Seeking stronger steel, systematic look at 120 combinations of alloy elements provides clues
Calculations consider how a dozen metals such as titanium combine with nitrogen or carbon to form bonds
2024-05-20
(Press-News.org)
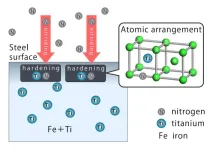
Decarbonization of automobiles not only requires a shift from gasoline engines to electric motors, but also quality steel parts that help the motors run while lessening the weight of vehicles. High-performance steel materials can offer quieter rides and resist the wear and tear from high-speed rotation in motors. To create them, the process of modifying the steel surface with carbon, nitrogen, and alloy elements needs to be optimized.
To understand the interactions between elements in steel, a systematic investigation has been conducted by an Osaka Metropolitan University research group led by Associate Professor Tokuteru Uesugi of the Graduate School of Informatics. The group theoretically calculated 120 combinations of how 12 alloy elements, including aluminum and titanium, interact with carbon during carburization and nitrogen in the nitriding process.
The results showed that when titanium is placed in a specific arrangement, it bonds with nitrogen or carbon, hardening the iron. The group’s analytical data also showed that the alloy element must have a larger metallic radius than the iron atom to bond well.
“Although it was not easy to elucidate the mechanism from the results of numerous calculations, we used multiple linear regression and stratified analysis through trial and error,” Professor Uesugi stated. “These results are expected to contribute to a better understanding of the mechanisms of steel strengthening and improved durability, and to the development of superior materials.”
The findings were published in ISIJ International.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-20
Dr. Hyuk-June Moon from the Bionics Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with Prof. Olaf Blanke’s team at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL), has successfully induced self-location illusions with multi-sensory virtual reality (VR) in the MRI scanner and observed corresponding changes in the human brain's grid cell activity.
The brain is known to contain grid cells and place cells, which perform global positioning system (GPS) functions that allow us to recognize where we are. While ...
2024-05-20
WASHINGTON, DC (May 20, 2024) — Gallbladder cancer rates have been stable or declining for most Americans over the last two decades, but cases have steadily risen among Blacks, with growing numbers not being diagnosed until later stages, according to a study scheduled for presentation at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
“Gallbladder cancer diagnosis at late stage can be highly detrimental,” said lead author Yazan Abboud, MD, internal medicine resident at Rutgers University New Jersey Medical School. “This could be due to a lack of timely ...
2024-05-20
Washington (May 14, 2024) — Cancer-related studies, including a diagnostic tool for gastric cancer and trends in gallbladder and colorectal cancers, will be presented this week at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2024. Abstracts are available to registered media, and press releases are available where noted. Studies are embargoed until 12:01 a.m. EDT the day of presentation, unless otherwise noted.
Here are summaries of the new research on the schedule:
Oral microbiome signatures as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer risk assessment, Abstract 949, will be presented Monday, May 20, at 4:15 p.m. EDT. (A press release is available upon request. Embargoed until 12:01 a.m. EDT ...
2024-05-20
Washington (May 14, 2024) — Studies featuring endoscopic and laparoscopic procedures, including patient views on artificial intelligence in endoscopy and hazards to healthcare personnel of smoke-producing procedures, will be presented this week at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2024. Abstracts are available to registered media, and press releases are available where noted. Research is embargoed until 12:01 a.m. EDT the day of presentation, unless otherwise noted.
Here are summaries of the new research:
Patients’ sentiments ...
2024-05-20
Washington (May 14, 2024) — Studies exploring the hunger hormone, weight-loss drugs, sauerkraut and antibiotic weight gain, the impact of physician gender on care, and the relationship between sleep patterns and digestive diseases will be presented this week at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2024. Abstracts are available to registered media. Embargos lift at 12:01 a.m. EDT on the day they are presented unless otherwise noted.
Here are summaries of the new research:
Performance of a machine-learning gene ...
2024-05-20
Peer-reviewed – Proof-of-concept study
University of East Anglia researchers have made a significant breakthrough in ocular device technology with the introduction of a novel resin for 3D printing intraocular devices. This innovation has potential to enhance the manufacture of eye implants universally used in cataract and refractive surgeries.
An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is primarily required for people with cataracts, a condition where the eye’s natural lens becomes cloudy, obscuring vision.
They can also be also used to correct refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), ...
2024-05-20
Experts have released robust research to show that phonics should be taught hand-in-hand with reading and writing to encourage true literacy and a love of reading, not through narrow synthetic phonics.
There is widespread disagreement globally across academic and educational spheres about the best way to teach children to learn to read and write. Despite a growing international trend towards a narrow approach to synthetic phonics, experts suggest there is a ‘better way’ to teach reading and writing.
In England, the system is among the most prescriptive in the world with ‘synthetic phonics’ being the ...
2024-05-20
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, 20 MAY 2024, 01:01 CEST (00:01 BST/London Time)
Meerkats use two different types of vocal interactions to stay in touch with their group mates. Sometimes the call simply broadcasts information, whereas other times meerkats engage in a call exchange with their neighbours, as researchers from the Centre for the Advanced Study of Collective Behaviour at the University of Konstanz and the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior present in a new publication published on 20 May in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B.
What does it sound like ...
2024-05-20
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 2:15 p.m. PT, May 19, 2024
Session: A95 – Climate Change and Health Disparities in Lung Disease
Extreme Heat and Asthma Hospitalizations in Children in California (2017-2020)
Date and Time: Sunday, May 19, 2024, 2:15 p.m. PT
Location: San Diego Convention Center, Room 24A-C (Upper Level)
ATS 2024, San Diego – For children seeking care at a California urban pediatric health center, extreme heat events were associated with increased asthma hospital visits, according to research published at the ATS 2024 International Conference.
“We found ...
2024-05-20
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 2:15 p.m. PT, Sunday, May 19, 2024
Session: Session A96 – Improving the Care of Patients with Diverse Pulmonary Conditions and Sleep Disordered Breathing
The State of Home Health Nursing for Medically Complex Children in the United States
Date and Time: Sunday, May 19, 2024, 2:15 p.m. PT
Location: San Diego Convention Center, Room 8 (Upper Level)
ATS 2024, San Diego – For American families with medically-complex children, access to home health nursing is often inadequate and the families face major financial burdens, according to research published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Seeking stronger steel, systematic look at 120 combinations of alloy elements provides clues
Calculations consider how a dozen metals such as titanium combine with nitrogen or carbon to form bonds




