(Press-News.org) Technology use is at an all-time high and understanding how this impacts daily life is crucial. When it comes to parent-child interactions, scientists have coined the term ‘technoference,’ meaning technology interference. It occurs when parent-child interaction and communication are disrupted by the use of digital devices.
But is distraction caused by digital devices more detrimental to parent-child interaction than when parental distraction comes from different sources? Researchers in Switzerland have investigated.
“In this study, we show that when parents are distracted, the quality and quantity of parent-child interaction is impaired compared to when parents are not being distracted,” said Prof Nevena Dimitrova, a researcher at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts Western Switzerland and principal investigator of the study published in Frontiers in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. “This was regardless of if that distraction came from a digital or a non-digital activity.”
Screening distraction
Although the negative impact of parents being distracted by their phones while around their children has been established, less is known about whether these negative effects come from the fact that the parent uses a screen or from the fact that the parent is distracted in general.
To fill this gap, the team around Dimitrova tasked 50 parent-child pairs, in which children were 22 months old on average, to play together for 10 minutes. Participant pairs were divided in three groups. In the first group, there was no disruption. In the second group, after five minutes of play, the parent was given a questionnaire to fill out on paper, whereas in the third group, also after five minutes, the parent was instructed to fill out the same questionnaire using a tablet. Parents that filled out the questionnaire were instructed to continue interacting with their children.
The researchers found that parents who filled out the questionnaire were less sensitive to children’s communication signals, and that children showed lower levels of social involvement towards their parents.
Technoference, however, did not affect parent-child interactions more negatively than non-digital distractions. Instead, all distraction, regardless of whether it was caused by screens or pen and paper, had negative effects on parents, children, and pairs. “We interpret this finding—that was equally surprising for us—as the possibility that screens are so ubiquitous nowadays that young children might be becoming used to the reality of seeing their parents use screens,” said Dimitrova.
Regardless of their findings, the researchers stressed that parent-child interaction is at its best when parents are not distracted at all. This might be especially important for parents who find it difficult to bond with their children.
Curbing a ‘moral panic’
In the media, mostly alarmistic messages about the risks of screen use are discussed, said the researchers. However, research does not support the thesis that screen use by or in the presence of children is exclusively bad. For example, positive effects of screens on child psychological development have been shown in previous research.
“This study shows how important it is to rely on scientific evidence rather that public opinion about screen use. We see that it’s not screens per se that are detrimental to the quality of parent-child interaction,” concluded Dimitrova. “Instead, it seems to be the fact that the parent is not fully engaged in the interaction that negatively impacts parent-child communication.”
The researchers, however, also pointed out that it is difficult to make definitive statements about parental screen use based on one study alone. This is partly because everyday parent-child interaction differs from the experimental set-up. For example, the ways in which parents use screen while around their children cannot always be replicated fully. Studies in naturalistic context are needed and might lead to different results, the scientists noted.
END
Screen time not the main factor making parent-child interactions worse, study finds
Researchers investigated if ‘technoference’ has worse effects on parent-child interactions than non-digital distractions and found that distraction itself – not its source – may be to blame
2024-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improving the effectiveness of earthquake early warning systems
2024-05-21
Mobile phones have become invaluable for receiving emergency alerts such as weather warnings, evacuation notices and notifications about missing persons. In Japan, where earthquakes are frequent, they are vital for delivering earthquake warnings and advising people to take protective actions beforehand. To deal with such situations promptly, the Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) system sends out notifications to areas expected to experience strong tremors by detecting primary seismic waves (P-waves) that arrive before the secondary waves (S-waves). However, the short time between receiving the notification and the arrival of S-waves ...
Addressing homelessness in older people
2024-05-21
Homelessness doesn’t only happen to young people but also affects older adults in growing numbers, write authors in an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) that describes this emerging crisishttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231493.
People experiencing homelessness are considered older adults at age 50, as visible aging is often evident at younger ages in individuals experiencing homelessness compared with individuals who have secure housing. Individuals experiencing homelessness often develop chronic ...
One in 5 adults in Canada without access to primary care
2024-05-21
More than 1 in 5 adults in Canada did not have access to primary care, with large regional gaps in access, found new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231372.
