(Press-News.org)
Engineers at MIT, Nanytang Technological University, and several companies have developed a compact and inexpensive technology for detecting and measuring lead concentrations in water, potentially enabling a significant advance in tackling this persistent global health issue.
The World Health Organization estimates that 240 million people worldwide are exposed to drinking water that contains unsafe amounts of toxic lead, which can affect brain development in children, cause birth defects, and produce a variety of neurological, cardiac, and other damaging effects. In the United States alone, an estimated 10 million households still get drinking water delivered through lead pipes.
“It’s an unaddressed public health crisis that leads to over 1 million deaths annually,” says Jia Xu Brian Sia, an MIT postdoc and the senior author of the paper describing the new technology.
But testing for lead in water requires expensive, cumbersome equipment and typically requires days to get results. Or, it uses simple test strips that simply reveal a yes-or-no answer about the presence of lead but no information about its concentration. Current EPA regulations require drinking water to contain no more that 15 parts per billion of lead, a concentration so low it is difficult to detect.
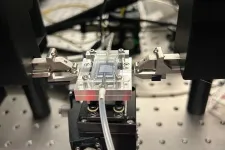
The new system, which could be ready for commercial deployment within two or three years, could detect lead concentrations as low as 1 part per billion, with high accuracy, using a simple chip-based detector housed in a handheld device. The technology gives nearly instant quantitative measurements and requires just a droplet of water.
The findings are described in a paper appearing today in the journal Nature Communications, by Sia, MIT graduate student and lead author Luigi Ranno, Professor Juejun Hu, and 12 others at MIT and other institutions in academia and industry.
The team set out to find a simple detection method based on the use of photonic chips, which use light to perform measurements. The challenging part was finding a way to attach to the photonic chip surface certain ring-shaped molecules known as crown ethers, which can capture specific ions such as lead. After years of effort, they were able to achieve that attachment via a chemical process known as Fischer esterification. “That is one of the essential breakthroughs we have made in this technology,” Sia says.
In testing the new chip, the researchers showed that it can detect lead in water at concentrations as low as one part per billion. At much higher concentrations, which may be relevant for testing environmental contamination such as mine tailings, the accuracy is within 4 percent.
The device works in water with varying levels of acidity, ranging from pH values of 6 to 8, “which covers most environmental samples,” Sia says. They have tested the device with seawater as well as tap water, and verified the accuracy of the measurements.
In order to achieve such levels of accuracy, current testing requires a device called an inductive coupled plasma mass spectrometer. “These setups can be big and expensive,” Sia says. The sample processing can take days and requires experienced technical personnel.
While the new chip system they developed is “the core part of the innovation,” Ranno says, further work will be needed to develop this into an integrated, handheld device for practical use. “For making an actual product, you would need to package it into a usable form factor,” he explains. This would involve having a small chip-based laser coupled to the photonic chip. “It’s a matter of mechanical design, some optical design, some chemistry, and figuring out the supply chain,” he says. While that takes time, he says, the underlying concepts are straightforward.
The system can be adapted to detect other similar contaminants in water, including cadmium, copper, lithium, barium, cesium, and radium, Ranno says. The device could be used with simple cartridges that can be swapped out to detect different elements, each using slightly different crown ethers that can bind to a specific ion.
“There’s this problem that people don’t measure their water enough, especially in the developing countries,” Ranno says. “And that’s because they need to collect the water, prepare the sample, and bring it to these huge instruments that are extremely expensive.” Instead, “having this handheld device, something compact that even untrained personnel can just bring to the source for on-site monitoring, at low costs,” could make regular, ongoing widespread testing feasible.
Hu, who is the John F. Elliott Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, says, “I’m hoping this will be quickly implemented, so we can benefit human society. This is a good example of a technology coming from a lab innovation where it may actually make a very tangible impact on society, which is of course very fulfilling.”
The team included researchers at MIT, at Nanyang Technological University and Temasek Laboratories in Singapore, at the University of Southampton in the U.K., and at companies Fingate Technologies, in Singapore, and Vulcan Photonics, headquartered in Malaysia. The work used facilities at MIT.nano, the Harvard University Center for Nanoscale Systems, NTU’s Center for Micro- and Nano-Electronics, and the Nanyang Nanofabrication Center.
