(Press-News.org) A certain biological pathway, a set of linked reactions in the body, drives the inflammation seen in the skin disease psoriasis, a new study finds. The work could lead to improved therapies for all inflammatory skin diseases, including atopic and allergic dermatitis and a type of boil called hidradenitis suppurativa, say the study authors. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to irritation and infection, but when out of control, it can lead to the reddish, flaky, itchy lesions that come with these skin diseases.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the new study found that the interleukin-17 (IL-17) pathway, whose activity is blocked by existing anti-inflammatory drugs, activates a protein called hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1-alpha) in psoriasis. Researchers say that IL-17 has long been known to be active in inflammation, but the role of HIF-1-alpha has until now been unclear.
The research team also found that HIF-1-alpha let inflamed skin cells more actively break down sugar for energy, supporting their metabolism and leading to the production of a waste product called lactate. When consumed by inflammatory T cells, lactate triggered production of IL-17, fueling even more inflammation.
Publishing in the journal Immunity online May 20, the findings show that in human skin tissue samples from people with psoriasis, measures of gene activity around IL-17 and HIF-1-alpha were similar, suggesting that these factors are interconnected. Experiments in mice treated to develop psoriasis found that subsequent treatment with an experimental drug that blocks the action of HIF-1-alpha, called BAY-87-2243, resolved inflammatory skin lesions.
Further, skin samples from 10 patients successfully treated with anti-inflammatory drug etanercept showed diminished activity for both IL-17 and HIF-1-alpha, suggesting to researchers that when IL-17 is blocked, so is HIF-1-alpha.
“Our study results broadly show that activation of HIF-1-alpha is at the crux of metabolic dysfunction observed in psoriasis and that its action is triggered by IL-17, another key inflammatory-signaling molecule,” said corresponding study author Shruti Naik, PhD, associate professor at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in the Departments of Pathology and Medicine, and the Ronald O. Perelman Department of Dermatology.
Further experiments were performed on skin samples from five patients with psoriasis whose healthy and inflamed skin was separately treated with either BAY-87-2243 or an existing combination of topical drugs (calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate). Researchers then compared differences in inflammatory gene activity as a measure of impact and found that the HIF-1-alpha inhibitor had a greater effect than existing topical drugs. Specifically, skin samples that responded to HIF-1-alpha therapy had 2,698 genes that were expressed differently, while standard-of-care–treated samples had 147 differently expressed genes.
Genetic analysis of skin samples from another 24 psoriatic patients treated with the IL-17A–blocking drug secukinumab showed only decreased, not heightened, gene activity connected to HIF-1-alpha when compared to HIF-1-alpha gene activity in nine healthy patients with no psoriatic disease. Researchers say this indicates HIF-1-alpha’s blocked action was codependent on blockage of IL-17.
Additional experiments in mice showed that blocking sugar (glucose) uptake in the skin slowed psoriatic disease growth by limiting glucose metabolism, or glycolysis. Both the number of immune T cells tied to inflammation and the cell levels of IL-17 also decreased. The researchers found further that levels of lactate, the main byproduct of glycolysis, in psoriatic skin cell cultures dropped once exposed to the glycolysis-inhibiting drug 2-DG.
Directly targeting lactate production in psoriatic mice using a topical skin cream containing lactate dehydrogenase, which breaks down lactate, also slowed disease progression in the skin, with reduced numbers of inflammatory gamma-delta T cells and reduced IL-17 activity. Gamma-delta T cells were shown to take up lactate and use it to produce IL-17.
“Our findings suggest that blocking either HIF-1-alpha’s action or its glycolytic metabolic support mechanisms could be effective therapies for curbing the inflammation,” added Naik, who is also the associate director for NYU Langone’s Judith and Stewart Colton Center for Autoimmunity.
“Evidence of HIF-1-alpha’s depressed action, or downregulation, could also serve as a biomarker, or molecular sign, that other anti-inflammatory therapies are working,” said study co-senior investigator Jose U. Scher, MD, the Steere Abramson Associate Professor of Medicine in the Department of Medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Scher, who also serves as director of NYU Langone’s Psoriatic Arthritis Center and the Judith and Stewart Colton Center for Autoimmunity, says the team plans to develop experimental drugs that can block HIF-1-alpha and lactate action in the skin “to end the underlying vicious cycle of IL-17–driven inflammation in skin disease. Our research fundamentally expands the scope of feasible therapeutic options.”
