(Press-News.org) The authors of a major study on the Critically Endangered Arabian leopard say that the release of captive bred animals carefully selected for their genes can make a significant contribution to the successful recovery of the dwindling wild population and avert the prospect of extinction.
An international collaboration led by scientists from the Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology (DICE) at the University of Kent, University of East Anglia (UEA), University College London (UCL), Nottingham-Trent University (NTU) and the Diwan of Royal Court in Oman, surveyed the remote Dhofar mountain range of southern Oman to determine how many of Arabia’s last big cat survive.
By deploying camera traps to identify individual leopards and performing DNA analyses from wild leopard scat alongside samples from the captive population, the team estimates there could be only 51 wild leopards remaining in Oman, distributed between three isolated, genetically impoverished but distinct subpopulations.
Despite revealing extremely low levels of genetic diversity in the wild leopard population in Oman, the team discovered higher levels of genetic diversity in captive leopards across the region, in particular among several individuals originating from neighbouring Yemen that helped found today’s captive-breeding population. This important genetic resource has the potential for a major role in successful recovery of the Arabian leopard.
The team’s research showed that the dwindling regional wild population, could most effectively be recovered thorough ‘genetic rescue’, namely, the introduction of offspring from captive-bred leopards — which harbour the greatest amount of genetic diversity — into the wild population. However, their predictions indicate that for genetic rescue to establish the most viable populations through leopard reintroductions, the benefit that new genes can bring needs to be carefully assessed, in particular because captive leopards may already be in-bred.
The study, published in Evolutionary Applications, used conservation genetic analysis at DICE, cutting-edge computer simulations developed at UEA, and extensive fieldwork in Oman, to closely examine Arabian leopard DNA and assess the risk of future extinction, as well as forecasting how genetic rescue can secure the leopard’s viability. The authors say their findings could help other threatened species.
Professor Jim Groombridge, who led the research at Kent’s DICE, explained how the genetic analysis was carried out: ‘In collaboration with the Diwan of Royal Court in Oman, we surveyed and collected leopard scats from across the Dhofar mountain range, and extracted DNA from them which we analysed using microsatellite DNA markers to quantify genetic diversity.
‘Using the genetic information, we were able to determine the number of leopard individuals that remain in the wild. We could then compare levels of genetic diversity between the wild leopard population and those in captivity.’
Dr Hadi Al Hikmani, Arabian leopard Conservation Lead at the Royal Commission for AlUla in Saudi Arabia, described the motivation for this study: ‘The Arabian leopard is one of the world’s rarest carnivores and is extraordinarily elusive. The only way to monitor these leopards in the wild is to deploy camera traps high up across the mountain ranges where the leopards live, and to collect the scats they leave behind on the mountain passes, for DNA analysis.’
Thomas Birley, a PhD researcher at UEA who performed the computer simulations for genetic rescue, said: ‘By using the genetic information from the wild and captive populations, we were able to forecast the best plan for genetic rescue to ensure long-term viability for this Critically Endangered big cat.’
Professor Cock van Oosterhout, of the School of Environmental Sciences at UEA, added: ‘The problem is that all individuals are somehow related to each other. They are the descendants of the few ancestors that managed to survive a major population crash. Hence, it becomes virtually impossible to stop inbreeding, and this exposes ‘bad’ mutations, what we call genetic load. In turn, this can increase the mortality rate, causing further population collapse.’
‘The genetic load poses a severe threat, but it can be alleviated by genetic rescue, and our study has projected the best way to do this. The wild population needs ‘genetic rescue’ from more genetically diverse leopards bred in captivity. These leopards are genetically more diverse, and they can help to reduce the level of inbreeding and genetic load. However, there is a risk that we could introduce other bad mutations from the captive population into the wild, so we will need a careful balance.’
END
Genes provide hope for the survival of Arabia’s last big cat
Study on the critically endangered Arabian leopard finds that the release of captive bred animals carefully selected for their genes can make a significant contribution to the recovery of the dwindling wild population and avert the prospect of extinction
2024-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Auburn biologists publish first work on avian migration conducted in the AU MitoMobile
2024-05-21
For Wendy Hood and Geoffrey Hill in Biological Sciences, Andreas Kavazis in Kinesiology, and their team, Emma Rhodes, Paulo Mesquita, and Jeff Yap, traveling the country to unlock the mystery of mitochondria in migrating aviary species has allowed them to make a significant contribution to research in an area that has not been investigated before. The first publication conducted in the AU MitoMobile van is featured in Scientific Reports, “Flexibility underlies differences in mitochondrial respiratory performance between ...
