(Press-News.org) BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- 53% of Americans give impulsively to charities at the checkout, and certain demographics tend to give more, according to a new survey conducted by faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
From supermarkets to retail, Americans are used to being asked for donations while making in-person or online purchases – whether by rounding up, donating a set amount or purchasing a token. Industry reports reveal how money is being raised – checkout charity campaigns brought in almost $750 million in 2022, with campaigns through Walgreens, PetSmart and eBay being among the nation’s largest – but so far no one has developed a profile of who gives or has compared them to traditional donors.
“There are always marketing reports that like to talk about how many people gave and how much it totaled to, but no one was talking about who to target when doing check-out asks for donations,” said Lauren Dula, an assistant professor of public administration and policy at Binghamton University. “The old-school donor profile of a moneyed, educated, older donor doesn't hold in this setting. It really is young and diverse people who are willing to add a little to the pot.”
Dula, along with Ruth Hansen from the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, surveyed nearly 1,400 Americans on impulse giving. Survey respondents self-reported whether they had donated money at a store checkout over the previous year. If they answered “yes,” five more questions followed:
Did you round up your total charge?
Did you add an additional amount, such as $1 or $5?
Did you purchase a small token that would be displayed within the store?
Thinking of the last time you donated this way, how familiar were you with the charity?
How much money do you think you have donated in this way over the past year?
Over half the respondents (53%) said they had given to charity within the past year while paying for purchases. Those who give said they donate about $50 a year.
“Among those who donate, the most common form of donating is rounding up their total to the nearest dollar,” said Dula. “Another popular form was adding an amount, such as $1, to their order. Less common are people who purchase tokens for in-store display.”
But who donates? Demographics were found to play a role in whether or not people give at the register.
“Our survey found that women and Black respondents were the top-giving demographics with checkout charity,” said Dula. “Middle-class individuals under 50 who have not attended college were also more likely to donate. These patterns contrast with formal donors or those who give directly to charitable organizations, who are usually older, higher-earning college graduates.”
The total raised from checkout campaigns has increased yearly since 2012, but the frequency of donation requests at checkout may lead to complacency or annoyance, said Dula.
“The numbers could take a dip when impulse giving isn’t so impulsive anymore, and ‘no thanks’ will become easier to say,” she said.
The researchers are working to get funding to re-run their survey in a "post-COVID" situation. This survey was conducted in 2021, when many were still avoiding shopping in person. Dula said that they would like to learn more about how frequently respondents may be asked to donate in a week and their general opinion of these requests.
“We are just delving into the motivations behind the impulse-giving phenomenon,” said Dula. “Having a profile of a giver is nice because it helps retailers and charities understand their clientele better. Also, while big-name charities can raise a lot of money due to name recognition, these campaigns can go hyper-local and raise the profile of organizations doing fantastic work in the customer's own community.”
The paper, “Who Will Spare a Dime? Impulse Giving Decisions at the Checkout,” was published in the Journal of Public and Nonprofit Affairs.
END
More than half of Americans give to charity at checkout, survey shows
Young and diverse Americans are more likely to donate
2024-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
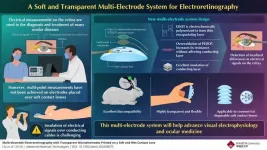
Taking electroretinography to the next level with a soft multi-electrode system
2024-05-13
Eye diseases are becoming more prevalent worldwide, partly because of the aging population, but also because of our greatly increased screen time compared to previous generations. Considering our use of displays will most likely keep rising due to technologies such as virtual and augmented reality, we must improve our diagnostic techniques for the early detection and monitoring of ocular diseases.
Among the arsenal of tools ophthalmologist have at their disposal, electroretinography (ERG) still holds much-untapped potential. Simply put, ERG consists of taking measurements of the electrical ...
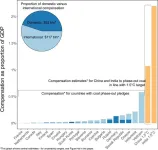
New Study: The price tag of phasing-out coal
2024-05-13
Coal phase-out is necessary to solve climate change, but can have negative impacts on workers and local communities dependent on coal for their livelihoods. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden and Central European University in Austria have studied government plans for coal phase-out around the world and discovered that more than half of such plans include monetary compensation to affected parties. This planned compensation globally amounts to USD 200 billion, but it excludes ...
