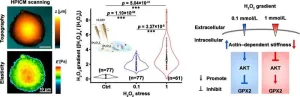
Exploring the effect of H2O2 eustress on individual cancer cells using hopping probe scanning ion conductance microscopy (HPICM)
2024-05-13
(Press-News.org)
In a recent study published in the multidisciplinary academic journal Science Bulletin, a semi-monthly high-caliber peer-reviewed research outlet covering a broad range of natural sciences and high-tech fields, researchers from the Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI) at Kanazawa University utilized hopping probe scanning ion conductance microscopy (HPICM) and highly sensitive platinum-functionalized nanoelectrodes to conduct an in-depth investigation of the dynamic response of individual living colorectal cancer Caco-2 cells to changes in intracellular and extracellular hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) gradients, specifically focusing on eustress, at the single-cell level and in real-time. Their findings hold promise for innovative therapies against cancer and H2O2-related inflammatory diseases.
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) production plays a significant role in various diseases, including atherosclerosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cancer. Despite promising preclinical antioxidant therapies, clinical trials have yielded unsatisfactory results. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a stable ROS derivative, acts as a crucial participant in physiological signaling by serving as a eustressor. The concentration of H2O2 in the tumor microenvironment is closely linked to the occurrence and progression of colorectal cancer. A deeper understanding of how H2O2 functions and its specific efficacy in individual cancer cells may pave the way for more effective ROS-related treatments.
The authors utilized hopping probe scanning ion conductivity microscopy (HPICM) alongside Pt-functionalized nanoelectrodes to quantitatively assess the dynamic response in cell morphology, cell mechanical properties, and extracellular to intracellular eustress H2O2 gradients of individual colorectal cancer Caco-2 cells under H2O2 eustress. The investigation revealed that exposure to 0.1 or 1 mmol/L H2O2 eustress increased the extracellular to intracellular H2O2 gradient from 0.3 to 1.91 or 3.04, respectively. Additionally, the study found that F-actin-dependent cell stiffness increased under eustress of 0.1 mmol H2O2 but decreased under eustress of 1 mmol H2O2. Furthermore, eustress-induced cell stiffness was positively regulated by AKT activation and negatively influenced the expression of the H2O2-scavenging enzyme GPX2, ultimately maintaining relatively stable cellular H2O2 levels.
This study suggests that the eustress induced by low levels of H2O2 may contribute to the failure of some H2O2 targeted therapies. The results uncover a novel interplay between cellular physical properties and biochemical signaling in cancer cells' antioxidant defense, shedding light on the utilization of H2O2 eustress for survival at the single-cell level. This understanding is critical for comprehending cancer development and other H2O2-related inflammatory diseases. Inhibiting GPX under H2O2 eustress resulted in cytotoxicity, suggesting a potential enhancement for colon cancer treatment. These findings hold promise for the development of innovative therapies targeting cancer and H2O2-related inflammatory diseases.
Funder
The work was supported by the World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI), MEXT, Japan, JSPS Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (21H01770, 22K04890).
Glossary
Hopping Probe Scanning Ion Conductance Microscopy (HPICM)
The principle of scanning ion conductance microscopy (SICM) relies on monitoring the ion current that flows through a nanopipette containing electrolyte. It can map the topography of a sample by adjusting the nanopipette height to maintain a constant ion current as it is scanned over the sample surface. The proximity to the sample surface has a measurable effect on the ion current flow and, hence, feedback-controlled nanopipette withdrawal before the nanopipette makes contact with the sample, making it useful for non-contact imaging of living biological specimens.
In this study, SICM has been used in hopping probe mode, named Hopping Probe Scanning Ion Conductance Microscopy (HPICM), where the nanopipette constantly approaches and retracts from the sample, further reducing the potential for sample damage, particularly where the sample surface is not flat. The authors demonstrated that their HPICM can detect the dynamic changes in both cellular mechanical properties and topographical morphology of individual cancer cells in real-time.
About the World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI)
The WPI program was launched in 2007 by Japan's Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) to foster globally visible research centers boasting the highest standards and outstanding research environments. Numbering more than a dozen and operating at institutions throughout the country, these centers are given a high degree of autonomy, allowing them to engage in innovative modes of management and research. The program is administered by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
See the latest research news from the centers at the WPI News Portal:
https://www.eurekalert.org/newsportal/WPI
Main WPI program site: www.jsps.go.jp/english/e-toplevel
Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI)
Kanazawa University
Understanding nanoscale mechanisms of life phenomena by exploring “uncharted nano-realms”
Cells are the basic units of almost all life forms. We are developing nanoprobe technologies that allow direct imaging, analysis, and manipulation of the behavior and dynamics of important macromolecules in living organisms, such as proteins and nucleic acids, at the surface and interior of cells. We aim at acquiring a fundamental understanding of the various life phenomena at the nanoscale.
