(Press-News.org) BOSTON--Yoga, mindfulness, meditation, breathwork, and other practices are gaining in popularity due to their potential to improve health and well-being. The effects of these practices are mostly positive and occasionally transformational, yet they are known to sometimes be associated with challenging altered states of consciousness.
New research by a team including investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that altered states of consciousness associated with meditation practice are far more common than expected.
Although many people reported positive outcomes, that were sometimes even considered transformational, from these experiences, for a substantial minority the experiences were negative. The results are published in the journal Mindfulness.
“With more people engaging in mindfulness, meditation, and other contemplative and mind-body practices, we thought that altered states and their effects might be common among the general population. We conducted a series of international surveys to investigate and indeed found that such experiences were widespread,” said senior author Matthew D. Sacchet, PhD, the director of the Meditation Research Program at Massachusetts General Hospital and an associate professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School.
“Altered states were most often followed by positive, and sometimes even transformational effects on wellbeing,” Sacchet adds.” With that said negative effects on well-being were also reported in some cases, with a small subset of individuals reporting substantial suffering.”
For the study, a panel of experts in psychiatry, neuroscience, meditation, and survey design developed a questionnaire on the experience of altered states of consciousness.
Among 3,135 adults in the US and the UK who completed the online questionnaire, 45% reported experiencing non-pharmacologically induced altered states of consciousness at least once in their lives.
This is far more than expected from the 5% (US) to 15% (UK) of these population estimated to have undertaken mindfulness practice.
The experiences included derealization (the feeling of being detached from your environment), unitive experiences (a sense of unity or “oneness”), ecstatic thrills, vivid perceptions, changes in perceived size, bodily heat or electricity, out-of-body experiences, and perception of non-physical lights.
Respondents reported a mix of positive and negative well-being following altered states, with 13% claiming moderate or greater suffering and 1.1% claiming life-threatening suffering. Of those who experienced suffering, 63% did not seek help.
“Rather than being extremely unusual and rare, our study found that altered states of consciousness are a common variant of normal human experience,” said Sacchet. “However, we’ve found that those who experience negative outcomes related to these altered states often do not seek help, and that clinicians are poorly prepared to recognize or support these kinds of experiences. This has contributed to what might be considered a public health issue as a certain proportion of people have difficulty integrating their experiences of altered states into their existing conceptions of self and reality.”
Sacchet noted that additional studies are needed to identify individual characteristics associated with experiencing altered states of consciousness, and with potential suffering associated with these states. He also stressed the importance of applying this research to patient care.
“We should not dismiss meditation and other practices as inherently dangerous but rather we need to better understand and support meditators to fully realize the potential of these practices,” he said. “Similar to psychotherapy, pharmacology, and other therapeutic tools it’s important that we learn to best implement and support people when engaging with these powerful practices.”
He added that “ancient meditation manuals from the wisdom traditions may be useful for classifying and understanding altered states of consciousness. They may provide guidance into how to better manage altered states when they may be difficult. We clearly need more research to further study and understand this possibility.”
“Clinical curriculum on altered states of consciousness should be developed to better support clinicians caring for patients experiencing suffering linked to these kinds of experiences,” Sacchet added.
“Also, those who teach meditation practices should ensure that participants are aware of potential risk,” he said. “Together, these kinds of safeguards will help to ensure that these very promising and powerful practices are taught and experienced safely.”
Authorship: M. J. Wright, J. Galante, J. S. Corneille, A. Grabovac, D. M. Ingram, and M. D. Sacchet.
Funding: Massey University and Emergence Benefactors
Paper cited: Wright MJ et al. “Altered States of Consciousness are Prevalent and Insufficiently Supported Clinically: A Population Survey” Mindfulness DOI: 10.1007/s12671-024-02356-z
###
About Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. MGH is a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
END
Cislunar space, which stretches from the Earth to just beyond the moon’s orbit, is about to become heavily trafficked over the next 10 years. With NASA’s planned Artemis missions and other countries joining in the cislunar space race, there’s an interest in observing, tracking and predicting the orbit of objects like asteroids and satellites so they don’t collide with spacecraft.
But the process of detecting and observing space objects, known as space domain awareness (SDA), faces challenges with the extensive volume of cislunar space.
“Cislunar space is vast,” says Tarek Elgohary, an associate professor ...
