints Dr. Jedd Wolchok to Board of Directors
2024-05-09
The Vilcek Foundation has announced the appointment of Dr. Jedd Wolchok to the board of directors, effective May 1, 2024. Wolchok is the Meyer Director of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center and a professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York.
“Jan, Marica, and I are delighted to welcome Jedd to the Vilcek Foundation board,” says Vilcek Foundation President Rick Kinsel. “We look to our board of directors for insight and perspective on our projects and programs: Jedd is not only a leader in immunotherapy and oncology, but an academic and scientific mentor, and a philanthropist in his own right. We are honored and grateful to have him ...
Local health equity and social impact entrepreneurs invited to apply for grants, training
2024-05-09
DALLAS, May 09, 2024 — A recent study revealed that, in the United States, local Black and Latino entrepreneurs receive just 2.6% of all venture capital investment.[1] To help bridge that gap and while addressing health inequities in these local communities, the American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service, is offering financial grants and expert business consulting to local social health impact entrepreneurs who are focused on achieving health equity. As the Association commemorates one hundred years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit ...
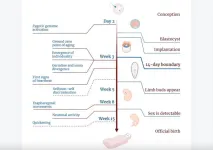
The beginning of becoming a human
2024-05-09
“Debates on when human life begins are rooted deep in philosophical history. However, until recently they have been limited by the state of technology.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 9, 2024 – A new review paper was published in advance by Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), entitled, “The beginning of becoming a human.”
According to birth certificates, the life of a child begins once their body comes out of the mother’s womb. In this new review, researchers Polina A. Loseva and Vadim N. Gladyshev from Harvard Medical School pose ...