NanoLSI website: https://nanolsi.kanazawa-u.ac.jp/en/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-13
European Society of Endocrinology and Endocrine Society publish Joint Guideline on Glucocorticoid-induced Adrenal Insufficiency (GC-AI)
As focal points for endocrinology and hormone research, both the European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) and the Endocrine Society (ES) regularly produce clinical guidelines with recommendations for patient care, either in collaboration with other Societies or independently. Guideline development at each society is overseen by a Clinical Committee, and all guidelines are subject to a rigorous review process before ...
2024-05-13
WASHINGTON—The joint guideline is designed to help clinicians manage patients who have, or are at risk of developing, glucocorticoid-induced adrenal insufficiency. At least 1% of the global population uses chronic glucocorticoid therapy as anti-inflammatory or immune-suppressive agents.
The guideline, titled “Diagnosis and Therapy of Glucocorticoid-induced Adrenal Insufficiency,” will appear in the May 2024 issues of the Societies’ respective journals, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism and the European Journal of Endocrinology. ...
2024-05-13
Annapolis, MD; May 13, 2024—While wildflowers and perennials are a must for supporting pollinators, there's no denying the popularity of many annual flowers for their colorful, visual appeal. Annuals are often thought of as pollinator "deserts," but a new study suggests choosing the right varieties can give annual flowers a role in nourishing bees and other pollinating insects in home gardens.
In a two-year study, researchers at Michigan State University observed pollinators visiting 25 different varieties, or cultivars, of the six most popular annual ...
2024-05-13
An experimental treatment made from a plant virus is effective at protecting against a broad range of metastatic cancers in mice, shows a new study from the University of California San Diego.
The treatment, composed of nanoparticles fashioned from the cowpea mosaic virus—a virus that infects black-eyed pea plants—showed remarkable success in improving survival rates and suppressing the growth of metastatic tumors across various cancer models, including colon, ovarian, melanoma and breast cancer. Similar outcomes were also observed when the treatment was administered to mice whose tumors were surgically removed.
The findings were published recently in Advanced Science.
The ...
2024-05-13
SAN ANTONIO — May 13, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute is studying the process of boiling liquids under partial gravity conditions in a series of parabolic flights. The internally funded project, conducted in collaboration with Texas A&M University, aims to better understand how liquids boil on different surfaces in partial gravity. Boiling liquids will likely be required during future extended space missions to the Moon or Mars to support surface power, life support systems, cryogenic fuel production and in situ resource utilization.
“We ...
2024-05-13
Men with prostate cancer could significantly reduce the chances of the disease worsening by eating more fruits, vegetables, nuts, and olive oil, according to new research by UC San Francisco.
A study of more than 2,000 men with localized prostate cancer found that eating a primarily plant-based diet was associated with a 47% lower risk that their cancer would progress, compared with those who consumed the most animal products.
This amounted to eating just one or two more servings per day of healthy foods, particularly vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, while eating fewer animal products, like dairy and meat. The study followed ...
2024-05-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Actually, sometimes consumers don’t want to talk to a real person when they’re shopping online, a new study suggests.
In fact, what they really want is a chatbot that makes it clear that it is not human at all.
In a new study, researchers at The Ohio State University found that people preferred interacting with chatbots when they felt embarrassed about what they were buying online – items like antidiarrheal medicine or, for some people, skin care products.
“In general, research shows people would rather interact with a human customer ...
2024-05-13
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 13, 2024 – Ultrasound imaging offers a valuable and noninvasive way to find and monitor cancerous tumors. However, much of the most crucial information about a cancer, such as specific cell types and mutations, cannot be learned from imaging and requires invasive and damaging biopsies. One research group developed a way to employ ultrasound to extract this genetic information in a gentler way.
At the University of Alberta, a team led by Roger Zemp explored how intense ultrasound can release biological indicators of disease, or biomarkers, from cells. These biomarkers, ...
2024-05-13
Lisbon, Portugal – 13 May 2024: Semaglutide reduces the need for loop diuretic use and dose, and has positive effects on symptoms, physical limitations, and body weight in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) regardless of diuretic use, according to late breaking research presented today at Heart Failure 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
HFpEF is a condition in which the heart pumps normally but is too stiff to fill properly, rendering the heart unable to support the body’s need for oxygen-rich blood. The condition is becoming more common as populations ...
2024-05-13
Civilized political debates may seem increasingly out of reach as democracies across the world face rising polarization, but people still want to discuss issues with people they disagree with – especially those who present themselves as balanced and willing to seek solutions that work for everyone or open to learning new information, according to two studies published by the American Psychological Association.
One study, published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, examined how U.S. politicians and ordinary Americans with opposing political beliefs could share their ideas on divisive issues in a way that improved respect regardless of political ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Exploring the effect of H2O2 eustress on individual cancer cells using hopping probe scanning ion conductance microscopy (HPICM)