Researchers develop perovskite X-ray detector for medical imaging
2024-05-21
(Press-News.org)
Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers at Central China Normal University, have developed a high-performance perovskite X-ray complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) detector for medical imaging.
The study was published in Nature Communications on Feb. 21.
X-ray imaging is vital for the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular and cancer diseases. Direct-conversion X-ray detectors made of semiconductor materials exhibit superior spatial and temporal resolution at lower radiation doses compared to indirect-conversion detectors made of scintillator materials. However, the currently available semiconductor materials, such as Si, a-Se, and CdZnTe/CdTe, are not ideal for general X-ray imaging due to their low X-ray absorption efficiency or high costs.
Perovskite is a promising alternative to conventional semiconductor materials. However, the feasibility of its combination with high-speed pixelated CMOS arrays is still unknown.
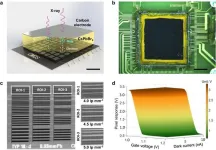
To address this issue, researchers developed a direct-conversion X-ray detector fabricated with a 300 μm thick inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite film printed on a dedicated CMOS pixel array.
Researchers found that the screen-printed thick CsPbBr3 film has a high μτ product of 5.2×10-4 cm2 V–1, a high X-ray detection sensitivity of 15891 µC Gyair–1 cm–2, and a low dose detection limit of 321 nGyair s–1.
Experimental X-ray 2D imaging results showed that the proposed perovskite CMOS detector can achieve very high spatial resolution (5.0 lp mm-1, hardware limit is 6.0 lp mm-1) and low-dose (260 nGy) imaging performance.
Moreover, 3D CT imaging was also validated with the proposed detector at a fast signal readout speed of 300 fps.
"Our work shows the potential of lead halide perovskites in revolutionizing the development of state-of-the-art X-ray detectors with significantly enhanced spatial resolution, readout speed, and low-dose detection efficiency,” said Prof. GE. "This paves the road for medical X-ray imaging applications to become gentler and safer in the future."
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-21
By Jade Boyd
Special to Rice News
Pioneering Rice University chemist Gustavo Scuseria has won the 2024 Schrödinger Medal from the World Association of Theoretical and Computational Chemists.
Awarded annually to a single recipient, the medal recognizes an outstanding body of work in theoretical and computational chemistry. Scuseria has pioneered quantum computational methods that are widely used to study the complex quantum states and electronic properties of a wide range of molecules and materials. In awarding the medal, ...
2024-05-21
□ DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee) announced on the 16th (Tue) that a research team led by Professor Jaehong Lee of the Department of Robotics and Mechanical Electronics has developed a new human implantable, wireless, health monitoring electronic suture system through joint research with a team from Yonsei University and Korea University. The developed wireless electronic suture can be easily applied in the medical field and is expected to be used in various orthopedic fields, such as patient-customized rehabilitation.
□ ...
2024-05-21
KYOTO, Japan – May 20, 2024
Infertility affects approximately 1 in 6 people in their lifetime worldwide according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Infertility —as defined by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM)— is a disease, condition, or status characterized by “the inability to achieve a successful pregnancy based on a patient’s medical, sexual, and reproductive history, age, physical findings, diagnostic testing, or any combination of those factors” or requiring medical intervention such as the use of mature donor gametes “to achieve a successful pregnancy ...
2024-05-21
Ikoma, Japan – With the growth of the Internet of Things, sustainable solution for powering wireless sensors and devices are considered important. Thermoelectric generators, for example, which have the ability to convert waste heat into electricity can offer a sustainable solution. Researchers around the world have been working on such solutions. A research team, led by Masakazu Nakamura from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan has also been working on flexible wearable thermoelectric generators that produce electricity from body heat by sewing nanomaterial called carbon nanotubes (CNTs) into fabric.
Effective ...
2024-05-21
The authors of a major study on the Critically Endangered Arabian leopard say that the release of captive bred animals carefully selected for their genes can make a significant contribution to the successful recovery of the dwindling wild population and avert the prospect of extinction.
An international collaboration led by scientists from the Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology (DICE) at the University of Kent, University of East Anglia (UEA), University College London (UCL), Nottingham-Trent University (NTU) and the Diwan of Royal Court in Oman, surveyed the remote Dhofar mountain range of southern Oman to determine how many of Arabia’s last big cat survive.
By ...
2024-05-21
For Wendy Hood and Geoffrey Hill in Biological Sciences, Andreas Kavazis in Kinesiology, and their team, Emma Rhodes, Paulo Mesquita, and Jeff Yap, traveling the country to unlock the mystery of mitochondria in migrating aviary species has allowed them to make a significant contribution to research in an area that has not been investigated before. The first publication conducted in the AU MitoMobile van is featured in Scientific Reports, “Flexibility underlies differences in mitochondrial respiratory performance between ...
2024-05-20
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with type 2 inflammation may soon gain access to a new drug — dupilumab — that showed rapid and sustained improvements in patients in a pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial, researchers report in the New England Journal of Medicine. This monoclonal antibody is the first biologic shown to improve clinical outcomes in COPD. The data supporting the use of dupilumab in COPD will be reviewed by the United States Food and Drug Administration in June.
The disease improvements — as measured by a significantly ...
2024-05-20
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 20 May 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
2024-05-20
Purdue-led fishing expedition nets new pupfish family member in New Mexico
Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. Scientists have identified a new member on the genetic family tree of an endangered pupfish native to south-central New Mexico.
“We went into this thinking that there was one species of conservation concern,” said J. Andrew DeWoody, professor of genetics in Purdue University’s Department of Forestry and Natural Resources. “The preponderance of evidence ...
2024-05-20
BOSTON--Yoga, mindfulness, meditation, breathwork, and other practices are gaining in popularity due to their potential to improve health and well-being. The effects of these practices are mostly positive and occasionally transformational, yet they are known to sometimes be associated with challenging altered states of consciousness.
New research by a team including investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that altered states of consciousness associated with meditation practice are far more common than expected.
Although many people reported positive outcomes, that were sometimes even considered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop perovskite X-ray detector for medical imaging