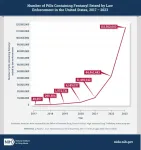
(Press-News.org) Law enforcement seizures of illicit fentanyl increased dramatically in number and size between 2017 to 2023 in the U.S., especially in pill form, according to a new study funded by the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). The number of individual pills containing fentanyl seized by law enforcement was 2,300 times greater in 2023 compared to 2017, with 115,562,603 pills seized in 2023 vs. 49,657 in 2017. The proportion of fentanyl pill seizures to the total number of fentanyl seizures more than quadrupled, with pills representing 49% of illicit fentanyl seizures in 2023 compared to 10% in 2017. The study also found a significant increase in the number and weight of fentanyl-containing powder seizures during this time.
“Fentanyl has continued to infiltrate the drug supply in communities across the United States and it is a very dangerous time to use drugs, even just occasionally,” said NIDA Director Nora D. Volkow, M.D. “Illicit pills are made to look identical to real prescription pills, but can actually contain fentanyl. It is urgently important that people know that any pills given to someone by a friend, purchased on social media, or received from any source other than a pharmacy could be potentially deadly – even after a single ingestion.”
Although fentanyl seizures were historically less common in the Western U.S., this analysis found that this region now accounts for most of law enforcement seizures of fentanyl overall, as well as total weight of fentanyl seized. The proportion of fentanyl pill seizures compared to the overall number of fentanyl seizures was also highest in the West, with 77.8% of all law enforcement seizures of fentanyl in the West being in pill form in 2023. These data emphasize the need for continued monitoring of regional shifts in the fentanyl supply, to help inform targeted prevention and public health responses.
In 2022, over 107,000 people died of a drug overdose, with 75% of those deaths involving an opioid. The overall rise in overdose deaths is largely attributable to the proliferation of illicit fentanyl, a synthetic opioid. Illicit fentanyl is highly potent, cheaply made, and easily transported, making it extremely profitable. Fentanyl is about 50 times more potent than heroin and a lethal dose may be as small as two milligrams.
While some people knowingly consume fentanyl, many people do not know if the drugs they plan to use contain fentanyl. This is especially true of illicit counterfeit pills, which are often made to resemble prescription medications such as oxycodone or benzodiazepines, but really contain fentanyl. Recent studies have reported a dramatic rise in overdose deaths among teens between 2010 to 2021, which remained elevated well into 2022 according to a NIDA analysis of CDC and Census data. This increase in deaths has been largely attributed to widespread availability of illicit fentanyl, the proliferation of counterfeit pills containing fentanyl, and the ease of purchasing pills through social media.
“Availability of illicit fentanyl is continuing to skyrocket in the U.S., and the influx of fentanyl-containing pills is particularly alarming,” said Joseph J. Palamar, Ph.D., M.P.H., associate professor in the Department of Population Health at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, and lead author on the paper. “Public health efforts are needed to help prevent these pills from falling into the hands of young people, and to help prevent overdose among people taking pills that unsuspectingly contain fentanyl.”
The data used for this analysis were collected through the High Intensity Drug Trafficking Areas (HIDTA) program, a grant program aimed at reducing drug trafficking and misuse administered by the Office of National Drug Control Policy. Though law enforcement seizures do not necessarily reflect prevalence of use, they represent an indicator of the availability of illicit drugs.
Unlike most survey data and surveillance systems which can be lagged for a year or more, HIDTA data are made available quarterly, allowing evaluation in almost real time. HIDTA data also distinguish between the presence of fentanyl in pill or powder form. Analyzing these data can therefore help identify trends in availability of illicit substances and act as a type of early warning system to shift public health education or interventional resources more quickly.
HIDTA data does not differentiate between fentanyl and its analogs, nor estimate the amount of fentanyl present in seized substances. However, given the small amount necessary for an overdose, the authors note that the presence of any fentanyl is an important indicator of overdose risk.
This analysis, published in the International Journal of Drug Policy, was led by researchers from the NIDA-funded National Drug Early Warning System (NDEWS). It builds on a previous NDEWS study (press release) of trends in seizures of powders and pills containing illicit fentanyl in the U.S. between 2018 through 2021.
If you or someone you know is struggling or in crisis, help is available. Call or text 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org. To learn how to get support for mental health, drug or alcohol issues, visit FindSupport.gov. If you are ready to locate a treatment facility or provider, you can go directly to FindTreatment.gov or call 800-662-HELP (4357).
Reference: J Palamar, et al. National and Regional Trends in Fentanyl Seizures in the United States, 2017-2023. International Journal of Drug Policy. DOI: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2024.104417 (2024).