A sensory process such as pain is no ordinary phenomenon—it’s a symphony of neural and vascular interactions orchestrated by the brain and spinal cord. Attempting to dissect this symphony by focusing on a single region is like trying to understand a complex melody by listening to just one instrument. It’s incomplete, potentially misleading, and may result in erroneous conclusions.
Enter the Carney Institute’s team of visionaries. Their mission? To develop tools that allow unprecedented observation of neural and vascular activity within the brain and spinal cord. They tackled two critical fronts: imaging hardware and bioluminescent (BL) molecular tools.
Innovative ...
A certain biological pathway, a set of linked reactions in the body, drives the inflammation seen in the skin disease psoriasis, a new study finds. The work could lead to improved therapies for all inflammatory skin diseases, including atopic and allergic dermatitis and a type of boil called hidradenitis suppurativa, say the study authors. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to irritation and infection, but when out of control, it can lead to the reddish, flaky, itchy lesions that come with these skin diseases.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the new study found that the interleukin-17 (IL-17) pathway, ...
Research Assistant Professor Christopher Fowler received the NASA 2023 Planetary Science Early Career Award for his project “Bringing Planetary Science to West Virginia”. The award is based on demonstrated leadership, involvement in the planetary science community, and potential for future impact.
The resources provided by the NASA Planetary Science Early Career Award will allow Fowler and team to undertake research-related activities that are not always possible within the scope of more “traditional” ...
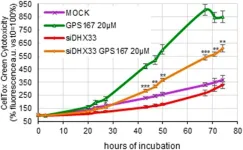
“[...] we have characterized a pair of compounds that impact multiple processes that are relevant to cancer cell proliferation but also, and possibly more importantly, to metastasis [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 16, 2024, entitled, “The anticancer potential of the CLK kinases inhibitors 1C8 and GPS167 revealed by their impact on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the antiviral immune response.”
The diheteroarylamide-based compound 1C8 and the aminothiazole carboxamide-related compound GPS167 inhibit the CLK kinases, and affect ...
Aging is contributing at the 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference in Barcelona, Spain, from June 2–7.
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – Aging is a contributor at the 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference (GRC) on “Systems Modeling, Aging Biomarkers, and Longevity Interventions” — taking place from June 2–7, 2024, in Castelldefels, Barcelona, Spain.
“The conference will present recent advances in systemic rejuvenation, multi-omics approaches, applications ...
The shortage of suitable donor meniscus grafts from the knee and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) impedes treatments for millions of patients. Vitrification offers a promising solution by transitioning these tissues into a vitreous state at cryogenic temperatures, protecting them from ice crystal damage using high concentrations of cryoprotectant agents (CPAs). However, vitrification's success is hindered for larger tissues (>3 mL) due to challenges in CPA penetration. Dense avascular meniscus tissues require extended CPA exposure for adequate penetration; however, ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — By converting their data into sounds, scientists discovered how hydrogen bonds contribute to the lightning-fast gyrations that transform a string of amino acids into a functional, folded protein. Their report, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers an unprecedented view of the sequence of hydrogen-bonding events that occur when a protein morphs from an unfolded to a folded state.
See video: Protein Sonification
“A protein must fold properly to become an enzyme or signaling molecule or whatever its function may be — all the many things that proteins do in our bodies,” said University of Illinois ...
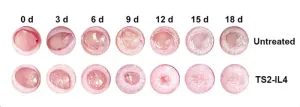
New York, NY [May 20, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have designed a regenerative medicine therapy to speed up diabetic wound repair. Using tiny fat particles loaded with genetic instructions to calm down inflammation, the treatment was shown to target problem-causing cells and reduce swelling and harmful molecules in mouse models of damaged skin.
Details on their findings were published in the May 20 online issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Diabetic wounds, often resistant to conventional treatments, ...
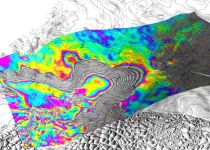
Irvine, Calif., May 20, 2024 — A team of glaciologists led by researchers at the University of California, Irvine used high-resolution satellite radar data to find evidence of the intrusion of warm, high-pressure seawater many kilometers beneath the grounded ice of West Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier.
In a study published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the UC Irvine-led team said that widespread contact between ocean water and the glacier – a process that is replicated throughout Antarctica and in Greenland – causes “vigorous melting” and may require a reassessment of ...