(Press-News.org) Men with prostate cancer could significantly reduce the chances of the disease worsening by eating more fruits, vegetables, nuts, and olive oil, according to new research by UC San Francisco.
A study of more than 2,000 men with localized prostate cancer found that eating a primarily plant-based diet was associated with a 47% lower risk that their cancer would progress, compared with those who consumed the most animal products.
This amounted to eating just one or two more servings per day of healthy foods, particularly vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, while eating fewer animal products, like dairy and meat. The study followed the men, whose median age was 65 years old, over time to see how dietary factors affected the progression of their cancer.
Plant-based diets include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, legumes, vegetable oils, tea and coffee. The researchers measured consumption using a plant-based index and compared the men who scored in the highest 20% to those who scored in the lowest 20%.
“These results could guide people to make better, more healthful choices across their whole diet, rather than adding or removing select foods,” said Vivian N. Liu, formerly lead clinical research coordinator at the UCSF Osher Center for Integrative Health and first author of the study, which appears in JAMA Network Open.
“Progressing to advanced disease is one of many pivotal concerns among patients with prostate cancer, their family, caregivers and physicians,” she said. “This adds to numerous other health benefits associated with consuming a primarily plant-based diet, such as a reduction in diabetes, cardiovascular disease and overall mortality.”
Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds
Plant-based diets are becoming increasingly popular in the United States, and evidence is accumulating that they can be beneficial to patients with prostate cancer, the most common cancer among men in the country after non-melanoma skin cancer.
Fruits and vegetables contain antioxidants, as well as anti-inflammatory compounds that have been shown to protect against prostate cancer, and prior research has consistently demonstrated the importance of dietary factors to overall health and well-being.
“Making small changes in one’s diet each day is beneficial,” said senior author Stacey A. Kenfield, ScD, a UCSF professor of urology and the Helen Diller Family Chair in Population Science for Urologic Cancer. “Greater consumption of plant-based food after a prostate cancer diagnosis has also recently been associated with better quality of life, including sexual function, urinary function and vitality, so it’s a win-win on both levels.”
Coauthors: From UCSF, other authors are Erin L. Van Blarigan, ScD; Li Zhang, PhD; Rebecca E. Graff, ScD; Crystal S. Langlais, PhD; Janet E. Cowan, MA; Peter R. Carroll, MD, MPH; and June M. Chan, ScD.
Funding and disclosures: Please see the paper.
About UCSF Health: UCSF Health is recognized worldwide for its innovative patient care, reflecting the latest medical knowledge, advanced technologies and pioneering research. It includes the flagship UCSF Medical Center, which is a top-ranked hospital, as well as UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals, with campuses in San Francisco and Oakland; Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital; UCSF Benioff Children’s Physicians; and the UCSF Faculty Practice. These hospitals serve as the academic medical center of the University of California, San Francisco, which is world-renowned for its graduate-level health sciences education and biomedical research. UCSF Health has affiliations with hospitals and health organizations throughout the Bay Area. Visit https://www.ucsfhealth.org/. Follow UCSF Health on Facebook or on Twitter
###
Follow UCSF
ucsf.edu | Facebook.com/ucsf | Twitter.com/ucsf | YouTube.com/ucsf
END
Prostate cancer study: More health benefits from plant-based diet
Eating more fruits, nuts, and vegetables each day – along with fewer animal products – is associated with a nearly 50% reduction in the risk of prostate cancer progression.
2024-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When consumers would prefer a chatbot over a person
2024-05-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Actually, sometimes consumers don’t want to talk to a real person when they’re shopping online, a new study suggests.
In fact, what they really want is a chatbot that makes it clear that it is not human at all.
In a new study, researchers at The Ohio State University found that people preferred interacting with chatbots when they felt embarrassed about what they were buying online – items like antidiarrheal medicine or, for some people, skin care products.
“In general, research shows people would rather interact with a human customer ...
Intense ultrasound extracts genetic info for less invasive cancer biopsies #ASA186
2024-05-13
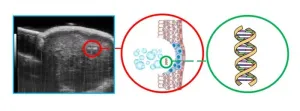
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 13, 2024 – Ultrasound imaging offers a valuable and noninvasive way to find and monitor cancerous tumors. However, much of the most crucial information about a cancer, such as specific cell types and mutations, cannot be learned from imaging and requires invasive and damaging biopsies. One research group developed a way to employ ultrasound to extract this genetic information in a gentler way.
