Mistaken identity cleared up of foodborne pathogen causing severe symptoms in children
Novel real-time PCR method might become diagnostic tool targeting emerging bacterium responsible for food poisoning outbreaks
2024-05-23
(Press-News.org) The prevalence of pathogenic E. coli has meant the frequent misidentification of a similar bacterium of the Escherichia genus. E. albertii is an emerging zoonotic foodborne pathogen, first isolated in Bangladesh in 1991. Large-scale outbreaks of food poisoning caused by E. albertii have since been reported especially in Japan, causing severe symptoms in both children and adults.
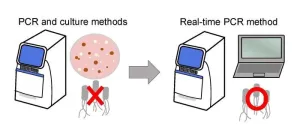
In the hopes of establishing a diagnostic method, a joint research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki and Dr. Sharda Prasad Awasthi, a specially appointed associate professor, from the Graduate School of Veterinary Science at Osaka Metropolitan University, have developed a way to detect E. albertii more accurately using a quantitative real-time PCR method.
Specimen examination using this technique showed that E. albertii survived in the human intestinal tract for approximately four weeks and continued to be found in feces. The identical genotype of the bacterial DNA of E. albertii that infected siblings also suggested that intrafamilial transmission may have occurred.
“These results and a novel real-time PCR developed in this study are expected to contribute not only to the selection of appropriate treatment for E. albertii gastroenteritis, but also to the elucidation of the source and route of infection,” Professor Yamasaki declared.
The findings were published in Heliyon.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-23
An exploration into the national U.S. dataset on children ever diagnosed with ADHD has revealed an “ongoing and ever-expanding” public health issue.
Findings published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology uncover that approximately one million more children, aged 3-17, had received an ADHD diagnosis in 2022 than in 2016.
The paper reveals around one in nine children have ever received an ADHD diagnosis – 11.4%, ...
2024-05-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio (May 23, 2024) — Positive sports experiences can be a game changer for kids, with physical, social, emotional and mental health benefits that last a lifetime, according to a new survey from The Kids Mental Health Foundation. However, youth mental health advocates with The Kids Mental Health Foundation stress the importance of ongoing conversations with young athletes about how their sports are impacting their confidence, self-esteem and happiness, whether it’s positive or negative.
The national survey conducted by Ipsos on behalf of The Kids Mental Health Foundation finds parents overwhelmingly ...
2024-05-23
A study from the University of Adelaide has discovered molecular pathways regulated by a gene traditionally used to control wheat-flowering behaviour could be altered to achieve greater yields.
The gene is called Photoperiod-1 (Ppd-1) and it is used regularly by breeders to ensure wheat crops flower and set grain earlier in the season, avoiding the harsh conditions of summer. However, there are known drawbacks.
“While this variation benefits wheat productivity by aligning pollination and grain development with more favourable environmental conditions, it also penalises yield by reducing the number of ...
2024-05-23
An increasing number of emerging quantum applications operate using optical technologies. Essentially, photons carry information at the speed of light and over long distances, making them good candidates for fast and secure communications and quantum computing. Many of these applications require photons that are identical (indistinguishable). When the photons are not identical, it can lead to errors in the data and quantum technologies become less reliable.
Currently, quantum photon sources are regularly taken offline to be tested and adjusted using ...
2024-05-23
A new study led by Griffith University predicts that future climate change impacts could disrupt the krill-heavy diet that humpback whales in the southern hemisphere consume.
Dr Jasmin Groß, who conducted the study as a PhD candidate at Griffith’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security analysed fatty acids and stable isotopes from blubber and skin samples of five different humpback whale populations around the southern hemisphere.
These levels were then compared to those of their primary prey item, Antarctic krill.
The team found that although there were distinct differences in the biochemical profiles, the diet of all tested ...
2024-05-23
The rapid development of electronic technology has resulted in the annual phase-out of a large amount of waste electrical and electronic equipment, known as “e-waste,” especially in developed countries. In the context of economic globalization, the lack of relevant environmental laws and policies in developing countries and less developed countries, as well as cheap labor, has attracted developed countries to export a large amount of domestic e-waste to these countries. The chemicals produced during the low-tech dismantling process enter the air, soil, and deep groundwater, contaminating ...
2024-05-23
A team of researchers from the University of Chicago has been named winners of the 2024 NSF CISE Expedition Program for their part in the proposal of computational decarbonization (CoDec). This prestigious award, granted by the National Science Foundation (NSF), underscores the groundbreaking potential of CoDec in revolutionizing societal decarbonization through computational innovation.
As the largest research award within the NSF's Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE) directorate, the Expeditions in Computing program recognizes pioneering endeavors poised to make profound impacts on both scientific understanding and societal advancement. The CoDec ...
2024-05-23
Having an epidural during labour is associated with a marked reduction in serious complications in the first few weeks after giving birth, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
Doctors refer to these complications as severe maternal morbidity (SMM), which can include heart attack, heart failure, sepsis, and hysterectomy.
Epidural analgesia is recommended for women with known risk factors for SMM, such as obesity, certain underlying conditions, or having more than one baby. These women are said to have a ‘medical indication’ for epidural analgesia in labour. Women delivering prematurely ...
2024-05-23
Plans to devolve responsibility for the quality of England’s 11 national screening services could result in significant safety risks, experts tell The BMJ in an exclusive report today.
Assistant news editor Gareth Iacobucci explains that NHS England is currently discussing proposals to delegate some of the functions of the national Screening Quality Assurance Service (SQAS) from NHSE to regional Integrated Care Boards (ICBs).
But concerned experts warn that devolving responsibility to local organisations will spread resources more thinly, lead to a loss of expertise and independence, and compromise ...
2024-05-22
Though most online dating apps have a minimum age requirement of 18 years, a new study finds a small number of 11 to 12 year-olds use them. Lesbian, gay, and bisexual (LGB) preteens are 13 times more likely to report engaging in online dating compared to their heterosexual peers.
“Lesbian, gay, or bisexual adolescents, including preteens, may have limited romantic partner options in their schools, where they may also face discrimination, bullying, and stigma because of their sexual orientation,” says lead author Jason Nagata, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mistaken identity cleared up of foodborne pathogen causing severe symptoms in children
Novel real-time PCR method might become diagnostic tool targeting emerging bacterium responsible for food poisoning outbreaks