(Press-News.org) A research team has demonstrated for the first time a proof-of-concept tandem solar cell using antimony selenide as the bottom cell material and a wide-bandgap organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite material as the top cell material. The device achieved a power conversion efficiency of over 20 percent. This study shows that antimony selenide has great potential for bottom cell applications.
The research is published in the journal Energy Materials and Devices on March 4, 2024.
Photovoltaic technology, that harnesses sunlight and converts it into electricity, is popular because it provides a clean, renewable energy source. Scientists continue to work to improve the power conversion efficiency, or the measure of efficiency, in solar cells. They have achieved power conversion efficiencies of over 20 percent in conventional single-junction solar cells. To achieve power efficiency above the Shockley-Queisser limit in single-junction solar cells would require much greater costs. However, the Shockley-Queisser limit of single-junction solar cells can be overcome through the fabrication of tandem solar cells. With tandem solar cells, researchers are able to gain a higher energy efficiency by stacking solar cell materials on top of each other.
The research team worked to create tandem solar cells, using a semiconductor called antimony selenide. Past research with antimony selenide has focused mainly on applications in single-junction solar cells. But the research team knew that from a band gap perspective, this semiconductor might prove to be an appropriate bottom cell material for tandem solar cells.
“Antimony selenide is a suitable bottom cell material for tandem solar cells. However, because of the rarity of reported tandem solar cells using it as a bottom cell, little attention has been paid to its application. We assembled a tandem solar cell with high conversion efficiency using it as the bottom cell to demonstrate the potential of this material,” said Tao Chen, professor of Materials Science and Engineering at the University of Science and Technology of China. Tandem solar cells are better able to absorb sunlight than single junction solar cells that use a single layer of semiconductor material. The tandem solar cells convert a larger portion of sunlight into electricity, so they are more energy efficient than single junction solar cells.
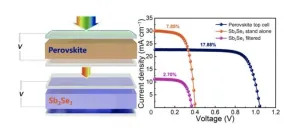
The team fabricated perovskite/antimony selenide tandem solar cells that have a transparent conducting electrode for an optimized spectral response. They were able to adjust the thickness of the transparent electrode layer of the top cell to obtain a high efficiency of greater than 17 percent. They optimized the antimony selenide bottom cell by introducing a double electron transport layer and achieved a power conversion efficiency of 7.58 percent.
When they mechanically assembled the top and bottom cells to create the four-terminal tandem solar cell, the power conversion efficiency exceeded 20.58 percent, which is higher than that of the independent subcells. Their tandem solar cell exhibits excellent stability with nontoxic compositional elements. “This work provides a new tandem device structure and demonstrates that antimony selenide is a promising absorber material for bottom cell applications in tandem solar cells,” said Chen.
Looking ahead, the team hopes to work toward a more integrated two-terminal tandem solar cell and further improve device performance. “The high stability of antimony selenide provides great convenience for the preparation of two-terminal tandem solar cell, which means that it may have good results when paired with quite a few different types of top cell materials.”
The research team includes Zhiyuan Cai, Huiling Cai, Yuehao Gu, Rongfeng Tang, Changfei Zhu, and Tao Chen from the University of Science and Technology of China, along with Jia Sun and Paifeng Luo from Hefei University of Technology.
This research is funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; National Natural Science Foundation of China; School-Local Cooperation Industrial Innovation Guidance Fund Key Project, Hefei University of Technology, China; Wuhu Major Engineering Application Project, China; and the Collaborative Innovation Program of Hefei Science Center, CAS.
About Energy Materials and Devices
Energy Materials and Devices is launched by Tsinghua University, published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, exclusively available via SciOpen, aiming at being an international, single-blind peer-reviewed, open-access and interdisciplinary journal in the cutting-edge field of energy materials and devices. It focuses on the innovation research of the whole chain of basic research, technological innovation, achievement transformation and industrialization in the field of energy materials and devices, and publishes original, leading and forward-looking research results, including but not limited to the materials design, synthesis, integration, assembly and characterization of devices for energy storage and conversion etc.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
This study is led by Professor Yan Wang (School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University (Naval Medical University), Shanghai, China). Her team found that the lack of MIR1 gene, which encodes mitochondrial phosphate carrier, can lead to severe virulence defects in Candida albicans.