Naik points out that while many available therapies for psoriasis, including steroids and immunosuppressive drugs, reduce inflammation and symptoms, they do not cure the disease. She said further experiments are needed to refine which experimental drug works best, with respect to HIA-1-alpha inhibition, before clinical trials could start. Indeed, Naik and study co-lead investigators Ipsita Subudhi and Piotr Konieczny have a patent application pending (U.S. application number 63/540,794) for inflammatory skin disease therapies derived from their work on HIA-1-alpha inhibition.
More than 8 million Americans and 125 million worldwide are estimated to have psoriatic disease. The condition affects men and women equally.
Funding support for the studies was provided by National Institutes of Health grants P30AR075043, R01AR080436, R01AI168462, UC2AR081029, K22AI135099, K99AR083536, T32AR069515, TL1TR001447, UL1TR001445, and DP2AR079173. Additional funding was provided by the National Psoriasis Foundation, the Judith and Stewart Colton Center for Autoimmunity, the Beatrice Snyder Foundation, the Riley Family Foundation, the American Association of Immunologists, the International Human Frontier Science Program, the Charles H. Revson Foundation, and the Pew-Stewart Scholar Award 00034119, as well as the New York Stem Cell Foundation.
Naik serves on the advisory boards of Seed Inc. and as a consultant for BiomX. She also receives research funding from Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Scher has served as a consultant for Janssen, Pfizer, UCB, and BMS. He also receives research funding from Janssen and Pfizer. All of these arrangements are being managed in accordance with the policies and practices of NYU Langone Health.
Besides Naik, Scher, Subudhi, and Konieczny, other NYU Langone investigators were Aleksandr Prystupa, Rochelle Castillo, Erica Sze-Tu, Yue Xing, Daniel Rosenblum, Ilana Reznikov, Ikjot Sidhu, Cynthia Loomis, Catherine Lu, and Aristotelis Tsirigos. Other study co-investigators were Niroshana Anandasabapathy, at Weill Cornell Medicine; Mayte Suarez-Farinas, at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; and Johann Gudjonsson, at the University of Michigan.
END
Studies show linked biological pathways driving skin inflammation
2024-05-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fowler awarded 2023 NASA Planetary Science Early Career Award
2024-05-20
Research Assistant Professor Christopher Fowler received the NASA 2023 Planetary Science Early Career Award for his project “Bringing Planetary Science to West Virginia”. The award is based on demonstrated leadership, involvement in the planetary science community, and potential for future impact.
The resources provided by the NASA Planetary Science Early Career Award will allow Fowler and team to undertake research-related activities that are not always possible within the scope of more “traditional” ...
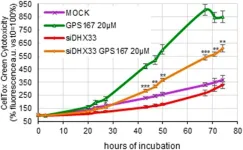
Anticancer potential of CLK kinase inhibitors 1C8 and GPS167 via EMT and antiviral immune response
2024-05-20
“[...] we have characterized a pair of compounds that impact multiple processes that are relevant to cancer cell proliferation but also, and possibly more importantly, to metastasis [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 16, 2024, entitled, “The anticancer potential of the CLK kinases inhibitors 1C8 and GPS167 revealed by their impact on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the antiviral immune response.”
The diheteroarylamide-based compound 1C8 and the aminothiazole carboxamide-related compound GPS167 inhibit the CLK kinases, and affect ...
Aging contributes to 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference
2024-05-20
Aging is contributing at the 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference in Barcelona, Spain, from June 2–7.
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – Aging is a contributor at the 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference (GRC) on “Systems Modeling, Aging Biomarkers, and Longevity Interventions” — taking place from June 2–7, 2024, in Castelldefels, Barcelona, Spain.
“The conference will present recent advances in systemic rejuvenation, multi-omics approaches, applications ...