At the University of Alberta, a team led by Roger Zemp explored how intense ultrasound can release biological indicators of disease, or biomarkers, from cells. These biomarkers, ...
Weight loss drug linked with reduced need for diuretics in heart failure patients
2024-05-13
Lisbon, Portugal – 13 May 2024: Semaglutide reduces the need for loop diuretic use and dose, and has positive effects on symptoms, physical limitations, and body weight in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) regardless of diuretic use, according to late breaking research presented today at Heart Failure 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
HFpEF is a condition in which the heart pumps normally but is too stiff to fill properly, rendering the heart unable to support the body’s need for oxygen-rich blood. The condition is becoming more common as populations ...
Getting out of the political echo chamber
2024-05-13
Civilized political debates may seem increasingly out of reach as democracies across the world face rising polarization, but people still want to discuss issues with people they disagree with – especially those who present themselves as balanced and willing to seek solutions that work for everyone or open to learning new information, according to two studies published by the American Psychological Association.
One study, published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, examined how U.S. politicians and ordinary Americans with opposing political beliefs could share their ideas on divisive issues in a way that improved respect regardless of political ...
Alarming rise of electronic vaping use in U.S. adolescents
2024-05-13
Electronic vapor products (EVPs), also known as e-cigarettes or vaping devices, have an allure because of their marketed image as a safer alternative to traditional cigarette smoking and for their variety of appealing flavors.
Yet, they contain many substances beyond nicotine, including propylene glycol, glycerin, flavorings and potentially harmful chemicals such as formaldehyde and metals, which could pose significant health risks such as respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease and cancer. Vaping also is strongly linked with a serious medical condition that damages the lungs due to the vitamin E acetate, an additive used ...
More than half of Americans give to charity at checkout, survey shows
2024-05-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- 53% of Americans give impulsively to charities at the checkout, and certain demographics tend to give more, according to a new survey conducted by faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
From supermarkets to retail, Americans are used to being asked for donations while making in-person or online purchases – whether by rounding up, donating a set amount or purchasing a token. Industry reports reveal how money is being raised – checkout charity campaigns brought in almost $750 million in 2022, with campaigns through ...
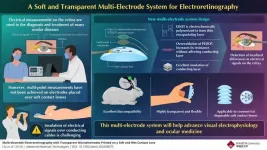
Taking electroretinography to the next level with a soft multi-electrode system
2024-05-13
Eye diseases are becoming more prevalent worldwide, partly because of the aging population, but also because of our greatly increased screen time compared to previous generations. Considering our use of displays will most likely keep rising due to technologies such as virtual and augmented reality, we must improve our diagnostic techniques for the early detection and monitoring of ocular diseases.
Among the arsenal of tools ophthalmologist have at their disposal, electroretinography (ERG) still holds much-untapped potential. Simply put, ERG consists of taking measurements of the electrical ...
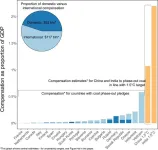
New Study: The price tag of phasing-out coal
2024-05-13
Coal phase-out is necessary to solve climate change, but can have negative impacts on workers and local communities dependent on coal for their livelihoods. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden and Central European University in Austria have studied government plans for coal phase-out around the world and discovered that more than half of such plans include monetary compensation to affected parties. This planned compensation globally amounts to USD 200 billion, but it excludes ...
Dramatic increase in fentanyl seized by authorities in last six years
2024-05-13
The number of illicit fentanyl seizures by law enforcement in the United States grew by more than 1,700 percent between 2017 and 2023, according to a new analysis. Further, the share of total fentanyl seizures that involved pills quadrupled over the same period–with the 115.6 million pills seized in 2023 representing 49 percent of total seizures.
This is the first time that such up-to-date seizure data has been published differentiating between fentanyl powder and pills, says the research team led by experts at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and the University of Florida.
Law enforcement drug seizures are used as a proxy for drug availability ...
What makes a memory? It may be related to how hard your brain had to work
2024-05-13
New Haven, Conn. — The human brain filters through a flood of experiences to create specific memories. Why do some of the experiences in this deluge of sensory information become “memorable,” while most are discarded by the brain?
A computational model and behavioral study developed by Yale scientists suggests a new clue to this age-old question, they report in the journal Nature Human Behavior.
“The mind prioritizes remembering things that it is not able to explain very well,” said Ilker Yildirim, an ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Prostate cancer study: More health benefits from plant-based dietEating more fruits, nuts, and vegetables each day – along with fewer animal products – is associated with a nearly 50% reduction in the risk of prostate cancer progression.