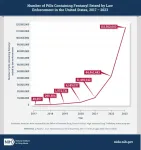
Dramatic increase in fentanyl seized by authorities in last six years
2024-05-13
The number of illicit fentanyl seizures by law enforcement in the United States grew by more than 1,700 percent between 2017 and 2023, according to a new analysis. Further, the share of total fentanyl seizures that involved pills quadrupled over the same period–with the 115.6 million pills seized in 2023 representing 49 percent of total seizures.
This is the first time that such up-to-date seizure data has been published differentiating between fentanyl powder and pills, says the research team led by experts at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and the University of Florida.
Law enforcement drug seizures are used as a proxy for drug availability ...
What makes a memory? It may be related to how hard your brain had to work
2024-05-13
New Haven, Conn. — The human brain filters through a flood of experiences to create specific memories. Why do some of the experiences in this deluge of sensory information become “memorable,” while most are discarded by the brain?
A computational model and behavioral study developed by Yale scientists suggests a new clue to this age-old question, they report in the journal Nature Human Behavior.
“The mind prioritizes remembering things that it is not able to explain very well,” said Ilker Yildirim, an ...
Over 115 million pills containing illicit fentanyl seized by law enforcement in 2023
2024-05-13
Law enforcement seizures of illicit fentanyl increased dramatically in number and size between 2017 to 2023 in the U.S., especially in pill form, according to a new study funded by the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). The number of individual pills containing fentanyl seized by law enforcement was 2,300 times greater in 2023 compared to 2017, with 115,562,603 pills seized in 2023 vs. 49,657 in 2017. The proportion of fentanyl pill seizures to the total number of fentanyl seizures more than quadrupled, ...
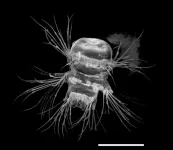
Nature's 3D printer: bristle worms form bristles piece by piece
2024-05-13
A new interdisciplinary study led by molecular biologist Florian Raible from the Max Perutz Labs at the University of Vienna provides exciting insights into the bristles of the marine annelid worm Platynereis dumerilii. Specialized cells, so-called chaetoblasts, control the formation of the bristles. Their mode of operation is astonishingly similar to that of a technical 3D printer. The project is a collaboration with researchers from the University of Helsinki, Vienna University of Technology and Masaryk University in Brno. The study was recently published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Chitin is ...
Research shows that ‘softer’ proteins can cross into the nucleus quicker
2024-05-13
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and King’s College London have discovered that how soft or rigid proteins are in certain regions can dictate how fast or slow they enter the nucleus.
Proteins need to come in and out of the nucleus, the control centre of the cell, to give different functions, such as telling the nucleus to switch on or off certain genes. These proteins cross using a channel on the edge of the nucleus called the ‘nuclear pore complex’.
Previous research has shown that the size and composition of these proteins change how easily they can cross, but now this research, published today in Nature Physics, has shown that mechanical properties can also ...
Birth by C-section more than doubles odds of measles vaccine failure
2024-05-13
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 LONDON TIME (BST)/ 05:00 US ET ON MONDAY 13 MAY 2024
A copy of the paper and photographs are available at:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Rfv2ywq7jhHLPuhKZ_ihs6TinuLHCJmU?usp=sharing
Peer-reviewed / Meta-analysis / People
A study by the University of Cambridge, UK, and Fudan University, China, has found that a single dose of the measles jab is up to 2.6 times more likely to be completely ineffective in children born by C-section, compared to those born naturally.
Failure of the vaccine means that the child’s immune system does not produce antibodies to fight ...
How do obesity and metabolic syndrome affect women’s risks of breast cancer and cancer-related death?
2024-05-13
In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) randomized trial, a low-fat diet reduced breast cancer mortality, especially in women with more metabolic syndrome (MetS) components (obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol). A recent analysis of WHI findings indicates that MetS and obesity each have different associations with breast cancer subtypes and mortality risk. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The analysis ...
KITECH develops deformable energy storage device via laser technology
2024-05-13
The joint research team, led by Dr. Chanwoo Yang and Researcher Seong Ju Park from Korea Institute of Industrial Technology(KITECH), along with Prof. Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim from POSTECH, has successfully developed a compact energy storage device with excellent elasticity. This research was published in the world-renowned journal in the field of electronic engineering, 'npj Flexible Electronics'.
Beyond foldable and rollable devices, the era of stretchable IT devices is arriving. For these devices, the development of small, elastic energy storage devices is essential. In this respect, micro supercapacitors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
[Press-News.org] More than half of Americans give to charity at checkout, survey showsYoung and diverse Americans are more likely to donate