(Press-News.org) Scientists have made several advances in the design of a class of HIV vaccines that could offer broad protection against the virus, according to four new research papers published this week in Science, Science Translational Medicine, and Science Immunology. “The studies […] exemplify progress in the rational design of [germline-targeting] HIV-1 vaccines, and what is being learned will guide [germline-targeting] programs for inducing [broadly neutralizing antibodies] against other human pathogens,” Rogier Sanders and John Moore write in a related Perspective on the new articles. As the HIV epidemic enters its fifth decade, scientists have poured time and resources into developing vaccine candidates for the virus. However, health authorities still lack a working, approved vaccine that induces broadly neutralizing antibodies, which can neutralize the most common circulating strains of HIV. One solution involves a process called germline targeting, where scientists use a series of proteins targeted by the immune system (immunogens) to shepherd and “prime” young B cells as they mature in sites called germinal centers, with the goal of coaxing the cells to produce broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV. In the first paper in Science, Jon Steichen and colleagues tested the protective effects of a new germline-targeting strategy based on the N332-GT5 trimer, a component of the HIV viral envelope. Leveraging cryo-electron microscopy, the team showed that their approach successfully primed and boosted quantities of B cells that secret precursors to BG18 – an anti-HIV broadly neutralizing antibody – in a group of eight rhesus macaques. Taking a different delivery approach in the second Science study, Zhenfei Xie and colleagues demonstrated they could prime B cells with N332-GT5 via mRNA, which they delivered via lipid nanoparticles. When given to humanized mice, the mRNA delivered both the primary immunogen (N332-GT5) and two additional immunogens that further primed the target B cells. Together, these immunogens kickstarted the activation and expansion of B cells that secreted precursors to BG18, with Xie et al. hypothesizing that their strategy could reduce undesirable off-target binding. Meanwhile, in a study in Science Translational Medicine, Christopher Cottrell and colleagues designed a new nanoparticle immunogen as a boost to germline-targeting HIV vaccines. They first primed mice with an immunogen named eOD-Gt8 60mer, which was previously found to induce precursors to anti-HIV, VRC01-class broadly neutralizing antibodies in a phase 1 trial. After priming, Cottrell et al. then vaccinated mice with another immunogen named core-g28v2 60mer (in both protein and mRNA form) as a “first boost.” They found that this prime-boost approach elicited VRC01-class antibodies that were precursors to broadly neutralizing antibodies and neutralized HIV-like pseudoviruses in culture. Finally, in a study in Science Immunology, Xuesong Wang and colleagues showed that they could deliver eOD-Gt8 60mer as an initial priming immunogen via mRNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. The researchers transferred several different humanized B cell lines into mice to mimic the competition between B cells that occurs during immunization. Their priming strategy coaxed B cells to diversify, participate in germinal centers, and acquire mutations and characteristics needed to secrete VRC01-class antibodies. In their related Perspective, Sanders and Moore add that the results provide a strong proof-of-concept for promising germline-targeting approaches, noting that the N332-GT5 trimer is now in a phase 1 trial.
END
Advances in priming B cell immunity against HIV pave the way to future HIV vaccines, shows quartet of new studies
2024-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Total energy cost of animal reproduction is higher than previously assumed
2024-05-16
The energy invested in animal reproduction is as much as 10 times greater than previously estimated when the metabolic load of bearing and caring for offspring is accounted for, according to a new study. The findings fundamentally challenge longstanding theories and biological models of animal growth and life histories. The act of reproduction is one of the largest energy investments an animal can make. This investment includes direct cost, the energy directly invested in the offspring themselves, and indirect costs, the energy expended to create, carry, and care for offspring before they are born. While the direct costs of reproduction are well understood, the indirect ...
Researchers discover new pathway to cancer cell suicide
2024-05-16
Researchers discover new pathway to cancer cell suicide
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells. But the way these cells die appears to be different than previously understood. Researchers from the Netherlands Cancer Institute, led by Thijn Brummelkamp, have uncovered a completely new way in which cancer cells die: due to the Schlafen11 gene. "This is a very unexpected finding. Cancer patients have been treated with chemotherapy for almost a century, but this route to cell death has never been observed before. Where and when this occurs in patients will need to be further investigated. This discovery could ultimately have implications for the treatment of cancer patients." They publish their ...
Researchers wrestle with accuracy of AI technology used to create new drug candidates
2024-05-16
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Artificial intelligence (AI) has numerous applications in healthcare, from analyzing medical imaging to optimizing the execution of clinical trials, and even facilitating drug discovery.
AlphaFold2, an artificial intelligence system that predicts protein structures, has made it possible for scientists to identify and conjure an almost infinite number of drug candidates for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. However recent studies have sown doubt about the accuracy of AlphaFold2 in modeling ligand binding sites, the areas on proteins where drugs attach and begin signaling ...
Breaking bonds to form bonds: Rethinking the Chemistry of Cations
2024-05-16
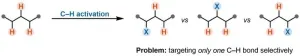
A team of chemists from the University of Vienna, led by Nuno Maulide, has achieved a significant breakthrough in the field of chemical synthesis, developing a novel method for manipulating carbon-hydrogen bonds. This groundbreaking discovery provides new insights into the molecular interactions of positively charged carbon atoms. By selectively targeting a specific C–H bond, they open doors to synthetic pathways that were previously closed – with potential applications in medicine. The study was recently published in the prestigious journal Science.
Living ...
New gene delivery vehicle shows promise for human brain gene therapy
2024-05-16
In an important step toward more effective gene therapies for brain diseases, researchers from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have engineered a gene-delivery vehicle that uses a human protein to efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier and deliver a disease-relevant gene to the brain in mice expressing the human protein. Because the vehicle binds to a well-studied protein in the blood-brain barrier, the scientists say it has a good chance at working in patients.
Gene therapy could potentially treat a range of severe genetic brain disorders, which currently ...
Finding quantum order in chaos
2024-05-16
If you zoom in on a chemical reaction to the quantum level, you’ll notice that particles behave like waves that can ripple and collide. Scientists have long sought to understand quantum coherence, the ability of particles to maintain phase relationships and exist in multiple states simultaneously; this is akin to all parts of a wave being synchronized. It has been an open question whether quantum coherence can persist through a chemical reaction where bonds dynamically break and form.
Now, for the first time, a team of Harvard scientists has demonstrated the survival of quantum coherence in a chemical reaction involving ultracold molecules. These findings highlight the potential of ...
Study suggests high-frequency electrical ‘noise’ results in congenital night blindness
2024-05-16
In what they believe is a solution to a 30-year biological mystery, neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have used genetically engineered mice to address how one mutation in the gene for the light-sensing protein rhodopsin results in congenital stationary night blindness.
The condition, present from birth, causes poor vision in low-light settings.
The findings, published May 14 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, demonstrate that the rhodopsin gene mutation, called ...
TeltoHeart wristband, developed by Lithuanians, receives important medical device certification
2024-05-16
Teltonika’s TeltoHeart, a multifunctional smart wristband system developed in cooperation between Lithuanian industry and universities has been given the CE MDR (Class IIa) medical device certification. This approval confirms that the product meets the comprehensive quality standards for medical devices and opens up new markets worldwide for this innovative product.
"This is an important recognition that we have been working towards since the start of this project in 2020. The CE MDR certification proves that TeltoHeart is a safe ...
Unique brain circuit is linked to Body Mass Index
2024-05-16
· One region is related to olfaction and reward, the other to negative feelings like pain · When the connection between these brain regions is weak, people have higher BMI
· Food may continue to be rewarding, even when these individuals are full
CHICAGO --- Why can some people easily stop eating when they are full and others can’t, which can lead to obesity?
A Northwestern Medicine study has found one reason may be a newly discovered structural connection ...
Noise survey highlights need for new direction at Canadian airports #ASA186
2024-05-16
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – The COVID-19 pandemic changed life in many ways, including stopping nearly all commercial flights. At the Toronto Pearson International Airport, airplane traffic dropped by 80% in the first few months of lockdown. For a nearby group of researchers, this presented a unique opportunity.
Julia Jovanovic will present the results of a survey conducted on aircraft noise and annoyance during the pandemic era Thursday, May 16, at 11:10 a.m. EDT as part of a joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and ...