(Press-News.org)
In the United States, about 30-40% of donor hearts aren't considered for transplant due to inadequate function in the donor.
This creates a drop in the number of donated hearts that are available to be matched with someone who needs a heart transplant.
A team at University of Michigan Health led by Alvaro Rojas-Pena, M.D., a research investigator with the section of transplantation surgery at University of Michigan Health has spent the past eight years looking at better ways to transport organs for donation, specifically hearts, to improve the number of organs that can be used for transplants.
Rojas-Pena’s team found through using a modified normothermic perfusion system heart preservation is feasible for up to 24 hours.
The system uses a blood-derived solution to perfuse the organs and has a hemofilter to remove toxins.
This system allows for prolonged preservation of longer than 12 hours without creating edema or damage to the organs.
The current standard for heart preservation between donation and transplant is up to six hours in cold static storage.
While some hearts can still be transplanted after this six-hour mark, they have increased posttransplant morbimortality rates.
“We can maintain heart viability by perfusion at coronary flows and we are able to remove toxins and control edema to the tissue,” said Rojas-Pena.
“Most importantly, our system can be used to objectively assess function of the organ prior to transplant including the ability to perform echocardiograms, compared to assessment of function in the donor.”
This research and current data prove the concept that normothermic perfusion has the potential to increase the organ pool by considering previously discarded hearts, performing an objective assessment of heart function, increasing the donor/recipient distance and developing heart-specific perfusion therapies.
By extending the time of organ preservation, logistics will become less of an issue and organs with borderline or questionable function can objectively be assessed and potentially considered for transplant.
This opens the option for “organ” therapy and conditioning prior to transplant.
Additional authors include Brianna L. Spencer, Spencer K. Wilhelm, Christopher Stephan, Kristopher A. Urrea, Daniela Pelaez Palacio and Robert H. Bartlett from the Extracorporeal Live Support Laboratory, Department of Surgery, University of Michigan Medical School. Daniel H. Drake from the Extracorporeal Live Support Laboratory, Department of Surgery, University of Michigan Medical School and the Department of Cardiac Surgery, University of Michigan Medical School.
This work was funded by the Maxime and Stuart Frankel Foundation, Michigan Fast Forward, and current work by the NIH R01-HL161139-02
Michigan Research Core: ULAM Pathology Core (formerly IVAC)
Paper cited: “Extending heart preservation to 24 h with normothermic perfusion,” Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1325169
Sign up for Health Lab newsletters today. Get medical tips from top experts and learn about new scientific discoveries every week by subscribing to Health Lab’s two newsletters, Health & Wellness and Research & Innovation.
Sign up for the Health Lab Podcast: Add us on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or wherever you get you listen to your favorite shows.
END
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Large language model-based chatbots have the potential to promote healthy changes in behavior. But researchers from the ACTION Lab at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have found that the artificial intelligence tools don’t effectively recognize certain motivational states of users and therefore don’t provide them with appropriate information.
Michelle Bak, a doctoral student in information sciences, and information sciences professor Jessie Chin reported their research in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Large language model-based chatbots — also known as generative conversational agents ...
AUSTIN, Texas -- The Securities and Exchange Commission acts as Wall Street’s traffic cop, fining companies for such infractions as securities fraud and insider trading. New research from Texas McCombs finds another parallel between the SEC and traffic enforcement: pressure to meet self-imposed quotas.
Assistant accounting professors Matthew Kubic and Sara Toynbee find that the agency files twice as many enforcement cases in September as in other months, a phenomenon they call the September spike. They also link the increase in cases to smaller fines that reduce what the government takes in from violators.
The reason for the ...
As researchers search for new insights into Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), there is an ever-greater need for data from clinical trials and research studies. However, many people living with ALS are not certain how to get involved with clinical research, and the demographics of current ALS clinical trial participants are not representative of the full population of people living with the disease worldwide.
To address the critical need for diversity and accessibility in ALS clinical trials and research studies, the Illinois-based Les Turner ALS Foundation has published a new ...
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago announces the launch of the Journal of Health Advocacy (JHA), the first of its kind peer-reviewed open access journal housed within the organization’s Patrick M. Magoon Institute for Healthy Communities. This new journal bridges the gap between knowledge and action to empower individuals and groups to address real-world challenges to health equity. It opened for submissions May 1, 2024.
“Disseminating and recognizing advocacy that is so often successful ...
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Ochsner Health is proud to announce its recognition as one of America’s Best Employers for Diversity for 2024. This honor, awarded by Forbes in collaboration with market research firm Statista, places Ochsner Health among the elite 500 companies leading the way in diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) initiatives within the United States.
Dedicated to enhancing access and opportunities for all its employees, Ochsner Health is a frontrunner in fostering a professional environment where diversity is celebrated, and every employee is empowered to contribute ...
About The Study: This study found significant sex differences in primary care–based chronic kidney disease management among patients at a care network affiliated with an academic medical center in the U.S., with females overall receiving worse care than males. Though many differences were of small magnitude, the disparity deserves further examination.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jorge A. Rodriguez, M.D., email jarodriguez1@partners.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
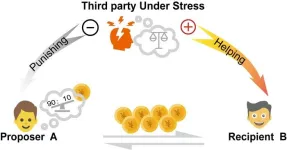
Being stressed while witnessing injustice may push your brain towards altruism, according to a study published on May 14th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Huagen Wang from Beijing Normal University, China, and colleagues.
It takes more cognitive effort to punish others than it does to help them. Studies show that when witnessing an act of injustice while stressed, people tend to behave selflessly, preferring to help the victim than to punish the offender. This aligns with theories proposing that distinct brain networks drive intuitive, fast decisions and deliberate, slow decisions, ...
Organic solid-state lasers (OSLs) hold immense promise for a wide range of applications due to their flexibility, colour tunability, and efficiency. However, they are difficult to make, and with over 150,000 possible experiments required to conduct to find successful new materials, discovering them all would be the work of several lifetimes. In fact, in the previous few decades, only 10-20 new OSL materials have been tested. Researchers with the Acceleration Consortium based at the University of Toronto, took up this challenge and used self-driving lab (SDL) technology that, once set up, enabled them to synthesize and test over 1000 potential OSL materials ...
Sea otters are one of the few animals that use tools to access their food, and a new study has found that individual sea otters that use tools — most of whom are female — are able to eat larger prey and reduce tooth damage when their preferred prey becomes depleted.
The study researchers and their enlisted volunteer “otter spotters” followed 196 radio-tagged southern sea otters off the coast of California to better understand how the threatened species uses tools in a rapidly changing environment. The research team from The University ...
Military physicians give patients whose military rank is higher better treatment than those who rank lower, according to a new study involving 1.5 million patient encounters. The findings provide evidence that the powerful enjoy better resources and support in a clinical context, often at the expense of the less powerful. “Our concern does not lie with the doctor-patient power imbalance itself, which is likely necessary for effective physician performance,” write the authors. “Rather, it lies with the inequitable variation in how that power is exercised, with the most vulnerable patients likely bearing the burden of this disparity, as ...