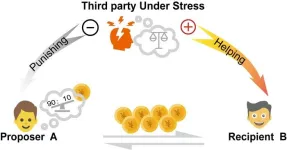
Under stress, an observer is more likely to help the victim than to punish the perpetrator
While performing a bystander intervention task in a brain scanner, stressed participants had different patterns of neural activation than non-stressed participants, and were more likely to help the victim
2024-05-16
(Press-News.org) Being stressed while witnessing injustice may push your brain towards altruism, according to a study published on May 14th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Huagen Wang from Beijing Normal University, China, and colleagues.
It takes more cognitive effort to punish others than it does to help them. Studies show that when witnessing an act of injustice while stressed, people tend to behave selflessly, preferring to help the victim than to punish the offender. This aligns with theories proposing that distinct brain networks drive intuitive, fast decisions and deliberate, slow decisions, but precisely how a bystander’s brain makes the trade-off between helping and punishing others in stressful situations is unclear.
To better understand the neural processes driving third-party intervention in the face of injustice, Wang and colleagues recruited 52 participants to complete a simulated third-party intervention task in an fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanner, where they watched someone decide how to distribute an endowment of cash between themself and another character, who had to passively accept the proposal. The participant then decided whether to take money away from the first character, or give money to the second. Roughly half of these participants submerged their hands in ice water for three minutes right before starting the task to induce stress.
Acute stress affected decision-making in extremely unfair situations, where the participant witnessed someone keep the vast majority of the cash they were supposed to split with someone else. The researchers observed higher dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) activation—a brain region typically linked to mentalizing and decision-making—when stressed participants chose to punish an offender. Computational modeling revealed that acute stress reduces bias towards punishment, raising the likelihood that someone will help a victim instead.
The authors state that their findings suggest that punishing others requires more deliberation, cognitive control, and reliance on calculations than helping a victim. These results align with a growing body of evidence suggesting that stressed individuals tend to act more cooperatively and generously, perhaps because people devote more of their cognitive resources towards deciding how to help the victim, rather than punishing the offender.
The authors add, “Acute stress shifts third-party intervention from punishing the perpetrator to helping the victim.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002195
Citation: Wang H, Wu X, Xu J, Zhu R, Zhang S, Xu Z, et al. (2024) Acute stress during witnessing injustice shifts third-party interventions from punishing the perpetrator to helping the victim. PLoS Biol 22(4): e3002195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002195
Author Countries: China
Funding: The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (https://www.nsfc.gov.cn/english/site_1/index.html, 32271092 to CL and 32130045 to SQ), Major Project of National Social Science Foundation (http://www.nopss.gov.cn/GB/219469/431028/ , 19ZDA363 to CL) and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (https://kw.beijing.gov.cn/ , Z151100003915122 to CL). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-16
Organic solid-state lasers (OSLs) hold immense promise for a wide range of applications due to their flexibility, colour tunability, and efficiency. However, they are difficult to make, and with over 150,000 possible experiments required to conduct to find successful new materials, discovering them all would be the work of several lifetimes. In fact, in the previous few decades, only 10-20 new OSL materials have been tested. Researchers with the Acceleration Consortium based at the University of Toronto, took up this challenge and used self-driving lab (SDL) technology that, once set up, enabled them to synthesize and test over 1000 potential OSL materials ...
2024-05-16
Sea otters are one of the few animals that use tools to access their food, and a new study has found that individual sea otters that use tools — most of whom are female — are able to eat larger prey and reduce tooth damage when their preferred prey becomes depleted.
The study researchers and their enlisted volunteer “otter spotters” followed 196 radio-tagged southern sea otters off the coast of California to better understand how the threatened species uses tools in a rapidly changing environment. The research team from The University ...