Second Phase 3 clinical trial again shows dupilumab lessens disease in COPD patients with type 2 inflammation
2024-05-20
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with type 2 inflammation may soon gain access to a new drug — dupilumab — that showed rapid and sustained improvements in patients in a pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial, researchers report in the New England Journal of Medicine. This monoclonal antibody is the first biologic shown to improve clinical outcomes in COPD. The data supporting the use of dupilumab in COPD will be reviewed by the United States Food and Drug Administration in June.
The disease improvements — as measured by a significantly ...
Autoimmune disease not associated with monoclonal gammopathy
2024-05-20
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 20 May 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Purdue-led fishing expedition nets new pupfish family member in New Mexico
2024-05-20
Purdue-led fishing expedition nets new pupfish family member in New Mexico
Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. Scientists have identified a new member on the genetic family tree of an endangered pupfish native to south-central New Mexico.
“We went into this thinking that there was one species of conservation concern,” said J. Andrew DeWoody, professor of genetics in Purdue University’s Department of Forestry and Natural Resources. “The preponderance of evidence ...
Yoga and meditation-induced altered states of consciousness are common in the general population
2024-05-20
BOSTON--Yoga, mindfulness, meditation, breathwork, and other practices are gaining in popularity due to their potential to improve health and well-being. The effects of these practices are mostly positive and occasionally transformational, yet they are known to sometimes be associated with challenging altered states of consciousness.
New research by a team including investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that altered states of consciousness associated with meditation practice are far more common than expected.
Although many people reported positive outcomes, that were sometimes even considered ...
UCF researcher is developing algorithms to further space, sea exploration
2024-05-20
Cislunar space, which stretches from the Earth to just beyond the moon’s orbit, is about to become heavily trafficked over the next 10 years. With NASA’s planned Artemis missions and other countries joining in the cislunar space race, there’s an interest in observing, tracking and predicting the orbit of objects like asteroids and satellites so they don’t collide with spacecraft.
But the process of detecting and observing space objects, known as space domain awareness (SDA), faces challenges with the extensive volume of cislunar space.
“Cislunar space is vast,” says Tarek Elgohary, an associate professor ...
Illuminating neuro-vascular dynamics throughout the body: 3D-printed implants and bioluminescence duet shed light on brain–spinal interactions
2024-05-20
A sensory process such as pain is no ordinary phenomenon—it’s a symphony of neural and vascular interactions orchestrated by the brain and spinal cord. Attempting to dissect this symphony by focusing on a single region is like trying to understand a complex melody by listening to just one instrument. It’s incomplete, potentially misleading, and may result in erroneous conclusions.
Enter the Carney Institute’s team of visionaries. Their mission? To develop tools that allow unprecedented observation of neural and vascular activity within the brain and spinal cord. They tackled two critical fronts: imaging hardware and bioluminescent (BL) molecular tools.
Innovative ...
Studies show linked biological pathways driving skin inflammation
2024-05-20
A certain biological pathway, a set of linked reactions in the body, drives the inflammation seen in the skin disease psoriasis, a new study finds. The work could lead to improved therapies for all inflammatory skin diseases, including atopic and allergic dermatitis and a type of boil called hidradenitis suppurativa, say the study authors. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to irritation and infection, but when out of control, it can lead to the reddish, flaky, itchy lesions that come with these skin diseases.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the new study found that the interleukin-17 (IL-17) pathway, ...
Fowler awarded 2023 NASA Planetary Science Early Career Award
2024-05-20
Research Assistant Professor Christopher Fowler received the NASA 2023 Planetary Science Early Career Award for his project “Bringing Planetary Science to West Virginia”. The award is based on demonstrated leadership, involvement in the planetary science community, and potential for future impact.
The resources provided by the NASA Planetary Science Early Career Award will allow Fowler and team to undertake research-related activities that are not always possible within the scope of more “traditional” ...
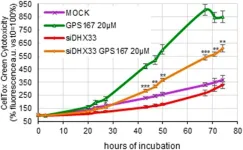
Anticancer potential of CLK kinase inhibitors 1C8 and GPS167 via EMT and antiviral immune response
2024-05-20
“[...] we have characterized a pair of compounds that impact multiple processes that are relevant to cancer cell proliferation but also, and possibly more importantly, to metastasis [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 20, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 16, 2024, entitled, “The anticancer potential of the CLK kinases inhibitors 1C8 and GPS167 revealed by their impact on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the antiviral immune response.”
The diheteroarylamide-based compound 1C8 and the aminothiazole carboxamide-related compound GPS167 inhibit the CLK kinases, and affect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Genes provide hope for the survival of Arabia’s last big catStudy on the critically endangered Arabian leopard finds that the release of captive bred animals carefully selected for their genes can make a significant contribution to the recovery of the dwindling wild population and avert the prospect of extinction