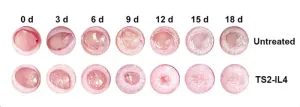
Pioneering research study makes significant contributions toward addressing the shortage of suitable knee meniscus and TMJ disc replacements
2024-05-20
The shortage of suitable donor meniscus grafts from the knee and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) impedes treatments for millions of patients. Vitrification offers a promising solution by transitioning these tissues into a vitreous state at cryogenic temperatures, protecting them from ice crystal damage using high concentrations of cryoprotectant agents (CPAs). However, vitrification's success is hindered for larger tissues (>3 mL) due to challenges in CPA penetration. Dense avascular meniscus tissues require extended CPA exposure for adequate penetration; however, ...
By listening, scientists learn how a protein folds
2024-05-20
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — By converting their data into sounds, scientists discovered how hydrogen bonds contribute to the lightning-fast gyrations that transform a string of amino acids into a functional, folded protein. Their report, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers an unprecedented view of the sequence of hydrogen-bonding events that occur when a protein morphs from an unfolded to a folded state.
See video: Protein Sonification
“A protein must fold properly to become an enzyme or signaling molecule or whatever its function may be — all the many things that proteins do in our bodies,” said University of Illinois ...
Nano drug accelerates diabetic wound healing in mice
2024-05-20
New York, NY [May 20, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have designed a regenerative medicine therapy to speed up diabetic wound repair. Using tiny fat particles loaded with genetic instructions to calm down inflammation, the treatment was shown to target problem-causing cells and reduce swelling and harmful molecules in mouse models of damaged skin.
Details on their findings were published in the May 20 online issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Diabetic wounds, often resistant to conventional treatments, ...
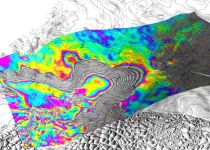
UC Irvine-led team uncovers ‘vigorous melting’ at Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier
2024-05-20
Irvine, Calif., May 20, 2024 — A team of glaciologists led by researchers at the University of California, Irvine used high-resolution satellite radar data to find evidence of the intrusion of warm, high-pressure seawater many kilometers beneath the grounded ice of West Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier.
In a study published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the UC Irvine-led team said that widespread contact between ocean water and the glacier – a process that is replicated throughout Antarctica and in Greenland – causes “vigorous melting” and may require a reassessment of ...
Warm seawater speeding up melting of ‘Doomsday Glacier,’ scientists warn
2024-05-20
EMBARGOED UNTIL 15:00 EDT MONDAY, MAY 20, 2024
For the first time, there is visible evidence showing that warm seawater is pumping underneath Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier—ominously nicknamed the Doomsday Glacier.
An international team of scientists—including a researcher from the University of Waterloo—observed it using satellite imagery and warns that it could accelerate catastrophic sea level rise in 10 to 20 years.
The intrusion of seawater causes the ice to continuously lift off the land and settle back down again. Ice melts intensely when it first touches seawater, ...
Can coal mines be tapped for rare earth elements?
2024-05-20
Deposits of designated critical minerals needed to transition the world’s energy systems away from fossil fuels may, ironically enough, be co-located with coal deposits that have been mined to produce the fossil fuel most implicated in climate change.
Now, research led by the University of Utah has documented elevated concentrations of a key subset of critical minerals, known as rare earth elements, or REEs, in active mines rimming the Uinta coal belt of Colorado and Utah.
These findings open the possibility that these mines could see a secondary resource stream in the form of metals used in renewable energy and numerous other high-tech ...
Electric school buses may yield significant health and climate benefits, cost savings
2024-05-20
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE: MONDAY, MAY 20, 2024, 3:00 PM ET
Key points:
Replacing an average diesel school bus from 2017 with an electric one may result in $84,200 in health and climate benefits—including fewer greenhouse gas emissions and reduced rates of mortality and childhood asthma—per individual bus.
Those benefits may increase to $247,600 per individual electric school bus replacing a diesel bus from 2005 or earlier in a large metropolitan area.
While the benefits of replacing diesel vehicles with electric ones are well known, this is the first study to specifically quantify the health and climate benefits of replacing diesel school buses with electric ...