Purdue-led fishing expedition nets new pupfish family member in New Mexico
Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation
2024-05-20
(Press-News.org)
Purdue-led fishing expedition nets new pupfish family member in New Mexico
Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. Scientists have identified a new member on the genetic family tree of an endangered pupfish native to south-central New Mexico.
“We went into this thinking that there was one species of conservation concern,” said J. Andrew DeWoody, professor of genetics in Purdue University’s Department of Forestry and Natural Resources. “The preponderance of evidence now suggests that there are two species where we thought there was one. So, if we had one endangered species, now we seem to have two.”
DeWoody and eight collaborators from Purdue, Ohio State, Auburn and Texas A&M universities will publish their findings this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The evolution of the White Sands pupfish into two species is unusual in that genetic drift was the driving force.
Genetic drift results from the random inheritance of different genes from an organism’s parents. Natural selection, by contrast, occurs when populations within a species change over time due to adaptation to diverse habitats.
The two species also diverged unusually quickly.
“Close relatives in mammals diverged from one another, on average, about two million years ago,” DeWoody said. “This is about four hundred times faster than the average mammalian speciation event.”
Cyprinodon tularosa, an endangered species, is native to the Tularosa Basin. Natural populations live in Salt Creek and Malpais Spring. Resource managers established the other two populations in Lost River and Mound Spring in the 1960s and 1970s, probably from Salt Creek.
“We knew they were different, but we did not know the evolutionary force causing this difference,” said Erangi Heenkenda, co-lead author of the PNAS paper who received her PhD in forestry and natural resources from Purdue this month.
The researchers considered selection as the driving evolutionary force because the salinity, water flow and parasites in the environments at Salt Creek and Malpais Spring were quite different, Heenkenda said.
The researchers sequenced the entire genome of individual pupfish. Previous research on these pupfish was based on limited genetic sampling. Heenkenda compared the whole-genome approach described in the PNAS study as reading an entire book instead of only a few pages.
“We expected to see some differences in the genes, but we did not see that difference with respect to selection,” said Heenkenda, who will soon begin working at the National Veterinary Services Laboratories in Ames, Iowa, on an Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education Postdoctoral Fellowship. But they did not detect any genes that conferred salt tolerance on the fish, for example.
“This divergence appears to have been primarily driven by high levels of genetic drift just over the last, 5,000 years, which we refer to as ‘drift speciation,’” said co-lead author Andrew Black, a former postdoctoral scientist in DeWoody’s research group. Now at Oregon State University’s Center for Quantitative Life Sciences, Black noted that there are many known cases of evolution occurring over dozens or thousands of generations.
“These are typically attributed to natural selection. The relative role of drift is commonly overlooked or ignored in speciation,” Black said. He noted that factors like small populations, geographic isolation and the harsh desert ecosystem that produced population bottlenecks favored genetic drift over natural selection in these pupfish populations.
“It makes me wonder if drift speciation is likely a common mechanism of evolution in other species of desert pupfish, too,” Black said.
The slowly erupting Carrizozo lava flow from a volcano in south-central New Mexico covered about 130 square miles over two or three decades about 5,000 years ago. That barrier likely contributed to the evolution of the new species.
“The genomic data, independently of the geological data, suggested these two species were one somewhere around 5,000 years ago,” DeWoody said. “Then you overlay the geologic data. This Carrizozo lava flow happened about then. It makes sense.”
In their analysis of the pupfish gene variants, the researchers found that the ancestral Malpais Spring population attained a large and stable population of more than 60,000 individuals for a long period. The ancestral population of about 15,000 at Salt Creek and Lost River was also stable.
Both populations underwent bottlenecks — sharp reductions in size — about 2,500 years ago. The bottlenecks affecting the Salt Creek and Lost River populations were far more severe, however, than the one experienced by the Malpais Spring pupfish.
As populations shrink, they experience random fluctuations of gene frequencies, or genetic drift. Small populations experience a great deal of genetic drift, which leaves large populations, such as the massive schools of sardines that ply the oceans, mostly unaffected. In such large populations, DeWoody said, “Natural selection can overpower drift, but in small populations, drift overpowers selection.”
Two populations of the White Sands pupfish previously received designation as meriting enhanced conservation measures. One population consists of the Malpais Spring pupfish. The Salt Creek and Lost River pupfish comprise the other population.
Their results led the researchers to call for a species-level revision of the pupfish’s classification. The scientists recommend that the new species be named “the enchanted pupfish,” a nod to the state of New Mexico, also known as “the Land of Enchantment.”
This study grew out of the biodiversity monitoring research that co-author Brian Pierce of Texas A&M University performs with funding from the U.S. Air Force. Additional funding was provided to Purdue by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-20
BOSTON--Yoga, mindfulness, meditation, breathwork, and other practices are gaining in popularity due to their potential to improve health and well-being. The effects of these practices are mostly positive and occasionally transformational, yet they are known to sometimes be associated with challenging altered states of consciousness.
