(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have recast diffusion in multicomponent alloys as a sum of individual contributions, called “kinosons.” Using machine learning to compute the statistical distribution of the individual contributions, they were able to model the alloy and calculate its diffusivity orders of magnitude more efficiently than computing whole trajectories. This work was recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We found a much more efficient way to calculate diffusion in solids, and at the same time, we learned more about the fundamental processes of diffusion in that same system,” says materials science & engineering professor Dallas Trinkle, who led this work, along with graduate student Soham Chattopadhyay.
Diffusion in solids is the process by which atoms move throughout a material. The production of steel, ions moving through a battery and the doping of semiconductor devices are all things that are controlled by diffusion.
Here, the team modeled diffusion in multicomponent alloys, which are metals composed of five different elements—manganese, cobalt, chromium, iron and nickel in this research—in equal amounts. These types of alloys are interesting because one way to make strong materials is to add different elements together like adding carbon and iron to make steel. Multicomponent alloys have unique properties, such as good mechanical behavior and stability at high temperatures, so it is important to understand how atoms diffuse in these materials.
To get a good look at diffusion, long timescales are needed since atoms randomly move around and, over time, their displacement from the starting point will grow. “If somebody tries to simulate the diffusion, it’s a pain because you have to run the simulation for a very long time to get the full picture,” Trinkle says. “That really limits a lot of the ways that we can study diffusion. More accurate methods for calculating transition rates often can’t be used because you wouldn’t be able to do enough steps of a simulation to get the longtime trajectory and get a reasonable value of diffusion.”
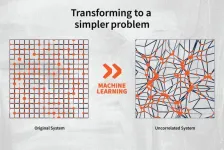
An atom might jump to the left but then it might jump back to the right. In that case, the atom hasn’t moved anywhere. Now, say it jumps left, then 1000 other things happen, then it jumps back to the right. That’s the same effect. Trinkle says, “We call that correlation because at one point the atom made one jump and then later it undid that jump. That’s what makes diffusion complicated. When we look at how machine learning is solving the problem, what it’s really doing is it’s changing the problem into one where there aren’t any of these correlated jumps.”
Therefore, any jump that an atom makes contributes to diffusion and the problem becomes a lot easier to solve. “We call those jumps kinosons, for little moves,” Trinkle says. “We’ve shown that you can extract the distribution of those, the probability of seeing a kinoson of a certain magnitude, and add them all up to get the true diffusivity. On top of that you can tell how different elements are diffusing in a solid.”
Another advantage of modeling diffusion using kinosons and machine learning is that it is significantly faster than calculating long-timescale, whole trajectories. Trinkle says that with this method, simulations can be done 100 times faster than it would take with the normal methods.
“I think this method is really going to change the way we think about diffusion,” he says. “It’s a different way to look at the problem and I hope that in the next 10 years, this will be the standard way of looking at diffusion. To me, one of the exciting things is not just that it works faster, but you also learn more about what’s happening in the system.”
*
Dallas Trinkle is also an affiliate of the Materials Research Laboratory at UIUC.
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation under Program NO MPS-1940303.
END
Simulating diffusion using 'kinosons' and machine learning
2024-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Far from toxic, lactate rivals glucose as body's major fuel after a carbohydrate meal
2024-05-14
As a student competing in track and field at his Parlier high school, Robert Leija was obsessed with how to improve his performance and, in particular, prevent the buildup of lactic acid in his muscles during training. Like many athletes, he blamed it for the performance fatigue and muscle soreness he experienced after intense workouts.
But as a kinesiology student at Fresno State, he was handed an out-of-print textbook that told him he had it all wrong. Lactate wasn't a danger sign that athletes had depleted their body's supply of oxygen, but likely a normal product of the metabolic activity required to fuel the muscles during sustained exercise.
Now, as a graduate student ...
AI for more caring institutions
2024-05-14
More and more public services — such as affordable housing, public school matching and child welfare — are relying on algorithms to make decisions and allocate resources. So far, much of the work that has gone into designing these systems has focused on workers’ experiences using them or communities’ perceptions of them.
But what about the actual impact of these programs have on people, especially when the decisions the systems make lead to denial of services? Can you design algorithms to help people make sense of and ...
