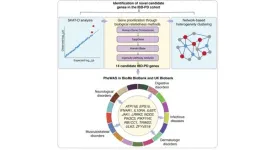
The team, led by Meltem Ece Kars, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine; Yuval Itan, PhD, Associate Professor of Genetics and Genomic Sciences; and Inga Peter, PhD, Professor of Genetics and Genomic Sciences at Icahn Mount Sinai, used advanced genomic analysis techniques to investigate the genetic overlap between IBD and PD. Their findings point to mutations in the LRRK2 gene as a common element linking both conditions and identify novel genes that are likely to be affected in people experiencing both IBD and PD.
Dr. Kars explained the core of their findings: "We've found that IBD and PD are caused by certain shared genetic factors, including variants in LRRK2 and other genes previously unknown for this combined condition. This could dramatically change our approach to these diseases, allowing for therapies that target both conditions simultaneously."
The study analyzed data from the Mount Sinai BioMe BioBank, the UK Biobank, and a cohort of 67 patients diagnosed with both IBD and PD from the Danish National Biobank. This combined dataset enabled the researchers to explore high-impact rare genetic variants and identify new genes and biological pathways that contribute to the IBD-PD comorbidity.
"Our research not only links these two diseases genetically but also sets the stage for new forms of treatment, and potentially prevention strategies, that could lessen the burden of these diseases on patients," Dr. Kars said.
The researchers used a variety of computational methods to uncover significant associations between the LRRK2 gene variants and the co-occurrence of IBD and PD, including the network-based heterogeneity clustering approach, which they have demonstrated to be highly effective for gene discoveries in small cohorts that cannot be analyzed by traditional gene association methods. Their analysis also revealed several pathways related to immunity, inflammation, and autophagy, the body’s cellular recycling system, that are involved in both conditions.
These insights have potential implications across multiple areas of medicine, suggesting that understanding genetic factors could lead to better-targeted therapies. The study underscores the importance of genetic research in developing personalized medicine approaches that could improve treatment for patients with both IBD and PD.
The promise of these findings extends beyond current treatment paradigms: "By pinpointing the genetic underpinnings common to both IBD and PD, we pave the way for innovative treatments, whether through the development of novel drug targets or the repurposing of existing drugs, that could potentially tackle the root causes of these conditions," Dr. Kars said.
The results of this study could also influence future research directions, encouraging a more integrated approach to studying diseases that may appear unrelated but share common genetic pathways.
This work was funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation, National Institute of Health’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke grant P20NS123220, and the Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine.
The paper is titled, “The landscape of rare genetic variation associated with inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson's disease comorbidity.”
-####-
About the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is internationally renowned for its outstanding research, educational, and clinical care programs. It is the sole academic partner for the eight- member hospitals* of the Mount Sinai Health System, one of the largest academic health systems in the United States, providing care to a large and diverse patient population.
Ranked 13th nationwide in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and among the 99th percentile in research dollars per investigator according to the Association of American Medical Colleges, Icahn Mount Sinai has a talented, productive, and successful faculty. More than 3,000 full-time scientists, educators, and clinicians work within and across 44 academic departments and 36 multidisciplinary institutes, a structure that facilitates tremendous collaboration and synergy. Our emphasis on translational research and therapeutics is evident in such diverse areas as genomics/big data, virology, neuroscience, cardiology, geriatrics, as well as gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
Icahn Mount Sinai offers highly competitive MD, PhD, and Master’s degree programs, with current enrollment of approximately 1,300 students. It has the largest graduate medical education program in the country, with more than 2,000 clinical residents and fellows training throughout the Health System. In addition, more than 550 postdoctoral research fellows are in training within the Health System.
A culture of innovation and discovery permeates every Icahn Mount Sinai program. Mount Sinai’s technology transfer office, one of the largest in the country, partners with faculty and trainees to pursue optimal commercialization of intellectual property to ensure that Mount Sinai discoveries and innovations translate into healthcare products and services that benefit the public.
Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to breakthrough science and clinical care is enhanced by academic affiliations that supplement and complement the School’s programs.
Through the Mount Sinai Innovation Partners (MSIP), the Health System facilitates the real-world application and commercialization of medical breakthroughs made at Mount Sinai. Additionally, MSIP develops research partnerships with industry leaders such as Merck & Co., AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, and others.
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is located in New York City on the border between the Upper East Side and East Harlem, and classroom teaching takes place on a campus facing Central Park. Icahn Mount Sinai’s location offers many opportunities to interact with and care for diverse communities. Learning extends well beyond the borders of our physical campus, to the eight hospitals of the Mount Sinai Health System, our academic affiliates, and globally.
-------------------------------------------------------
* Mount Sinai Health System member hospitals: The Mount Sinai Hospital; Mount Sinai Beth Israel; Mount Sinai Brooklyn; Mount Sinai Morningside; Mount Sinai Queens; Mount Sinai South Nassau; Mount Sinai West; and New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
END