(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research chemists have accomplished a long elusive feat in synthetic chemistry: the invention of a broadly useful method for constructing “gamma chiral centers” on simple starting compounds called carboxylic acids. The method, published on May 16, 2024 in Science, significantly extends the ability of chemists to build and modify complex pharmaceutical molecules and other valuable chemical products.
The term chiral refers to a type of asymmetry that allows some chemical compounds to exist in left-handed and right-handed forms. Often, only one of these forms has the desired biochemical activity, but for synthetic chemists, stereoselective reactions—those that yield just the desired form—are almost always challenging.
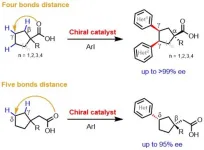
The new method enables what had been impossible except in narrow cases: creating a center of chiral asymmetry at a hard-to-reach position called the “gamma” position on a cyclic carboxylic acid.
“This approach offers unprecedented and relatively easy access to a broad set of chiral carbocycles that are privileged structures for pharma industry drug discovery programs,” says study senior author Jin-Quan Yu, PhD, Frank and Bertha Hupp Professor of Chemistry and Bristol Myers Squibb Endowed Chair in Chemistry at Scripps Research.
The co-first authors were Tao Zhang, PhD, and Zi-Yu Zhang, PhD, both postdoctoral research associates in the Yu lab.
A potentially valuable but elusive method
The development of small molecule pharmaceuticals or other chemical products typically involves the construction of many hundreds or thousands of compounds, each representing a variation on a central structural theme. Once these “libraries” of compounds are constructed, they are methodically tested for the desired biological or chemical activity; in this way, developers can zero in on the best compound for further refinement. Naturally, in constructing these libraries and in making more refined variants, chemists would like to have easy and versatile techniques for building and modifying molecules. But while their tools have greatly improved over the years, some types of molecular transformation have remained essentially undoable, despite the obvious value they would have. Gamma chiral center construction using readily available carboxylic acids has been one of these, defying the efforts of prominent synthetic chemistry labs.
The Yu lab’s success hinged on the development of special “ligand” molecules containing both oxazoline and pyridone structural elements. Ligand molecules help bring the reaction catalyst to the right spot on the initial compound. In this case, they fasten to one point on the starting carboxylic acid—which contains a ring of mostly carbon atoms—and direct a bond-breaking palladium atom to the distant gamma position on the other side of the ring. The effect is to remove a hydrogen atom from the backbone carbon atom at the targeted spot, allowing a new cluster of atoms to bond to the carbon—thus adding complexity to the molecule in a precise way.
This type of reaction is called a “C-H activation,” and over the past decade, Yu and his team have reported similar C-H activation methods for constructing chiral centers at “alpha” and “beta” positions on carboxylic acids.
The chemists demonstrated the power and versatility of their new method by using it to make gamma chiral centers on a wide variety of relatively simple carboxylic acid starting compounds containing rings of from five to eight carbon atoms. In one case, they achieved a single-step synthesis of a chiral version of a cancer drug molecule called an HDAC inhibitor—whose standard, patented synthesis method requires 10 steps and a costly separation to obtain pure samples of the left-handed or right-handed form.
The team also used the new technique to add complexity to existing drug molecules, including the steroid hormone pregnenolone.
Finally, the chemists showed they could use their new approach sequentially on a starting molecule to construct three chiral centers—including a very challenging “delta” chiral center.
The Yu lab is now working to extend the new approach so it can be used for making other types of chiral molecules.
“Enantioselective Remote Methylene C−H (Hetero)Arylation of Cycloalkane Carboxylic Acids” was co-authored by Tao Zhang, Zi-Yu Zhang, Guowei Kang, Tao Sheng, Jie-Lun Yan, Yuan-Bin Yang, Yuxin Ouyang and Jin-Quan Yu, all of Scripps Research.
Support for the research was provided by the National Institutes of Health (2R01GM084019).
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
END
Scripps Research chemists develop new method for making gamma chiral centers on simple carboxylic acids
C-H activation-based method should speed drug molecule design and diversification.
2024-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024 SIAM Annual Meeting (AN24) with online component including SIAM Conference on Discrete Mathematics (DM24) and the SIAM Conference on Applied Mathematics in Education (ED24)
2024-05-16
The SIAM Annual Meeting provides a broad view of the state of the art in applied mathematics, computational and data science, and their applications through invited presentations, prize lectures, minitutorials, minisymposia, contributed presentations, and posters. END ...