Astronomers spot a giant planet that is as light as cotton candy
2024-05-14
Astronomers at MIT, the University of Liège in Belgium, and elsewhere have discovered a huge, fluffy oddball of a planet orbiting a distant star in our Milky Way galaxy. The discovery, reported today in the journal Nature Astronomy, is a promising key to the mystery of how such giant, super-light planets form.
The new planet, named WASP-193b, appears to dwarf Jupiter in size, yet it is a fraction of its density. The scientists found that the gas giant is 50 percent bigger than Jupiter, and about a tenth as dense — an extremely low density, comparable to that of cotton candy.
WASP-193b is the second lightest planet discovered to date, ...
Sleep experts to convene in Houston for SLEEP 2024 annual meeting
2024-05-14
DARIEN, IL – Leading sleep and circadian scientists, sleep clinicians, and industry innovators will gather June 2-5 in Houston at SLEEP 2024, the 38th annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC. Thousands of sleep professionals will connect, explore, and grow at the world’s premier clinical and scientific sleep meeting, held jointly by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
“Every year, SLEEP brings together the world’s ...
Rice’s Mamouras wins NSF CAREER Award
2024-05-14
HOUSTON – (May 14, 2024) – As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows larger and more complex, it becomes increasingly difficult to develop applications.
“A common approach to this problem is to move data from the sensing devices to a central location, such as the cloud, for processing,” said Konstantinos Mamouras, assistant professor of computer science at Rice University. “But this centralized approach underutilizes the small IoT devices at the edge of the network and can overwhelm it due to the large movement of data.”
With his five-year, $547,555 National Science Foundation CAREER Award, Mamouras aims to decentralize the IoT, relieve network congestion and ...
ISS National Lab announces up to $750,000 in funding for technology development in low Earth orbit
2024-05-14
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), May 14, 2024 – The International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory is soliciting flight concepts for technology development that would utilize the space-based environment of the orbiting laboratory. This solicitation, “Technology Development and Applied Research Leveraging the ISS National Lab,” is open to a broad range of technology areas, including chemical and material synthesis in space, translational medicine, in-space edge computing, and ISAM (in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing). ...
Counterfeit coins can be detected more easily thanks to a novel approach developed at Concordia
2024-05-14
Metal coins may be just about the oldest medium of exchange still in use today, but ensuring their worth requires some of the most state-of-the-art technology available. Counterfeit coins remain a threat to global currencies, with malicious actors flooding markets with fakes. European police broke up a Spain-based criminal ring in late April, demonstrating the issue’s ongoing urgency.
However, no counterfeit is completely detection-proof, no matter how genuine it appears. There are always some tell-tale signals of forgery, even if they are not ...
Professors elected to Academy of Distinguished Scholars
2024-05-14
The University of Texas at Arlington has elected two longtime professors to the Academy of Distinguished Scholars, considered the University’s most prestigious research and scholarship honor.
Ramon Lopez, professor of physics, and Michael D. Nelson, associate professor of kinesiology, are being recognized for their sustained and significant contributions to research and creativity.
“Members of the Academy of Distinguished Scholars exemplify UTA’s commitment to quality research and creative activity,” said Kate C. Miller, vice president of research and innovation. “Mike and Ramon have both ...
UTA biology students receive awards for excellence
2024-05-14
Thirteen undergraduate and graduate students at The University of Texas at Arlington are being honored for excellence in academics, research, mentoring and/or teaching with awards. The awards are a mix of direct applications from students and others where they were nominated by faculty advisors. A committee of biology faculty then voted on the competitive awards.c
“It’s so rewarding to be able to honor the next generation of biologists,” said Melissa Walsh, who chaired the selection committee ...
Making every hair appointment a sound experience #ASA186
2024-05-14
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 14, 2024 – Walking out of a hair salon can have customers feeling brand new, but the noisy environment may have negative effects at the cost of a new “do.” At Image Creators salon in Maryland, owner Silvia Campana along with her employees and customers noticed they had to work hard to understand each other’s words while in the salon, but they couldn’t put their finger on exactly why. In addition to difficulties understanding speech, Campana experienced increased ear pain and tinnitus after long-term exposure to ...