(Press-News.org) A ruined building in the middle of the Pyrenees records a tragedy for the people who lived there — a devastating fire which burned a settlement to the ground, destroying everything down to a hidden gold earring. Now archaeologists’ excavation of Building G, in the strategically placed Iron Age site of Tossal de Baltarga, reveals a way of life derailed by violence: potentially, a forgotten episode of the war between Carthage and Rome.
“The destruction was dated around the end of the third century BCE, the moment where the Pyrenees were involved in the Second Punic War and the passage of Hannibal’s troops,” said Dr Oriol Olesti Vila of the Autonomous University of Barcelona, lead author of the article in Frontiers in Environmental Archaeology. “It is likely that the violent destruction of the site was connected to this war. The general fire points to anthropic destruction, intentional and very effective — not only Building G, but all the buildings of the site, were destroyed. In Building D we found a complete dog, burned…”
Buried treasure
Tossal de Baltarga was a hillfort of the Cerretani community, who had a major settlement at nearby Castellot de Bolvir. It seems to have lacked defensive walls, but commanded an excellent view over the river and critical travel routes. Its sudden destruction preserved organic remains, which allowed archaeologists to paint a detailed picture of the life that its occupants lived until it was set alight.
“These valleys were an important territory economically and strategically,” said Olesti Vila. “We know that Hannibal passed the Pyrenees fighting against the local tribes, likely the Cerretani. Not many archaeological remains of this expedition are preserved. Tossal de Baltarga is likely one of the best examples.”
Building G had two floors. The fire burned so fiercely that the roof, support beams, and wooden upper floor fell in, but some of the valuables survived the fall: the archaeologists found an iron pickaxe and the gold earring, concealed in a little pot.
This upper floor seems to have been divided into spaces for cooking and textile production. Numerous spindle whorls and loom weights were found, which could have been used to spin and weave wool from the sheep and goat that lived on the lower floor. Archaeologists also found edible grains like oats and barley, and some cooking vessels, with residues that showed the people who used Building G had been drinking milk and eating pork stews.
A memory of conflict
While no human remains were found in Building G, six animals did not escape. The four sheep, goat, and horse — which may have been ridden by the owners of Building G; it was old enough and a metal horse bit was found — were penned up in their wooden enclosures with their feed. They could even have been trapped by a closed door, which would explain burned wood found in the entrance. This penning might have been a departure from usual practices, caused by the fear of conflict: isotope analysis indicates some sheep had previously grazed in lowland pastures, possibly by arrangement with other communities.
“These mountain communities were not closed in the highlands, but connected with neighboring areas, exchanging products and, likely, cultural backgrounds,” said Olesti Vila. “The complex economy indicates an Iron Age society adapted to their environment and taking advantage of their resources in the highlands. But it also shows their contact with other communities.”
“Our reconstruction implies a sudden destruction, with no time to open the door of the stall and save the animals,” added Olesti Vila. “This could be just an unexpected local fire. But the presence of a hidden gold earring indicates the anticipation by the local people of some kind of threat, likely the arrival of an enemy. Also, the keeping of such a high number of animals in a little stall suggests the anticipation of a danger.”
Archaeologists don’t know what became of the people who were living at Tossal de Baltarga, but it was eventually reoccupied, and garrisoned by the Romans. Some part of the community likely survived the conflagration. Perhaps remembering the burning of Building G and its neighbors, these later occupants of Tossal de Baltarga constructed defenses — including an impressive watchtower.
END
A devastating fire 2,200 years ago preserved a moment of life and war in Iron Age Spain — right down to a single gold earring
A violent blaze, possibly linked to the Carthaginian army crossing the Pyrenees to fight the Romans, flared up so quickly people couldn’t save their animals or their valuables
2024-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
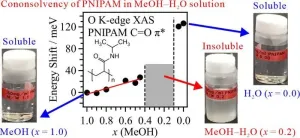
Exploration of polymer cononsolvency mechanism through soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy
2024-05-17
This study investigates the cononsolvency mechanism of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), which is soluble in pure methanol (MeOH) and water but insoluble in aqueous MeOH solutions. Combining oxygen K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with theoretical calculations executed in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and inner-shell calculations, it was found that hydrophobic interactions between PNIPAM and MeOH clusters play a key role in PNIPAM aggregation and cononsolvency emergence.
PNIPAM is ...
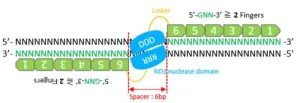
Researchers use machine-learning modeling tools to improve zinc-finger nuclease editing technology
2024-05-17
Genome editing is making inroads into biomedical research and medicine. By employing biomolecule modeling tools, a Japanese research team is accelerating the pace and cutting the cost of zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) technology, a primary gene editing tool.
