(Press-News.org) About The Study: Adolescents with overweight or obesity may be more vulnerable to negative cognitive effects following sleep restriction. Improved sleep hygiene and duration in this group may positively impact their cognitive health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Aaron D. Fobian, Ph.D., email afobian@uabmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.1332)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.1332?guestAccessKey=e6f39acb-146d-41ad-b9ae-5f7000613f06
END
Effect of sleep restriction on adolescent cognition by adiposity
JAMA Neurology
2024-05-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Webb Telescope offers first glimpse of an exoplanet’s interior
2024-05-20
A surprisingly low amount of methane and a super-sized core hide within the cotton candy–like planet WASP-107 b.
The revelations, based on data obtained by the James Webb Space Telescope, mark the first measurements of an exoplanet’s core mass and will likely underpin future studies of planetary atmospheres and interiors, a key aspect in the search for habitable worlds beyond our solar system.
“Looking into the interior of a planet hundreds of light-years away sounds almost impossible, but when you know the mass, radius, atmospheric composition, and hotness of its interior, you’ve got ...
Alkyl-aromatic hybrid micelles formed from emergent umbrella-shaped molecules
2024-05-20
Micelles assemble in water from amphiphilic molecules, composed of hydrophilic and hydrophobic frameworks. They can be found all around us, for example in soaps, detergents, and shampoos. Their main application is the water-solubilization of insoluble molecules through encapsulation into hydrophobic cavities. These cavities are conventionally composed of linear alkyl-chains, providing good interactions with alkyl-based guests, yet poor interactions with aromatic compounds. In addition, the rather weak intermolecular alkyl-alkyl type ...
First study from the African Ancestry Neuroscience Research Initiative identifies key genes in the brain that account for higher rates of some brain disorders in Black Americans
2024-05-20
BALTIMORE, Md. (May 20, 2024) – Scientists seeking to counter the neglect of African Americans in neuroscience research have found evidence that genetic ancestry is responsible for the increased prevalence of certain neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and stroke, and decreased prevalence of others, including Parkinson’s disease, in Black Americans, according to new research published May 20 as the June cover story in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
In contrast, the scientists from the Lieber Institute for Brain Development did not find evidence that genetic ancestry is responsible for differences in the ...
NIH awards Coast-to-Coast Consortium $5.6 million for All of Us Research Program
2024-05-20
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have been awarded a $5.6 million grant through the Coast-to-Coast Consortium (C2C) to further their pioneering efforts with the National Institutes of Health's (NIH) All of Us Research Program.
The award is designated to facilitate participant engagement, enrollment, data collection, and retention. C2C will build on the foundation set by the UCSD-led California Precision Medicine Consortium (CAPMC), established in 2018, which enrolled more than 65,500 participants to the program.
This award follows the program's ...
Ben-Gurion University scientist hunts for drug candidate to treat brain tumors
2024-05-20
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, May 20, 2024 – When you disable the brakes on a race car, it quickly crashes. Dr. Barak Rotblat wants to do something similar to brain cancer cells. He wants to disable their ability to survive glucose starvation. In fact, he wants to speed the tumor cells up, so they just as quickly die out. It is a novel approach to brain cancer based on a decade of research in his lab.
He and his students' and co-lead researcher Gabriel Leprivier of the Institute of Neuropathology at University Hospital Düsseldorf ...
New Health Blueprint maps healthier future for rural, underserved Southwest Virginia
2024-05-20
A sweeping new Health Blueprint for Southwest Virginia highlights the grave health challenges that grip the rural region but also proposes solutions to help residents live longer, healthier lives.
The Blueprint was assembled by the University of Virginia College at Wise’s Healthy Appalachia Institute, the Southwest Virginia Health Authority, UVA Health’s Center for Telehealth and a coalition of residents and regional healthcare providers. The document identifies priority health concerns for the three health districts in the southwestern corner of Virginia: Lenowisco, Cumberland Plateau and Mount Rogers. These are areas ...
Survival benefit associated with participation in clinical trials of anticancer drugs
2024-05-20
About The Study: Many studies suggest a survival benefit for cancer trial participants. However, these benefits were not detected in studies using designs addressing important sources of bias and confounding. Pooled results of high-quality studies are not consistent with a beneficial effect of trial participation on its own.
Quote from corresponding author Jonathan Kimmelman, Ph.D.:
“Many physicians, policymakers, patient advocates, and research sponsors believe patients have better outcomes when they participate in trials, even if they are in the comparator arm. Educational ...
Expanding on the fundamental principles of liquid movement
2024-05-20
Fukuoka, Japan—From the rain drops rolling down your window, to the fluid running across a COVID rapid test, we cannot go a day without observing the world of fluid dynamics. Naturally, how liquids traverse across, and through, surfaces are a heavily researched subject, where new discoveries can have profound effects in the fields of energy conversion technology, electronics cooling, biosensors, and micro-/nano-fabrications.
Now, using mathematical modeling and experimentation, researchers from Kyushu University’s Faculty of Engineering have expanded on a fundamental principle in fluid dynamics. Their new findings may ...
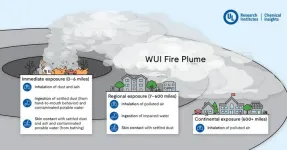
Chemical Insights Research Institute partners with Duke University and the East-West Center to examine dust and ash from devastating Hawai’ian wildfires
2024-05-20
ATLANTA - Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes applies cutting edge technologies to evaluate the toxicity of burn-impacted land areas affected by the August 2023 Lahaina wildfires. Created with CIRI research partners from Duke University and the East-West Center (EWC) in Hawai’i, the study known as Lahaina Environmental Assessment Project (LEAP), will collect and analyze residual dust, soil and ash samples from properties affected by the fires. These residues, including fine dust, ...
NCCN publishes new resource for patients with intestinal cancer type most have never heard of before diagnosis
2024-05-20
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [May 20, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) today announced publication of new NCCN Guidelines for Patients®: Small Bowel Adenocarcinoma. This free resource for people facing cancer and caregivers is focused on a rare cancer type that typically occurs in the small intestine, where routine screening is impossible, even for high-risk individuals. The small amount of patient information that exists for this cancer type tends to combine it with other cancers of the small intestine (such as sarcomas, neuroendocrine tumors, or lymphomas) despite very different treatment approaches and results.
The NCCN Guidelines for Patients: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Effect of sleep restriction on adolescent cognition by adiposityJAMA Neurology