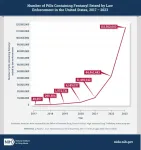
(Press-News.org) The number of illicit fentanyl seizures by law enforcement in the United States grew by more than 1,700 percent between 2017 and 2023, according to a new analysis. Further, the share of total fentanyl seizures that involved pills quadrupled over the same period–with the 115.6 million pills seized in 2023 representing 49 percent of total seizures.
This is the first time that such up-to-date seizure data has been published differentiating between fentanyl powder and pills, says the research team led by experts at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and the University of Florida.
Law enforcement drug seizures are used as a proxy for drug availability or supply, but do not necessarily indicate the prevalence of illicit drug use. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid up to 50 times more potent than heroin and involved in approximately two-thirds of all U.S. overdoses. More than 100,000 people continue to die from drug overdoses each year.
The findings, published online May 13 in the International Journal of Drug Policy, also indicated that fentanyl seizures varied by U.S. region. Fentanyl seizures were initially less common in the West; however, by 2023, the West had the greatest number of all seizures by weight, and 85 percent of all confiscated fentanyl pills. The greatest number of fentanyl seizures in powder form—which can easily be used to adulterate other drugs and make them deadlier—was highest in the South. While the Midwest had fewer fentanyl seizures overall, researchers saw a particularly noteworthy spike in fentanyl pill seizures there.
“About half of seized fentanyl is now in pill form, suggesting that the illicit drug landscape has rapidly changed,” said study lead author Joseph J. Palamar, PhD, MPH, an associate professor in the Department of Population Health at NYU Langone Health and deputy director of the National Drug Early Warning System (NDEWS). “Fentanyl in pill form not only makes it easier for people to initiate use, but also increases the chances that people who buy illicit pills could be unintentionally exposed to fentanyl since it is commonly present in counterfeit pills pressed to resemble oxycodone, Xanax, or even Adderall.”
How the Study was Conducted
Palamar and colleagues analyzed annual trends in seizures of pills and powders containing fentanyl using data from the High Intensity Drug Trafficking Areas (HIDTA) program for the U.S. overall, as well as by region, from 2017 through 2023. Unlike most survey data and surveillance systems which can lag by a year or more, HIDTA data are made available quarterly, which allows for analysis in almost real time.
The team of investigators measured eight indicators of potential shifts in illicit fentanyl supply or availability including the number of total seizures, powder seizures, pill seizures, and the total weight of seizures. They also looked at the percentage of pill seizures in comparison to total seizures.
In the U.S. overall between 2017 and 2023, there were 66,303 seizures, with 67.3 percent of fentanyl seizures being in powder form and 32.7 percent in pill form. The total number of seizures during that time period increased by more than 1,700 percent.
In 2023, states with the greatest number of seizures included Florida, Arizona, and California respectively. The highest number of pill seizures were in Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. The Northeast had the fewest pills seized in 2023.
The West always had the largest proportion of fentanyl pills relative to all seizures, most likely to proximity to the Mexican border, said Palamar, but his team’s findings show all regions are slowly catching up and that pills are dominating much of the fentanyl market. States with the highest percentage of seizures in pill form include New Mexico (98.4 percent), Colorado (94.8%) and Wyoming (93.8 percent)
One study limitation identified by Palamar was that due to the nature of HIDTA data collection, the investigators were unable to differentiate whether seizures were solely fentanyl, fentanyl combined with other drugs, or fentanyl analogs (such as carfentanil, one of the most potent opioids in existence). Even so, Palamar maintains that detection of any fentanyl in a drug seizure can be an important indicator for risk of overdose.
In addition to Palamar, co-investigators include Linda B. Cottler, PhD, MPH, and Nicole Fitzgerald at the University of Florida in Gainesville; Thomas H. Carr, at the University of Baltimore in Maryland; senior author Daniel Ciccarone, MD, MPH, at the University of California, San Francisco.
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health under grant numbers U01DA051126, T32DA035167, and R01DA057289. The content of this research is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Media Inquiries:
Sasha Walek
Sasha.walek@nyulangone.org
917-838-9607
END
Dramatic increase in fentanyl seized by authorities in last six years
Nearly half of seizures in pill form last year
2024-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What makes a memory? It may be related to how hard your brain had to work
2024-05-13
New Haven, Conn. — The human brain filters through a flood of experiences to create specific memories. Why do some of the experiences in this deluge of sensory information become “memorable,” while most are discarded by the brain?
A computational model and behavioral study developed by Yale scientists suggests a new clue to this age-old question, they report in the journal Nature Human Behavior.
“The mind prioritizes remembering things that it is not able to explain very well,” said Ilker Yildirim, an ...