In a recently published study, researchers from Hiroshima University and the Japanese National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology demonstrated how machine learning-driven modular assembly systems can improve gene editing.
The study was published on April 10 in the journal Advanced Science.
“Genome editing is ...
USC researcher awarded $3.1 million to study early brain development of babies born to mothers with diabetes in pregnancy
2024-05-17
It has long been understood that pregnant women with diabetes are more likely to have children with obesity than women who do not have diabetes during pregnancy. But scientists have not fully understood the cause or why babies born to mothers with diabetes are also more likely to develop obesity and associated metabolic disorders later in life.
To help find answers, Keck School of Medicine of USC researcher Shan Luo, PhD, has been awarded $3.1 million in funding from the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Diabetes ...
Men at greater risk of major health effects of diabetes than women
2024-05-17
Men are at greater risk than women of the major health effects of diabetes (types 1 and 2), suggests a long term study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Rates of cardiovascular disease, leg, foot, and kidney complications, and the sight-threatening eye disease diabetic retinopathy are all higher in men, regardless of whether they had diabetes for more or less than 10 years, the findings show.
The global prevalence of diabetes is similar in men and women, and is projected to rise to 783 million by 2045, note the researchers.
But ...
Likelihood of kids and young people smoking and vaping linked to social media use
2024-05-17
The more time spent on social media, the greater the likelihood that children and young people will both smoke and/or vape, suggests research published online in the respiratory journal Thorax.
Clocking up a weekday tally of 7 or more hours was associated with a more than a doubling in risk among 10 to 25 year olds, the findings indicate, reinforcing concerns about the marketing clout of these platforms, say the researchers.
The existing body of research on social media use and smoking and ...
Global life expectancy to increase by nearly 5 years by 2050 despite geopolitical, metabolic, and environmental threats, reports new global study
2024-05-17
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time], 6:30 p.m. [EDT] May 16, 2024**
Global Burden of Disease
The latest findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) 2021, published today in The Lancet, forecast that global life expectancy will increase by 4.9 years in males and 4.2 years in females between 2022 and 2050.
Increases are expected to be largest in countries where life expectancy is lower, contributing to a convergence of increased life expectancy across geographies. The trend is largely driven by public health measures that ...
High primary health coverage significantly reduces child mortality in Latin America
2024-05-17
The implementation of primary health care (PHC) over the last two decades has prevented more than 300,000 child deaths in four Latin American countries, and could prevent more than 140,000 by 2030 in a scenario of economic crisis. This is the main conclusion of a study coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, published in The Lancet Global Health.
The 2018 Astana Declaration highlighted the critical role of PHC in ensuring that everyone enjoys the highest possible standard of health, and in achieving universal health coverage. The Declaration also stressed the ...
Ubiquitin trailblazer elected Fellow of prestigious Royal Society
2024-05-17
WEHI division head and pioneer of ubiquitination Professor David Komander has been elected a Fellow of the esteemed Royal Society, the UK’s national science academy.
Prof Komander was recognised for his significant research contributions towards understanding ubiquitin, the ‘kiss of death’ protein which tells our cells which proteins to break down or recycle – a vital process that helps cells stay healthy and function correctly. Prof Komander’s work has helped unravel the ‘ubiquitin code’ that enables ubiquitin to perform many ...
A new ‘rule of biology’ may have come to light, expanding insight into evolution and aging
2024-05-17
By Darrin S. Joy
A molecular biologist at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences may have found a new “rule of biology.”
A rule of biology, sometimes called a biological law, describes a recognized pattern or truism among living organisms. Allen’s rule, for example, states that among warm-blooded animals, those found in colder areas have shorter, thicker limbs (to conserve body heat) than those in hotter regions, which need more body surface area to dissipate heat.
Zoologist Joel Allen formulated this idea in 1877, and though he wasn’t the first or the last to present a rule of biology, his ...
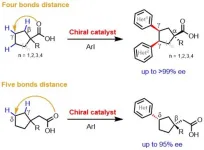
Scripps Research chemists develop new method for making gamma chiral centers on simple carboxylic acids
2024-05-17
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research chemists have accomplished a long elusive feat in synthetic chemistry: the invention of a broadly useful method for constructing “gamma chiral centers” on simple starting compounds called carboxylic acids. The method, published on May 16, 2024 in Science, significantly extends the ability of chemists to build and modify complex pharmaceutical molecules and other valuable chemical products.
The term chiral refers to a type of asymmetry that allows some chemical compounds to exist in left-handed and right-handed forms. Often, only one of these forms has the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
[Press-News.org] A devastating fire 2,200 years ago preserved a moment of life and war in Iron Age Spain — right down to a single gold earringA violent blaze, possibly linked to the Carthaginian army crossing the Pyrenees to fight the Romans, flared up so quickly people couldn’t save their animals or their valuables