###
About the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): NIDA is a component of the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIDA supports most of the world’s research on the health aspects of drug use and addiction. The Institute carries out a large variety of programs to inform policy, improve practice, and advance addiction science. For more information about NIDA and its programs, visit www.nida.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
About substance use disorders: Substance use disorders are chronic, treatable conditions from which people can recover. In 2022, nearly 49 million people in the United States had at least one substance use disorder. Substance use disorders are defined in part by continued use of substances despite negative consequences. They are also relapsing conditions, in which periods of abstinence (not using substances) can be followed by a return to use. Stigma can make individuals with substance use disorders less likely to seek treatment. Using preferred language can help accurately report on substance use and addiction. View NIDA’s online guide.
END
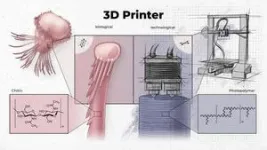
A new interdisciplinary study led by molecular biologist Florian Raible from the Max Perutz Labs at the University of Vienna provides exciting insights into the bristles of the marine annelid worm Platynereis dumerilii. Specialized cells, so-called chaetoblasts, control the formation of the bristles. Their mode of operation is astonishingly similar to that of a technical 3D printer. The project is a collaboration with researchers from the University of Helsinki, Vienna University of Technology and Masaryk University in Brno. The study was recently published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Chitin is ...
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and King’s College London have discovered that how soft or rigid proteins are in certain regions can dictate how fast or slow they enter the nucleus.
Proteins need to come in and out of the nucleus, the control centre of the cell, to give different functions, such as telling the nucleus to switch on or off certain genes. These proteins cross using a channel on the edge of the nucleus called the ‘nuclear pore complex’.
Previous research has shown that the size and composition of these proteins change how easily they can cross, but now this research, published today in Nature Physics, has shown that mechanical properties can also ...
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 LONDON TIME (BST)/ 05:00 US ET ON MONDAY 13 MAY 2024
A copy of the paper and photographs are available at:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Rfv2ywq7jhHLPuhKZ_ihs6TinuLHCJmU?usp=sharing
Peer-reviewed / Meta-analysis / People
A study by the University of Cambridge, UK, and Fudan University, China, has found that a single dose of the measles jab is up to 2.6 times more likely to be completely ineffective in children born by C-section, compared to those born naturally.
Failure of the vaccine means that the child’s immune system does not produce antibodies to fight ...
In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) randomized trial, a low-fat diet reduced breast cancer mortality, especially in women with more metabolic syndrome (MetS) components (obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol). A recent analysis of WHI findings indicates that MetS and obesity each have different associations with breast cancer subtypes and mortality risk. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The analysis ...
The joint research team, led by Dr. Chanwoo Yang and Researcher Seong Ju Park from Korea Institute of Industrial Technology(KITECH), along with Prof. Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim from POSTECH, has successfully developed a compact energy storage device with excellent elasticity. This research was published in the world-renowned journal in the field of electronic engineering, 'npj Flexible Electronics'.
Beyond foldable and rollable devices, the era of stretchable IT devices is arriving. For these devices, the development of small, elastic energy storage devices is essential. In this respect, micro supercapacitors ...
Many programs ‘deeply entrenched in school culture’ are harmful to children and can cause potentially lasting damage, psychologists have warned.
They say these practices, from abstinence-only sex education to zero tolerance policies, can direct considerable funds away from evidence-based strategies, as well as giving pupils misleading information.
In new book Investigating School Psychology, researchers have carried out an exhaustive review of current literature to look at practices that continue to exist with little to no scientific ...
The number of cancer cases and deaths in Canada is expected to increase because of a growing and aging population, but the overall rates of people being diagnosed with and dying from cancer will continue to decline, according to the latest cancer trends research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240095.
The study is the result of a collaboration between the Canadian Cancer Society, Statistics Canada, and the Public Health Agency of Canada. It provides estimates of the number ...
Prices paid to hospitals during 2022 by employers and private insurers for both inpatient and outpatient services averaged 254% of what Medicare would have paid, with wide variation in prices among states, according to a new RAND report.
Some states (Arkansas, Iowa, Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi) had relative prices under 200% of Medicare, while other states (California, Florida, Georgia, New York, South Carolina, West Virginia, Wisconsin) had relative prices that were above 300% of Medicare.
Even as the number of hospitals and insurance claims analyzed has grown across multiple rounds of the RAND Hospital ...
Pioneering measures to tackle sedentary behaviour among children in China have proved effective, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Bristol, reveals regulations recently introduced by the Chinese government to reduce school children’s sedentary behaviour by restricting online gaming companies catering for this age group, limiting the amount of homework schoolteachers can assign, and curtailing when private tuition businesses can provide lessons, significantly reduced total sedentary time as well as how long they spent on different sedentary activities. The measures were associated with a 13.8% daily sedentary drop overall, ...
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), reveals the anti-inflammatory power of moderate-to-vigorous aerobic exercise in adults living with the low-grade inflammation of obesity, shedding light on its potential to help prevent multiple metabolic diseases including type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis (clogged arteries).
Excessive fat accumulation in adipose tissue (fat cells) leads to chronic low-grade inflammation, characterised by chronically elevated levels of ...