###
Written by David L. Chandler, MIT News
Paper: “Crown ether decorated silicon photonics for safeguarding against lead poisoning”
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47938-6
END
Irvine, Calif., May 14, 2024 — A research team led by the University of California, Irvine has revealed the link between the frequency of sleep apnea events during the rapid-eye-movement stage and the severity of verbal memory impairment in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Verbal memory refers to the cognitive ability to retain and recall information presented through spoken words or written text and is particularly vulnerable to Alzheimer’s.
The study, recently published online in the journal Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, discovered a specific correlation between the severity of sleep apnea – when breathing pauses while ...
A recent study published in Analytical Science Journal conducted by Schmid College of Science and Technology Professor Rosalee Hellberg and students Calin Harris, Diane Kim, Miranda Miranda and Chevon Jordan, reveal that some supplement companies may mislead customers with unproven health claims and undeclared ingredients.
The researchers focused on supplements that have been associated with the purported treatment or prevention of COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses. During the pandemic, the use of dietary supplements skyrocketed throughout the world. “There was a big spike in purchase and use of these types ...
A project led by the University of Washington to better understand our atmosphere’s complexity is a finalist for NASA’s next generation of Earth-observing satellites. The space agency this week announced the projects that will each receive $5 million to advance to the next stage and conduct a one-year concept study.
STRIVE seeks to better understand the troposphere that we inhabit and the stratosphere above it, where the ozone layer is, as well as the interface where these two layers meet. That interface, about 6 miles (10 kilometers) above the surface, is where important ...
Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have recast diffusion in multicomponent alloys as a sum of individual contributions, called “kinosons.” Using machine learning to compute the statistical distribution of the individual contributions, they were able to model the alloy and calculate its diffusivity orders of magnitude more efficiently than computing whole trajectories. This work was recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We found a much more efficient way to calculate diffusion in solids, and at the same time, we learned more ...
As a student competing in track and field at his Parlier high school, Robert Leija was obsessed with how to improve his performance and, in particular, prevent the buildup of lactic acid in his muscles during training. Like many athletes, he blamed it for the performance fatigue and muscle soreness he experienced after intense workouts.
But as a kinesiology student at Fresno State, he was handed an out-of-print textbook that told him he had it all wrong. Lactate wasn't a danger sign that athletes had depleted their body's supply of oxygen, but likely a normal product of the metabolic activity required to fuel the muscles during sustained exercise.
Now, as a graduate student ...
More and more public services — such as affordable housing, public school matching and child welfare — are relying on algorithms to make decisions and allocate resources. So far, much of the work that has gone into designing these systems has focused on workers’ experiences using them or communities’ perceptions of them.
But what about the actual impact of these programs have on people, especially when the decisions the systems make lead to denial of services? Can you design algorithms to help people make sense of and ...
Astronomers at MIT, the University of Liège in Belgium, and elsewhere have discovered a huge, fluffy oddball of a planet orbiting a distant star in our Milky Way galaxy. The discovery, reported today in the journal Nature Astronomy, is a promising key to the mystery of how such giant, super-light planets form.
The new planet, named WASP-193b, appears to dwarf Jupiter in size, yet it is a fraction of its density. The scientists found that the gas giant is 50 percent bigger than Jupiter, and about a tenth as dense — an extremely low density, comparable to that of cotton candy.
WASP-193b is the second lightest planet discovered to date, ...
DARIEN, IL – Leading sleep and circadian scientists, sleep clinicians, and industry innovators will gather June 2-5 in Houston at SLEEP 2024, the 38th annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC. Thousands of sleep professionals will connect, explore, and grow at the world’s premier clinical and scientific sleep meeting, held jointly by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
“Every year, SLEEP brings together the world’s ...
HOUSTON – (May 14, 2024) – As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows larger and more complex, it becomes increasingly difficult to develop applications.
“A common approach to this problem is to move data from the sensing devices to a central location, such as the cloud, for processing,” said Konstantinos Mamouras, assistant professor of computer science at Rice University. “But this centralized approach underutilizes the small IoT devices at the edge of the network and can overwhelm it due to the large movement of data.”
With his five-year, $547,555 National Science Foundation CAREER Award, Mamouras aims to decentralize the IoT, relieve network congestion and ...
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), May 14, 2024 – The International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory is soliciting flight concepts for technology development that would utilize the space-based environment of the orbiting laboratory. This solicitation, “Technology Development and Applied Research Leveraging the ISS National Lab,” is open to a broad range of technology areas, including chemical and material synthesis in space, translational medicine, in-space edge computing, and ISAM (in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing). ...