In the Caenorhabditis elegans candidiasis model, the survival rate of the wild-type strain infected group dropped to about 20% at 120 h, while the survival rate of the mir1Δ/Δ-infected group remained about 90% at 120 h. Similar results were obtained in the murine model. None of the mice infected with mir1Δ/Δ mutant died during 21 days of ...
Spontaneous coagulation casting (SCC), a new type of colloidal forming process, has garnered significant attention since 2011 due to various advantages of a high bulk density and non-toxicity, as well as the ability to achieve dispersion and coagulation with very low additions (< 1 wt%) of copolymers of isobutylene and maleic anhydride (PIBM). Further research has revealed that the green bodies formed by this method are brittle, and the smaller the powder particle size used the more brittle the green bodies are. This paper reports ...
Background and Aims
Olaparib is a selective poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor. However, its clinical application is hindered by low solubility and undesired pharmacokinetic profiles (e.g., relatively short circulation). Therefore, the present study aims to exploit polymeric micelles as a safe solubilizer and nanocarrier of olaparib, in order to improve its solubility and pharmacokinetics.
Methods
Poly (ε-caprolactone)-co-poly (benzyl 5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylate), i.e., benzyl-functionalized trimethylene carbonate)-b-poly (ethylene glycol) (P(CL-co-TMC-Bz)-PEG), was synthesized by ring-opening polymerization, ...
Background and Aims
Clinical unmet need in managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a common liver disorder affecting 25–30% of American adults is to develop noninvasive and robust biomarkers.
Methods
We re-measured liver AC by placing a region of interest (ROI, 3 cm tall and 3 cm wide) at 4.5 cm, 6 cm, and 7.5 cm from the skin and a large ROI (6.0 cm tall and 7.3 cm wide) on pre-recorded ATI images from 117 participants screened for NAFLD. The difference in AC value at variable ROI depths was tested using one-way ANOVA (analysis of variance). Diagnostic ...
A new study – published in the Human-Animal Interactions journal – reveals that cows who are cuddled as therapy animals showed a strong preference for interactions with women when compared to men.
In turn, the research, which opens a new era on whether some therapies may be initially stronger based upon gender and not procedure, highlighted that the women also reported greater attachment behaviours towards the steers.
Dr Katherine Compitus, Clinical Assistant Professor at New York University, and Dr Sonya Bierbower, Associate Professor at United States Military Academy West Point, conducted the research using the ...
I’m not touching you! When another person’s finger hovers over your skin, you may get the sense that they’re touching you, feeling not necessarily contact, but their proximity. Similarly, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have designed a soft, flexible film that senses the presence of nearby objects without physically touching them. The study features the new sensor technology to detect eyelash proximity in blink-tracking glasses.
Noncontact sensors can identify or measure an object without directly touching it. Examples of these devices include ...
Discoveries and progress in materials science often lay the foundation for technological breakthroughs that reshape many industrial and commercial fields, including medicine, consumer electronics, and energy generation, to name a few. Yet, the development of experimental techniques crucially underpins the exploration of new materials, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries. These techniques allow scientists to delve into a material’s chemical and physical properties, unlocking insights essential for realizing their potential applications.
In a recent study ...
Toronto, ON, May 22, 2024 – A new study published in the journal Psychological Medicine estimates that teens using cannabis are at 11 times higher risk of developing a psychotic disorder compared to teens not using cannabis.
This finding suggests that the association between cannabis and psychotic disorders may be stronger than indicated by previous research, which has relied largely on older data when cannabis was less potent than today. For context, the average THC potency of cannabis in Canada has increased from roughly 1% in 1980 to 20% in 2018.
Researchers from the University of Toronto, the Centre for Addiction and Mental ...
Background and objectives
Patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer (PCA) face the critical decision of whether to undergo treatment with curative intent (TCI, surgery or radiation) or conservative treatment on the background of a cancer where the potential for over-treatment and under-treatment is real. This study aimed to investigate the influence of cancer- and patient-related factors on the initial treatment decision for men with a new diagnosis of PCA and to evaluate treatment decisions against relevant guidelines.
Methods
This study undertook a retrospective ...
Background and objectives
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a cost-efficient technique for the management of thyroid nodules. Changes in the World Health Organization classification of thyroid tumors can influence reliability of cytology. The 2023 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology has adapted cytological nomenclature to these changes. The aim of this paper was to review the management of atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) in our institution.
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2771-165X/JCTP-2023-00062
Methods
Retrospective review of thyroid FNAC diagnosed with AUS in a single hospital between 2014 and 2022. We analyzed the management ...