(Press-News.org) As researchers search for new insights into Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), there is an ever-greater need for data from clinical trials and research studies. However, many people living with ALS are not certain how to get involved with clinical research, and the demographics of current ALS clinical trial participants are not representative of the full population of people living with the disease worldwide.
To address the critical need for diversity and accessibility in ALS clinical trials and research studies, the Illinois-based Les Turner ALS Foundation has published a new guide to ALS & Participation in Clinical Research, now available in both English and Spanish.
“We want to empower people living with ALS and their families to make informed decisions about whether to participate and break down the complexity around clinical research,” said Lauren Webb, Chief Advocacy and Outreach Officer.
Published on May 13, 2024, during ALS Awareness Month, this new guide was developed in partnership with Boston-based NEALS (Northeast Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Consortium), the world’s largest consortium of clinical research sites dedicated to rapidly translating scientific advances into clinical research and new treatments for people with ALS and motor neuron disease (MND).
Clinicians and healthcare professionals can use this guide to educate people living with ALS, their families, and their caregivers about what to expect when participating in an ALS clinical trial or research study – and how participation affects the broader field of ALS research. The authors aim to enrich ALS research with diverse perspectives and data, which are essential for developing more effective treatments and ultimately, finding cures for ALS.
With clear, detailed descriptions of the clinical trial phases, the various types of studies, and the rights and expectations of participants, this comprehensive guide demystifies ALS clinical trials and research studies. It includes insights from healthcare professionals alongside real-life experiences from people living with ALS, offering a broad and wide-ranging overview of the clinical research landscape.
Whether someone living with ALS is considering participation in a clinical trial for the first time or looking to understand more about the research process, this guide is designed to help them navigate their options and understand potential impacts on their treatment journey.
Increasing participation in clinical research is a critical step at clinical research sites across the U.S., including the Lois Insolia ALS Clinic at the Les Turner ALS Center at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, supported by the Les Turner ALS Foundation.
“It’s important for people with many different backgrounds and experiences to get involved in ALS research,” said Webb. “When people of all ages, genders, races, and ethnicities participate in research, scientists can learn more about how ALS affects everyone — and develop treatments that work for as many people as possible.
CONTACT:
Mark Heiden, Chief Communications Officer
Les Turner ALS Foundation
mheiden@lesturnerals.org
About the Les Turner ALS Foundation
Founded in 1977, the Les Turner ALS Foundation is one of the longest-serving ALS groups in the U.S. Our support services team helps people living with ALS receive the best quality of care and access to the most promising therapies, and we offer support groups, ALS resources and webinars, and live events to provide answers and encouragement.
Our Les Turner ALS Center at Northwestern Medicine and Lois Insolia ALS Clinic are led by the most well-respected scientists and clinicians in the field, advancing vital research into causes, treatments, and cures for the disease.
Website: lesturnerals.org
END
New guide demystifies participation in ALS clinical research
2024-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lurie Children’s Hospital launches first peer-reviewed journal on health advocacy
2024-05-16
Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago announces the launch of the Journal of Health Advocacy (JHA), the first of its kind peer-reviewed open access journal housed within the organization’s Patrick M. Magoon Institute for Healthy Communities. This new journal bridges the gap between knowledge and action to empower individuals and groups to address real-world challenges to health equity. It opened for submissions May 1, 2024.
“Disseminating and recognizing advocacy that is so often successful ...
Ochsner Health recognized as one of America’s Best Employers for Diversity by Forbes
2024-05-16
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Ochsner Health is proud to announce its recognition as one of America’s Best Employers for Diversity for 2024. This honor, awarded by Forbes in collaboration with market research firm Statista, places Ochsner Health among the elite 500 companies leading the way in diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) initiatives within the United States.
Dedicated to enhancing access and opportunities for all its employees, Ochsner Health is a frontrunner in fostering a professional environment where diversity is celebrated, and every employee is empowered to contribute ...
Sex differences in primary care–based chronic kidney disease management
2024-05-16
About The Study: This study found significant sex differences in primary care–based chronic kidney disease management among patients at a care network affiliated with an academic medical center in the U.S., with females overall receiving worse care than males. Though many differences were of small magnitude, the disparity deserves further examination.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jorge A. Rodriguez, M.D., email jarodriguez1@partners.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
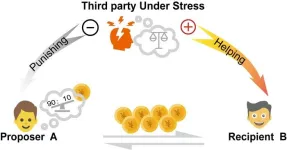
Under stress, an observer is more likely to help the victim than to punish the perpetrator
2024-05-16
Being stressed while witnessing injustice may push your brain towards altruism, according to a study published on May 14th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Huagen Wang from Beijing Normal University, China, and colleagues.
It takes more cognitive effort to punish others than it does to help them. Studies show that when witnessing an act of injustice while stressed, people tend to behave selflessly, preferring to help the victim than to punish the offender. This aligns with theories proposing that distinct brain networks drive intuitive, fast decisions and deliberate, slow decisions, ...
Ground-breaking accelerated discovery research unveils 21 novel materials for advanced organic solid-state laser technology: a global collaboration success story
2024-05-16
Organic solid-state lasers (OSLs) hold immense promise for a wide range of applications due to their flexibility, colour tunability, and efficiency. However, they are difficult to make, and with over 150,000 possible experiments required to conduct to find successful new materials, discovering them all would be the work of several lifetimes. In fact, in the previous few decades, only 10-20 new OSL materials have been tested. Researchers with the Acceleration Consortium based at the University of Toronto, took up this challenge and used self-driving lab (SDL) technology that, once set up, enabled them to synthesize and test over 1000 potential OSL materials ...
Otters, especially females, use tools to survive a changing world
2024-05-16
Sea otters are one of the few animals that use tools to access their food, and a new study has found that individual sea otters that use tools — most of whom are female — are able to eat larger prey and reduce tooth damage when their preferred prey becomes depleted.
The study researchers and their enlisted volunteer “otter spotters” followed 196 radio-tagged southern sea otters off the coast of California to better understand how the threatened species uses tools in a rapidly changing environment. The research team from The University ...
Military physicians give high-ranking military patients preferential treatment over lower-ranking patients
2024-05-16
Military physicians give patients whose military rank is higher better treatment than those who rank lower, according to a new study involving 1.5 million patient encounters. The findings provide evidence that the powerful enjoy better resources and support in a clinical context, often at the expense of the less powerful. “Our concern does not lie with the doctor-patient power imbalance itself, which is likely necessary for effective physician performance,” write the authors. “Rather, it lies with the inequitable variation in how that power is exercised, with the most vulnerable patients likely bearing the burden of this disparity, as ...
Tool use promotes foraging success and dental health in sea otters
2024-05-16
Using tools, like shells and rocks, to open their often thick-shelled mollusk prey increases foraging success in sea otters and protects their teeth from damage by allowing the animals to eat prey that would otherwise be difficult to obtain. The findings suggest that this behavior is a necessity for the survival of some otters in environments where competition is high and preferred prey is in short supply. Sea otters are well-known tool users. Aside from crushing prey with their teeth, sea otters have been observed using rocks, shells, human litter, and even the hulls of boats to bash open hard prey, including ...
Advances in priming B cell immunity against HIV pave the way to future HIV vaccines, shows quartet of new studies
2024-05-16
Scientists have made several advances in the design of a class of HIV vaccines that could offer broad protection against the virus, according to four new research papers published this week in Science, Science Translational Medicine, and Science Immunology. “The studies […] exemplify progress in the rational design of [germline-targeting] HIV-1 vaccines, and what is being learned will guide [germline-targeting] programs for inducing [broadly neutralizing antibodies] against other human pathogens,” Rogier Sanders and John Moore write in a related ...
Total energy cost of animal reproduction is higher than previously assumed
2024-05-16
The energy invested in animal reproduction is as much as 10 times greater than previously estimated when the metabolic load of bearing and caring for offspring is accounted for, according to a new study. The findings fundamentally challenge longstanding theories and biological models of animal growth and life histories. The act of reproduction is one of the largest energy investments an animal can make. This investment includes direct cost, the energy directly invested in the offspring themselves, and indirect costs, the energy expended to create, carry, and care for offspring before they are born. While the direct costs of reproduction are well understood, the indirect ...