Detecting influence campaigns on X with AI and network science
2024-05-16
In the age of generative-AI and large language models (LLMs), massive amounts of inauthentic content can be rapidly broadcasted on social media platforms. As a result, malicious actors are becoming more sophisticated, hijacking hashtags, artificially amplifying misleading content, and mass resharing propaganda.
These actions are often orchestrated by state-sponsored information operations (IOs), which attempt to sway public opinion during major geopolitical events such as the US elections, the Covid-19 pandemic, and more.
Combating ...
Offering both colonoscopy and at-home tests doubled colorectal cancer screening
2024-05-16
The rate of colorectal cancer screenings more than doubled when patients were given a choice between which type of screening they wanted—a take-home kit or colonoscopy—compared to those who were only offered the colonoscopy, according to new research led by the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Facilitated through a community health center in which about half of patients had Medicaid insurance, the study—published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology—provides insights about how to boost screenings among groups ...
A powerful tool speeds success in achieving highly efficient thermoelectric materials
2024-05-16
HOUSTON, May 16, 2024 – Thermoelectric materials could play an important role in the clean energy transition, as they can produce electricity from sources of heat that would otherwise go to waste without generating additional greenhouse gases or requiring large up-front investment. But their promise has been slowed by the fact that most current thermoelectric materials don’t efficiently produce enough power to be useful for many practical applications.
The search for new, more efficient materials involving complex chemical ...
Oropharyngeal cancer staging health record extraction using AI
2024-05-16
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that artificial intelligence may be associated with enhanced patient care and oncological decision-making in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma through detection of localized versus advanced cancer stages. Further model refinement and external validation with electronic health records at different institutions are necessary to improve algorithm accuracy and clinical applicability.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Antoine Eskander, M.D., email antoine.eskander@mail.utoronto.ca.
To access the ...
Airborne technology developed at USC brings new hope to map shallow aquifers in Earth’s most arid deserts
2024-05-16
Water shortages are expanding across the Earth. This is particularly acute in desert areas of the Middle East that are subject to both drought and extreme conditions such as flooding. As a result of these uncertainties, there is an increasing reliance on shallow aquifers to mitigate these shortages. However, the characteristics of these aquifers remain poorly understood due to the reliance on sporadic well logs for their management.
To address this challenge a team of researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering along with collaborators ...
Mount Sinai experts to present new research on preeclampsia, preterm birth, doula care and more at the 2024 ACOG Annual Clinical and Scientific Meeting
2024-05-16
Women’s health experts from the Raquel and Jaime Gilinski Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will present new research at the 2024 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Annual Clinical and Scientific Meeting in San Francisco from May 17–19. Please let me know if you would like to coordinate an interview about their forthcoming presentations. Mount Sinai obstetricians and gynecologists are also available to comment on breaking news and other trending topics on prenatal care and women’s ...
Normothermic perfusion system extends life of organs waiting for transplant
2024-05-16
In the United States, about 30-40% of donor hearts aren't considered for transplant due to inadequate function in the donor.
This creates a drop in the number of donated hearts that are available to be matched with someone who needs a heart transplant.
A team at University of Michigan Health led by Alvaro Rojas-Pena, M.D., a research investigator with the section of transplantation surgery at University of Michigan Health has spent the past eight years looking at better ways to transport organs for donation, specifically hearts, to improve the number of organs ...
Study: Large language models can’t effectively recognize users’ motivation, but can support behavior change for those ready to act
2024-05-16
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Large language model-based chatbots have the potential to promote healthy changes in behavior. But researchers from the ACTION Lab at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have found that the artificial intelligence tools don’t effectively recognize certain motivational states of users and therefore don’t provide them with appropriate information.
Michelle Bak, a doctoral student in information sciences, and information sciences professor Jessie Chin reported their research in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Large language model-based chatbots — also known as generative conversational agents ...
In September, securities watchdogs bark more, bite less
2024-05-16
AUSTIN, Texas -- The Securities and Exchange Commission acts as Wall Street’s traffic cop, fining companies for such infractions as securities fraud and insider trading. New research from Texas McCombs finds another parallel between the SEC and traffic enforcement: pressure to meet self-imposed quotas.
Assistant accounting professors Matthew Kubic and Sara Toynbee find that the agency files twice as many enforcement cases in September as in other months, a phenomenon they call the September spike. They also link the increase in cases to smaller fines that reduce what the government takes in from violators.
The reason for the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Scripps Research chemists develop new method for making gamma chiral centers on simple carboxylic acidsC-H activation-based method should speed drug molecule design and diversification.