“Translated to the population of Canada, our survey estimates that more than 6.5 million adults across the country don’t have access to a family doctor or nurse practitioner they can see regularly,” says Dr. Tara Kiran, a family physician and researcher at the MAP Centre for Urban Health Solutions at St. Michael’s Hospital, Unity Health Toronto and the University ...
Studies on risks of weight-loss drugs and more presented at Digestive Disease Week
2024-05-21
Washington (May 14, 2024) — Studies examining the risks of GLP-1 weight-loss drugs, distinguishing alpha-gal syndrome from other GI disorders, and comparing medications to slow the progression of liver disease in patients with alcohol-use disorder will be presented this week at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2024. Abstracts are available to registered media. Embargos lift at 12:01 a.m. EDT on the day they are presented.
Here are summaries of the new research:
Re-examining the risks of gastrointestinal adverse events associated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for weight loss with more stringent criteria on a comprehensive ...
Pancreatic cancer research receives $8m philanthropic funding boost
2024-05-21
An exceptional $8 million, 10-year philanthropic investment will spearhead new treatments for pancreatic cancer and create a new dedicated research centre at WEHI.
The centre, to be established thanks to an investment by Australian business leader and WEHI President Jane Hemstritch AO, aims to help close the significant survival gap between pancreatic cancer and other cancers.
The Hemstritch Centre of Excellence for Pancreatic Cancer Research will provide a leading team of scientists and clinicians with long-term funding to ask big research questions. They aim to make major ...
'Hunting for treasures' with AI: Astronomers detect rare neutral atomic-carbon absorbers with deep neural network
2024-05-21
Recently, an international team led by Prof. GE Jian from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted a search for rare weak signals in quasar spectral data released by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey III (SDSS-III) program using deep learning neural networks. By introducing a new method to explore galaxy formation and evolution, the team showcased the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in identifying rare weak signals in astronomical big data. This study was published ...
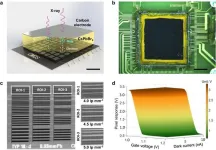
Researchers develop perovskite X-ray detector for medical imaging
2024-05-21
Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers at Central China Normal University, have developed a high-performance perovskite X-ray complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) detector for medical imaging.
The study was published in Nature Communications on Feb. 21.
X-ray imaging is vital for the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular and cancer diseases. Direct-conversion X-ray detectors made of semiconductor materials exhibit superior spatial and temporal resolution at lower radiation doses compared to indirect-conversion detectors made of scintillator materials. However, the currently available semiconductor ...
Rice chemist Gustavo Scuseria wins 2024 Schrödinger Medal
2024-05-21
By Jade Boyd
Special to Rice News
Pioneering Rice University chemist Gustavo Scuseria has won the 2024 Schrödinger Medal from the World Association of Theoretical and Computational Chemists.
Awarded annually to a single recipient, the medal recognizes an outstanding body of work in theoretical and computational chemistry. Scuseria has pioneered quantum computational methods that are widely used to study the complex quantum states and electronic properties of a wide range of molecules and materials. In awarding the medal, ...
Monitoring the recovery process accurately with a medical needle and thread!
2024-05-21
□ DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee) announced on the 16th (Tue) that a research team led by Professor Jaehong Lee of the Department of Robotics and Mechanical Electronics has developed a new human implantable, wireless, health monitoring electronic suture system through joint research with a team from Yonsei University and Korea University. The developed wireless electronic suture can be easily applied in the medical field and is expected to be used in various orthopedic fields, such as patient-customized rehabilitation.
□ ...
One essential step for a germ cell, one giant leap for the future of reproductive medicine
2024-05-21
KYOTO, Japan – May 20, 2024
Infertility affects approximately 1 in 6 people in their lifetime worldwide according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Infertility —as defined by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM)— is a disease, condition, or status characterized by “the inability to achieve a successful pregnancy based on a patient’s medical, sexual, and reproductive history, age, physical findings, diagnostic testing, or any combination of those factors” or requiring medical intervention such as the use of mature donor gametes “to achieve a successful pregnancy ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Screen time not the main factor making parent-child interactions worse, study findsResearchers investigated if ‘technoference’ has worse effects on parent-child interactions than non-digital distractions and found that distraction itself – not its source – may be to blame