(Press-News.org) The iconic baobabs, also known as upside-down trees, or the tree of life, have much cultural significance, inspiring innumerable arts, folklore, and traditions. A research published in Nature, involving international collaboration between Wuhan Botanical Garden (China), Royal Botanic Gardens (Kew, UK), University of Antananarivo (Madagascar) and Queen Mary University of London (UK) reveal a remarkable example of species radiation in Madagascar followed by long distance dispersal to Africa and Australia. With speciation, an astonishing divergence of pollination mechanisms evolved, that exploit hawkmoths, bats and lemurs for a simple nectar reward.
The charismatic baobabs have astonishing growth forms, reaching huge sizes with massive trunks, but apparently diminutive crowns, giving them their iconic appearance as upside-down trees. The team first assembled the genomes of the eight recognised species and worked out their patterns of speciation. They then analysed the genomes themselves and discovered that the ancestor of all eight species most likely radiated in Madagascar, where they made hybrids, before two species underwent astonishing long-distance travels, one to Africa and another to Australia. In that radiation the species evolved different flower structures to attract hawkmoths, lemurs and bats.
Quote: Professor Andrew Leitch at Queen Mary University of London said, “We were delighted to be involved in this project uncovering patterns of baobab speciation in Madagascar followed by the astonishing long-distance dispersal of two species, one to Africa and another to Australia. This was accompanied by the evolution of some fascinating pollination syndromes involving hawkmoths, lemurs and bats.”
Quote: Dr. Ilia Leitch at Royal Botanic Garden Kew said, “This work has uncovered new insights into the patterns of speciation in baobabs and shows how climate change has influenced baobab distribution and speciation patterns over millions of years.”
Quote: Husband and wife team Andrew and Ilia Leitch at Queen Mary University of London and Royal Botanic Gardens Kew said. ‘We were delighted to be involved in this project uncovering patterns of baobab speciation in Madagascar before the astonishing long-distance dispersal of two species, one to Africa and another to Australia. The work also provides new insights into how climate change has influenced baobab distribution and speciation patterns over millions of years’.
END
The origin and long-distance travels of upside down trees
Scientists have solved the mystery behind the origin, evolution and dispersal around the world of iconic baobabs
2024-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Some mice may owe their monogamy to a newly evolved type of cell
2024-05-15
NEW YORK, NY — What makes the oldfield mouse steadfastly monogamous throughout its life while its closest rodent relatives are promiscuous? The answer may be a previously unknown hormone-generating cell, according to a new study published online today in Nature from scientists at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute.
"The hormone from these cells was actually first discovered in humans many decades ago, but nobody really knew what it did," said Andrés Bendesky, MD, PhD, a principal investigator at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute. "We’ve discovered ...
Mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 vs influenza in fall-winter 2023-2024
2024-05-15
About The Study: This study found that in fall-winter 2023-2024, the risk of death in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 was greater than the risk of death in patients hospitalized for seasonal influenza.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ziyad Al-Aly, M.D., email ziyad.alaly@va.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.7395)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # ...
First ‘warm-blooded’ dinosaurs may have emerged 180 million years ago
2024-05-15
The ability to regulate body temperature, a trait all mammals and birds have today, may have evolved among some dinosaurs early in the Jurassic period about 180 million years ago, suggests a new study led by UCL and University of Vigo researchers.
In the early 20th century, dinosaurs were considered slow-moving, “cold-blooded” animals like modern-day reptiles, relying on heat from the sun to regulate their temperature. Newer discoveries indicate some dinosaur types were likely capable of generating their own body heat but when this adaptation occurred is unknown.
The new study, published in the journal Current Biology, looked at ...
Next-generation sustainable electronics are doped with air
2024-05-15
Semiconductors are the foundation of all modern electronics. Now, researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new method where organic semiconductors can become more conductive with the help of air as a dopant. The study, published in the journal Nature, is a significant step towards future cheap and sustainable organic semiconductors.
“We believe this method could significantly influence the way we dope organic semiconductors. All components are affordable, easily accessible, and potentially environmentally friendly, which is a prerequisite for future sustainable ...
Disparities in patient portal engagement among patients with hypertension treated in primary care
2024-05-15
About The Study: This cohort study of patients with hypertension found clear sociodemographic disparities in patient portal engagement among those treated in primary care. Without special efforts to engage patients with portals, interventions that use patient portals to target hypertension may exacerbate disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rasha Khatib, Ph.D., M.H.S., email rasha.alkhatib@aah.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.11649)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Dose-dependent association between body mass index and mental health and changes over time
2024-05-15
About The Study: This study revealed a U-shaped association between adolescent body mass index and mental health, which was consistent across sex and grades and became stronger over time. These insights emphasize the need for targeted interventions addressing body image and mental health, and call for further research into underlying mechanisms.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shanquan Chen, Ph.D., email Shanquan.chen@lshtm.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.0921)
Editor’s ...
The doctor is in…. but what’s behind them?
2024-05-15
Americans have gotten used to seeing their doctors and other health care providers using telehealth video visits in the past four years. But a new study reveals that what a doctor has behind them during a telehealth visit can make a difference in how the patient feels about them and their care.
Even if the doctor is miles away from their usual in-person clinic or exam room, they should make it look like they’re there, the study suggests.
Even better: sitting in an office with their diplomas hanging ...
Structural evolution and high-temperature sensing performance of polymer-derived SiAlBCN ceramics
2024-05-15
The group of Gang Shao from Zhengzhou University, China recently investigated the structural evolution of pentagonal polymer-derived SiAlBCN ceramics (PDCs) and outlined PDC-based sensor technology for high-temperature extreme environments. The high-performance temperature sensing materials including high sensitivity, fast response, wide detection range are scarce and needful. This research developed a ceramic-based temperature with attractive performance that can be applied in high-temperature environments ...
An environmental CGE model of China’s economy: Modeling choices and application
2024-05-15
The general equilibrium framework of the CGE model widely used in cost-benefit analysis in the field of energy and environmental policy. Based on standard micro- and macroeconomic theories, the CGE model establishes quantitative connections between various sectors of the economy, enabling the examination of both direct and indirect effects resulting from exogenous changes in the economy, as well as their global impacts on the overall economy.
A team of energy economists by Yu Liu from Peking University in Beijing, China recently outlined the detailed content of their CGE model. This model is constructed based on the CGE model theory of the Australian Center ...
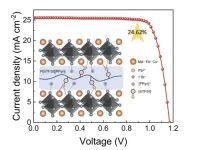
Adding polymerized ionic liquid improves performance of perovskite solar cells
2024-05-15
Perovskite solar cells, which use materials with the same crystal structure as perovskite, are lightweight, flexible, easy to manufacture, and inexpensive. They can be attached to many different surfaces and are a promising technology. However, current perovskite solar cells are not durable, and they tend to be inefficient. New research shows how additive engineering with a polymerized ionic liquid to the metal halide perovskite material can improve the solar cell’s function, helping to pave the way for the future wide adoption of perovskite solar ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
[Press-News.org] The origin and long-distance travels of upside down treesScientists have solved the mystery behind the origin, evolution and dispersal around the world of iconic baobabs