Over 115 million pills containing illicit fentanyl seized by law enforcement in 2023
2024-05-13
Law enforcement seizures of illicit fentanyl increased dramatically in number and size between 2017 to 2023 in the U.S., especially in pill form, according to a new study funded by the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). The number of individual pills containing fentanyl seized by law enforcement was 2,300 times greater in 2023 compared to 2017, with 115,562,603 pills seized in 2023 vs. 49,657 in 2017. The proportion of fentanyl pill seizures to the total number of fentanyl seizures more than quadrupled, ...
Nature's 3D printer: bristle worms form bristles piece by piece
2024-05-13
A new interdisciplinary study led by molecular biologist Florian Raible from the Max Perutz Labs at the University of Vienna provides exciting insights into the bristles of the marine annelid worm Platynereis dumerilii. Specialized cells, so-called chaetoblasts, control the formation of the bristles. Their mode of operation is astonishingly similar to that of a technical 3D printer. The project is a collaboration with researchers from the University of Helsinki, Vienna University of Technology and Masaryk University in Brno. The study was recently published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Chitin is ...
Research shows that ‘softer’ proteins can cross into the nucleus quicker
2024-05-13
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and King’s College London have discovered that how soft or rigid proteins are in certain regions can dictate how fast or slow they enter the nucleus.
Proteins need to come in and out of the nucleus, the control centre of the cell, to give different functions, such as telling the nucleus to switch on or off certain genes. These proteins cross using a channel on the edge of the nucleus called the ‘nuclear pore complex’.
Previous research has shown that the size and composition of these proteins change how easily they can cross, but now this research, published today in Nature Physics, has shown that mechanical properties can also ...
Birth by C-section more than doubles odds of measles vaccine failure
2024-05-13
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 LONDON TIME (BST)/ 05:00 US ET ON MONDAY 13 MAY 2024
A copy of the paper and photographs are available at:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Rfv2ywq7jhHLPuhKZ_ihs6TinuLHCJmU?usp=sharing
Peer-reviewed / Meta-analysis / People
A study by the University of Cambridge, UK, and Fudan University, China, has found that a single dose of the measles jab is up to 2.6 times more likely to be completely ineffective in children born by C-section, compared to those born naturally.
Failure of the vaccine means that the child’s immune system does not produce antibodies to fight ...
How do obesity and metabolic syndrome affect women’s risks of breast cancer and cancer-related death?
2024-05-13
In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) randomized trial, a low-fat diet reduced breast cancer mortality, especially in women with more metabolic syndrome (MetS) components (obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol). A recent analysis of WHI findings indicates that MetS and obesity each have different associations with breast cancer subtypes and mortality risk. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The analysis ...
KITECH develops deformable energy storage device via laser technology
2024-05-13
The joint research team, led by Dr. Chanwoo Yang and Researcher Seong Ju Park from Korea Institute of Industrial Technology(KITECH), along with Prof. Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim from POSTECH, has successfully developed a compact energy storage device with excellent elasticity. This research was published in the world-renowned journal in the field of electronic engineering, 'npj Flexible Electronics'.
Beyond foldable and rollable devices, the era of stretchable IT devices is arriving. For these devices, the development of small, elastic energy storage devices is essential. In this respect, micro supercapacitors ...
Deeply entrenched school psychology practices can be ‘harmful to children’
2024-05-13
Many programs ‘deeply entrenched in school culture’ are harmful to children and can cause potentially lasting damage, psychologists have warned.
They say these practices, from abstinence-only sex education to zero tolerance policies, can direct considerable funds away from evidence-based strategies, as well as giving pupils misleading information.
In new book Investigating School Psychology, researchers have carried out an exhaustive review of current literature to look at practices that continue to exist with little to no scientific ...
Projected estimates of cancer in Canada in 2024
2024-05-13
The number of cancer cases and deaths in Canada is expected to increase because of a growing and aging population, but the overall rates of people being diagnosed with and dying from cancer will continue to decline, according to the latest cancer trends research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240095.
The study is the result of a collaboration between the Canadian Cancer Society, Statistics Canada, and the Public Health Agency of Canada. It provides estimates of the number ...
Private health plans paid hospitals 254% of what Medicare would pay during 2022
2024-05-13
Prices paid to hospitals during 2022 by employers and private insurers for both inpatient and outpatient services averaged 254% of what Medicare would have paid, with wide variation in prices among states, according to a new RAND report.
Some states (Arkansas, Iowa, Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi) had relative prices under 200% of Medicare, while other states (California, Florida, Georgia, New York, South Carolina, West Virginia, Wisconsin) had relative prices that were above 300% of Medicare.
Even as the number of hospitals and insurance claims analyzed has grown across multiple rounds of the RAND Hospital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
[Press-News.org] Dramatic increase in fentanyl seized by authorities in last six yearsNearly half of seizures in pill form last year