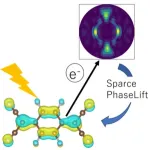
(Press-News.org) I’m not touching you! When another person’s finger hovers over your skin, you may get the sense that they’re touching you, feeling not necessarily contact, but their proximity. Similarly, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have designed a soft, flexible film that senses the presence of nearby objects without physically touching them. The study features the new sensor technology to detect eyelash proximity in blink-tracking glasses.
Noncontact sensors can identify or measure an object without directly touching it. Examples of these devices include infrared thermometers and vehicle proximity notification systems. One type of noncontact sensor relies on static electricity to detect closeness and small motions, and has the potential to enhance smart devices, such as allowing phone screens to recognize more finger gestures. So far, however, they’ve been limited in what types of objects get detected, how long they stay charged and how hard they are to fabricate. So, Xunlin Qiu, Yiming Wang, Fuzhen Xuan and coworkers wanted to create a flexible static electricity-based sensor that overcame these problems.
The researchers began by simply fabricating a three-part system: fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) for the top sensing layer, with an electrically conductive film and flexible plastic base for the middle and bottom layers, respectively. FEP is an electret, a type of material that’s electrically charged and produces an external electrostatic field, similar to the way a magnet produces a magnetic field. Then they electrically charged the FEP-based sensor making it ready for use.
As objects approached the FEP surface, their inherent static charge caused an electrical current to flow in the sensor, thereby “feeling” the object without physical contact. The resulting clear and flexible sensor detected objects — made of glass, rubber, aluminum and paper — that were nearly touching it but not quite, from 2 to 20 millimeters (less than an inch) away. The sensor held its charge for over 3,000 different approach-withdraw cycles over almost two hours.
In a demonstration of the new sensing film, the researchers attached it to the inner side of an eyeglass lens. When worn by a person, the glasses noticed the approach of eyelashes and identified when the wearer blinked Morse code for “E C U S T,” the abbreviation for the researchers’ institution. In the future, the researchers say their noncontact sensors could be used to help people who are unable to speak or use sign language communicate or even detect drowsiness when driving.
The authors acknowledge funding from Natural Science Foundation of China Grants, Shanghai Pilot Program for Basic Research, the “Chenguang Program” supported by the Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, National Key Research and Development Program of China, Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, and the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering.
The paper’s abstract will be available on May 22 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.4c02741
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Discoveries and progress in materials science often lay the foundation for technological breakthroughs that reshape many industrial and commercial fields, including medicine, consumer electronics, and energy generation, to name a few. Yet, the development of experimental techniques crucially underpins the exploration of new materials, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries. These techniques allow scientists to delve into a material’s chemical and physical properties, unlocking insights essential for realizing their potential applications.
In a recent study ...
Toronto, ON, May 22, 2024 – A new study published in the journal Psychological Medicine estimates that teens using cannabis are at 11 times higher risk of developing a psychotic disorder compared to teens not using cannabis.
This finding suggests that the association between cannabis and psychotic disorders may be stronger than indicated by previous research, which has relied largely on older data when cannabis was less potent than today. For context, the average THC potency of cannabis in Canada has increased from roughly 1% in 1980 to 20% in 2018.
Researchers from the University of Toronto, the Centre for Addiction and Mental ...
Background and objectives
Patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer (PCA) face the critical decision of whether to undergo treatment with curative intent (TCI, surgery or radiation) or conservative treatment on the background of a cancer where the potential for over-treatment and under-treatment is real. This study aimed to investigate the influence of cancer- and patient-related factors on the initial treatment decision for men with a new diagnosis of PCA and to evaluate treatment decisions against relevant guidelines.
Methods
This study undertook a retrospective ...
Background and objectives
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a cost-efficient technique for the management of thyroid nodules. Changes in the World Health Organization classification of thyroid tumors can influence reliability of cytology. The 2023 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology has adapted cytological nomenclature to these changes. The aim of this paper was to review the management of atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) in our institution.
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2771-165X/JCTP-2023-00062
Methods
Retrospective review of thyroid FNAC diagnosed with AUS in a single hospital between 2014 and 2022. We analyzed the management ...
As much as 70% of California was covered by wildfire smoke during parts of 2020 and 2021, according to a study from the University of California, Davis. The study, published today in the journal Communications: Earth & Environment, combined lake-based sensors with satellite imagery to find that maximum smoke cover has increased by about 116,000 square miles since 2006.
The study measured lake responses to wildfire smoke in 2018, 2020 and 2021 — the three largest fire seasons on record in California. It found the lakes were exposed ...
Embargoed for release: Wednesday, May 22, 2024, 5:00 AM ET
Key points:
In a large, multinational investigation of the link between extreme temperatures and stroke mortality, researchers found that of every 1,000 ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke deaths, about 11 were attributable to extreme cold and hot days.
The study also found that low-income countries bore a higher burden of heat-related hemorrhagic stroke mortality than high-income countries.
The researchers foresee an increase in fatal strokes, as well as a widening disparity ...
Osaka, Japan – Part of what makes us human is our ability to think about people, places, or events that aren’t currently present—but we still don’t know exactly how our brains do this. Now, researchers from Osaka University have identified a specific kind of brain activity linked with these kinds of thoughts, such as when we daydream or let our minds wander.
When we think about things that aren’t actually happening, like when we daydream, the brain is essentially making up information rather than receiving and ...
New research led by King’s College London has found that thousands of DNA sequences originating from ancient viral infections are expressed in the brain, with some contributing to susceptibility for psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression.
Published in Nature Communications, the study was part-funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre and the US National Institutes of Health (NIH).
About eight percent of our genome is comprised of sequences called Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs), which are products of ancient viral infections ...
The discovery of thousands of stone artefacts and animal bones in a deep cave in Timor Island has led archaeologists to reassess the route that early humans took to reach Australia.
Researchers from The Australian National University (ANU), Flinders University, University College London (UCL) and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Australian Biodiversity and Heritage dated and analysed the artefacts and sediment at the Laili rock shelter in central-north Timor-Leste, north of Australia, to pinpoint the arrival ...
Background and objectives
About 30% of lung cancer patients are accessible to targeted therapy or immunotherapy based on the current criteria. In this study, a novel gene cluster expression analysis was introduced with a goal to potentially expand the treatments to more patients based on the proposed criteria.
Methods
Selected gene expression omnibus data sets were downloaded, normalized, and analyzed. A univariate recurrence prediction model was built based on the receiver operating characteristic, for which an optimal cutoff was determined to set abnormality status, called ...