New research by a team including investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that altered states of consciousness associated with meditation practice are far more common than expected.
Although many people reported positive outcomes, that were sometimes even considered ...
2024-05-20
Cislunar space, which stretches from the Earth to just beyond the moon’s orbit, is about to become heavily trafficked over the next 10 years. With NASA’s planned Artemis missions and other countries joining in the cislunar space race, there’s an interest in observing, tracking and predicting the orbit of objects like asteroids and satellites so they don’t collide with spacecraft.
But the process of detecting and observing space objects, known as space domain awareness (SDA), faces challenges with the extensive volume of cislunar space.
“Cislunar space is vast,” says Tarek Elgohary, an associate professor ...
2024-05-20
A sensory process such as pain is no ordinary phenomenon—it’s a symphony of neural and vascular interactions orchestrated by the brain and spinal cord. Attempting to dissect this symphony by focusing on a single region is like trying to understand a complex melody by listening to just one instrument. It’s incomplete, potentially misleading, and may result in erroneous conclusions.
Enter the Carney Institute’s team of visionaries. Their mission? To develop tools that allow unprecedented observation of neural and vascular activity within the brain and spinal cord. They tackled two critical fronts: imaging hardware and bioluminescent (BL) molecular tools.
Innovative ...
2024-05-20
A certain biological pathway, a set of linked reactions in the body, drives the inflammation seen in the skin disease psoriasis, a new study finds. The work could lead to improved therapies for all inflammatory skin diseases, including atopic and allergic dermatitis and a type of boil called hidradenitis suppurativa, say the study authors. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to irritation and infection, but when out of control, it can lead to the reddish, flaky, itchy lesions that come with these skin diseases.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the new study found that the interleukin-17 (IL-17) pathway, ...
2024-05-20
Research Assistant Professor Christopher Fowler received the NASA 2023 Planetary Science Early Career Award for his project “Bringing Planetary Science to West Virginia”. The award is based on demonstrated leadership, involvement in the planetary science community, and potential for future impact.
The resources provided by the NASA Planetary Science Early Career Award will allow Fowler and team to undertake research-related activities that are not always possible within the scope of more “traditional” ...
2024-05-20
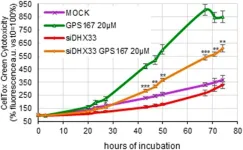
“[...] we have characterized a pair of compounds that impact multiple processes that are relevant to cancer cell proliferation but also, and possibly more importantly, to metastasis [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 16, 2024, entitled, “The anticancer potential of the CLK kinases inhibitors 1C8 and GPS167 revealed by their impact on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the antiviral immune response.”
The diheteroarylamide-based compound 1C8 and the aminothiazole carboxamide-related compound GPS167 inhibit the CLK kinases, and affect ...
2024-05-20
Aging is contributing at the 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference in Barcelona, Spain, from June 2–7.
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – Aging is a contributor at the 2024 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference (GRC) on “Systems Modeling, Aging Biomarkers, and Longevity Interventions” — taking place from June 2–7, 2024, in Castelldefels, Barcelona, Spain.
“The conference will present recent advances in systemic rejuvenation, multi-omics approaches, applications ...
2024-05-20
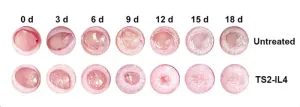
The shortage of suitable donor meniscus grafts from the knee and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) impedes treatments for millions of patients. Vitrification offers a promising solution by transitioning these tissues into a vitreous state at cryogenic temperatures, protecting them from ice crystal damage using high concentrations of cryoprotectant agents (CPAs). However, vitrification's success is hindered for larger tissues (>3 mL) due to challenges in CPA penetration. Dense avascular meniscus tissues require extended CPA exposure for adequate penetration; however, ...
2024-05-20
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — By converting their data into sounds, scientists discovered how hydrogen bonds contribute to the lightning-fast gyrations that transform a string of amino acids into a functional, folded protein. Their report, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers an unprecedented view of the sequence of hydrogen-bonding events that occur when a protein morphs from an unfolded to a folded state.
See video: Protein Sonification
“A protein must fold properly to become an enzyme or signaling molecule or whatever its function may be — all the many things that proteins do in our bodies,” said University of Illinois ...
2024-05-20
New York, NY [May 20, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have designed a regenerative medicine therapy to speed up diabetic wound repair. Using tiny fat particles loaded with genetic instructions to calm down inflammation, the treatment was shown to target problem-causing cells and reduce swelling and harmful molecules in mouse models of damaged skin.
Details on their findings were published in the May 20 online issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Diabetic wounds, often resistant to conventional treatments, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Purdue-led fishing expedition nets new pupfish family member in New Mexico
Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation