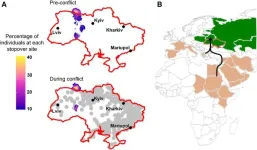
(Press-News.org) When migrating through Ukraine in 2022, Greater Spotted Eagles were exposed to multiple conflict events that altered their migratory course, according to a study reported on May 20 in the journal Current Biology. Greater Spotted Eagles are large raptors that are classified as a vulnerable species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
“Armed conflicts can have wide-ranging impacts on the environment, including changes in animal behavior,” says Charlie Russell (@CJG_Russell) of the University of East Anglia, UK. “Our study provides the first quantitative evidence of this, showing how migrating eagles made deviations to avoid conflict events and spent less time refueling at stopover sites. It also indicates that there are potentially many human activities, beyond wars, that likely change or impact animal behavior.”
Researchers from The Estonian University of Life Sciences University, British Trust for Ornithology (BTO), and their in-country partners started tagging Greater Spotted Eagles that were breeding in Belarusian Polesia in 2017. Although the eagles are no longer found in most of Europe, Polesia remains a stronghold for the species. The goal was to track the raptors and identify important areas that the species relies on to inform future conservation efforts.
Then, on February 24, 2022, the Russian Federation invaded Ukraine. On March 3, the first of 21 tagged Greater Spotted Eagles crossed into Ukraine on their usual migration. By that time, the conflict had spread from Kyiv and eastern regions to most major cities.
“We did not expect to be following these birds as they migrated through an active conflict zone,” Russell says.
While they may not have expected it, the researchers recognized an opportunity to document the effects of human conflict on wildlife. It’s clear that such human activities must have major impacts, but the effects are usually hard to quantify, especially in conflict zones.
Using GPS tracking and conflict data, the researchers quantified changes in the eagles’ expected behavior. In comparison to earlier and more peaceful years, they found that Greater Spotted Eagles used stopover sites less. Stopover sites are essential places to get food, water, and shelter for migrating birds during their long journeys. The eagles also made large deviations from their earlier routes.
The changes to their migratory behavior patterns delayed their arrival to the breeding grounds and likely increased the energetic costs to the birds in detrimental ways. Although all the tagged birds survived, the researchers suspect their experience may continue to affect them into the breeding period and possibly beyond.
“Similar responses have been recorded for birds residing in military training zones, but these new findings that show an impact for migratory species means that disturbance events can have more far-reaching impacts across many more individuals, over greater distances,” says Adham Ashton-Butt (@Adhamab90) of BTO. “The size of the effect on migratory behavior was also quite large, substantial enough to be detected in a relatively small sample size.”
The findings serve as an important reminder that the effects of armed conflicts are wide ranging and stretch beyond the immediate humanitarian crisis, the researchers say. As such, they note, post-conflict recovery also should consider the environmental impact on species and whole ecosystems. The findings also raise important questions about how the conflict in Ukraine—as well as other extreme disturbances caused by humans—may affect many different species, including hundreds of threatened species and millions of migratory birds.
###
This work was supported by the Cambridge Conservation Initiative.
Current Biology, Russell et al. “Active European warzone impacts raptor migration” https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)00519-0
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
A new study reveals for the first time the impact of ongoing conflicts on the migration of an endangered bird species.
Researchers from the University of East Anglia (UEA), the British Trust for Ornithology (BTO) and the Estonian University of Life Sciences compared the movement and migration of the Greater Spotted Eagle through Ukraine, before and shortly after it was invaded by Russia in February 2022.
They were already studying the species when the war started, with the dangers faced by migratory birds usually related to disruptive weather or drought, changes in land use affecting traditional stopping-off ...
Higher fluoride levels in pregnant women are linked to increased odds of their children exhibiting neurobehavioral problems at age 3, according to a new study led by a University of Florida College of Public Health and Health Professions researcher.
The findings, based on an analysis involving 229 mother-child pairs living in a U.S. community with typical fluoride exposure levels for pregnant women in fluoridated regions in North America, appear May 20 in the journal JAMA Network Open. It is believed to be the first U.S.-based study to examine associations of prenatal fluoride exposure ...
Columbia Engineers use nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to examine lithium metal batteries through a new lens -- their findings may help them design new electrolytes and anode surfaces for high-performance batteries
New York, NY—May 20, 2024—A Columbia Engineering team has published a paper in the journal Joule today that details how nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques can be leveraged to design the anode surface in lithium metal batteries. The researchers also present new data and interpretations for how this method can be used to gain unique insight into the structure of these surfaces to share with the field.
“We ...
In the age of smartwatches, monitoring step counts has never been easier, but current physical activity guidelines do not explicitly recommend specific step counts for health. A new study from researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, suggests that both step and time-based exercise targets are equivalently associated with lower risks of early death and cardiovascular disease. Thus, whether one chooses a time or step goal may not be as important as choosing a goal aligned with personal preferences. Results are published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Physical activity reduces the risk of acquiring chronic illness and ...
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of patients with cancer and SARS-CoV-2, racial and ethnic inequities existed in treatment delays and discontinuations throughout the pandemic; however, the disproportionate burden among racially and ethnically minoritized patients with cancer varied across SARS-CoV-2 waves. These inequities may lead to downstream adverse impacts on cancer mortality among minoritized adults in the United States.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jessica Y. Islam, Ph.D., M.P.H., email jessica.islam@moffitt.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12050)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: Adolescents with overweight or obesity may be more vulnerable to negative cognitive effects following sleep restriction. Improved sleep hygiene and duration in this group may positively impact their cognitive health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Aaron D. Fobian, Ph.D., email afobian@uabmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.1332)
Editor’s ...
A surprisingly low amount of methane and a super-sized core hide within the cotton candy–like planet WASP-107 b.
The revelations, based on data obtained by the James Webb Space Telescope, mark the first measurements of an exoplanet’s core mass and will likely underpin future studies of planetary atmospheres and interiors, a key aspect in the search for habitable worlds beyond our solar system.
“Looking into the interior of a planet hundreds of light-years away sounds almost impossible, but when you know the mass, radius, atmospheric composition, and hotness of its interior, you’ve got ...
Micelles assemble in water from amphiphilic molecules, composed of hydrophilic and hydrophobic frameworks. They can be found all around us, for example in soaps, detergents, and shampoos. Their main application is the water-solubilization of insoluble molecules through encapsulation into hydrophobic cavities. These cavities are conventionally composed of linear alkyl-chains, providing good interactions with alkyl-based guests, yet poor interactions with aromatic compounds. In addition, the rather weak intermolecular alkyl-alkyl type ...
BALTIMORE, Md. (May 20, 2024) – Scientists seeking to counter the neglect of African Americans in neuroscience research have found evidence that genetic ancestry is responsible for the increased prevalence of certain neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and stroke, and decreased prevalence of others, including Parkinson’s disease, in Black Americans, according to new research published May 20 as the June cover story in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
In contrast, the scientists from the Lieber Institute for Brain Development did not find evidence that genetic ancestry is responsible for differences in the ...
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have been awarded a $5.6 million grant through the Coast-to-Coast Consortium (C2C) to further their pioneering efforts with the National Institutes of Health's (NIH) All of Us Research Program.
The award is designated to facilitate participant engagement, enrollment, data collection, and retention. C2C will build on the foundation set by the UCSD-led California Precision Medicine Consortium (CAPMC), established in 2018, which enrolled more than 65,500 participants to the program.
This award follows the program's ...