2024-05-16
Military physicians give patients whose military rank is higher better treatment than those who rank lower, according to a new study involving 1.5 million patient encounters. The findings provide evidence that the powerful enjoy better resources and support in a clinical context, often at the expense of the less powerful. “Our concern does not lie with the doctor-patient power imbalance itself, which is likely necessary for effective physician performance,” write the authors. “Rather, it lies with the inequitable variation in how that power is exercised, with the most vulnerable patients likely bearing the burden of this disparity, as ...
2024-05-16
Using tools, like shells and rocks, to open their often thick-shelled mollusk prey increases foraging success in sea otters and protects their teeth from damage by allowing the animals to eat prey that would otherwise be difficult to obtain. The findings suggest that this behavior is a necessity for the survival of some otters in environments where competition is high and preferred prey is in short supply. Sea otters are well-known tool users. Aside from crushing prey with their teeth, sea otters have been observed using rocks, shells, human litter, and even the hulls of boats to bash open hard prey, including ...
2024-05-16
Scientists have made several advances in the design of a class of HIV vaccines that could offer broad protection against the virus, according to four new research papers published this week in Science, Science Translational Medicine, and Science Immunology. “The studies […] exemplify progress in the rational design of [germline-targeting] HIV-1 vaccines, and what is being learned will guide [germline-targeting] programs for inducing [broadly neutralizing antibodies] against other human pathogens,” Rogier Sanders and John Moore write in a related ...
2024-05-16
The energy invested in animal reproduction is as much as 10 times greater than previously estimated when the metabolic load of bearing and caring for offspring is accounted for, according to a new study. The findings fundamentally challenge longstanding theories and biological models of animal growth and life histories. The act of reproduction is one of the largest energy investments an animal can make. This investment includes direct cost, the energy directly invested in the offspring themselves, and indirect costs, the energy expended to create, carry, and care for offspring before they are born. While the direct costs of reproduction are well understood, the indirect ...
2024-05-16
Researchers discover new pathway to cancer cell suicide
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells. But the way these cells die appears to be different than previously understood. Researchers from the Netherlands Cancer Institute, led by Thijn Brummelkamp, have uncovered a completely new way in which cancer cells die: due to the Schlafen11 gene. "This is a very unexpected finding. Cancer patients have been treated with chemotherapy for almost a century, but this route to cell death has never been observed before. Where and when this occurs in patients will need to be further investigated. This discovery could ultimately have implications for the treatment of cancer patients." They publish their ...
2024-05-16
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Artificial intelligence (AI) has numerous applications in healthcare, from analyzing medical imaging to optimizing the execution of clinical trials, and even facilitating drug discovery.
AlphaFold2, an artificial intelligence system that predicts protein structures, has made it possible for scientists to identify and conjure an almost infinite number of drug candidates for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. However recent studies have sown doubt about the accuracy of AlphaFold2 in modeling ligand binding sites, the areas on proteins where drugs attach and begin signaling ...
2024-05-16
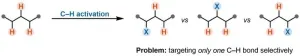
A team of chemists from the University of Vienna, led by Nuno Maulide, has achieved a significant breakthrough in the field of chemical synthesis, developing a novel method for manipulating carbon-hydrogen bonds. This groundbreaking discovery provides new insights into the molecular interactions of positively charged carbon atoms. By selectively targeting a specific C–H bond, they open doors to synthetic pathways that were previously closed – with potential applications in medicine. The study was recently published in the prestigious journal Science.
Living ...
2024-05-16
In an important step toward more effective gene therapies for brain diseases, researchers from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have engineered a gene-delivery vehicle that uses a human protein to efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier and deliver a disease-relevant gene to the brain in mice expressing the human protein. Because the vehicle binds to a well-studied protein in the blood-brain barrier, the scientists say it has a good chance at working in patients.
Gene therapy could potentially treat a range of severe genetic brain disorders, which currently ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Under stress, an observer is more likely to help the victim than to punish the perpetrator
While performing a bystander intervention task in a brain scanner, stressed participants had different patterns of neural activation than non-stressed participants, and were more likely to help the victim