Autophagy in pancreatitis
2024-05-24
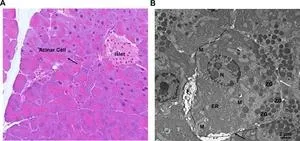
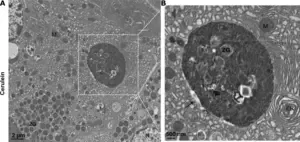
(Press-News.org) Researchers are exploring a new potential avenue for pancreatitis treatment: autophagy, a cellular recycling process. Autophagy helps maintain healthy pancreatic acinar cells by removing damaged organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
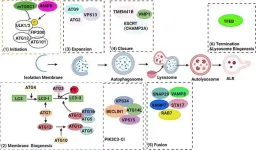
A new review published in eGastroenterology highlights the link between defective autophagy and pancreatitis. Impaired autophagy contributes to pancreatitis by allowing damaged organelles to accumulate within acinar cells. This accumulation disrupts cellular function and can ultimately lead to cell death.
"Autophagy plays a vital role in keeping pancreatic acinar cells healthy," explains Dr. Wen-Xing Ding, lead author of the study. "When autophagy is defective, damaged organelles build up, stressing the cells and potentially contributing to pancreatitis."
The review also explores the role of mitochondrial dysfunction and lysosomal dysfunction in pancreatitis. Mitochondria are the cell's powerhouses, and lysosomes are the compartments responsible for breaking down cellular waste. Both mitochondrial damage and impaired lysosomal function are observed in pancreatitis, further hindering the cell's ability to clear out damaged components.
The research team identified several potential therapeutic targets within the autophagy pathway. VMP1, a protein involved in both autophagy and ER-phagy (removal of damaged ER), is downregulated in pancreatitis. TFEB, a master regulator of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy, is also decreased. Additionally, alcohol consumption disrupts autophagy by increasing ATG4B, a protease that regulates LC3-II, a key autophagy protein.
"Animal studies suggest that manipulating these proteins can influence the severity of pancreatitis," Dr. Wen-Xing Ding says." Upregulating VMP1 or TFEB, or downregulating ATG4B, enhances autophagy and protects against pancreatitis."
While further research is needed, targeting autophagy may offer a novel therapeutic approach for pancreatitis. Future studies will focus on the specific role of autophagy receptors in targeting damaged organelles during pancreatitis and the potential for manipulating autophagy to treat the disease in humans.
See the article:
Ding W-X, Ma X, Kim S, et al. Recent insights about autophagy in pancreatitis. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100057. doi:10.1136/egastro-2023-100057
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-24
In the early 2010s, LightSquared, a multibillion-dollar startup promising to revolutionize cellular communications, declared bankruptcy. The company couldn’t figure out how to prevent its signals from interfering with those of GPS systems.
Now, Penn Engineers have developed a new tool that could prevent such problems from ever happening again: an adjustable filter that can successfully prevent interference, even in higher-frequency bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
“I ...
2024-05-24
TAMPA, Fla. (May 24, 2024) – Through high-tech imaging and virtual reality, a University of South Florida medical engineering professor is creating a detailed map of the brain that can be used to better understand developmental disorders, such as autism, and provide earlier, more effective treatments for brain injuries and diseases.
Funded by a $3.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, George Spirou is expanding on his four decades of brain research to focus on the part of the brain that ...
2024-05-24
Semaglutide significantly reduces risk of major kidney disease events, cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, groundbreaking study reveals
A pioneering study has demonstrated that semaglutide significantly reduces the risk of major kidney disease events, cardiovascular outcomes, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.1 The landmark trial, presented today at the 61st ERA Congress, will pave the way for new treatment strategies and ...
2024-05-24
Enhancing drug development for life-threatening diseases like cancer hinges on a deep understanding of protein kinases, making it a focal point for researchers. These enzymes, encoded by more than 500 human genes, serve as critical players in cellular signaling pathways. However, if these signals are dysregulated, they can disrupt the normal cellular mechanisms, leading to diseases such as cancer. Protein kinase inhibitors have therefore provided a promising avenue in therapeutic intervention to disrupt the aberrant signaling ...
2024-05-24
In recent years, global environmental concerns have prompted a shift toward eco-friendly manufacturing in the field of organic synthetic chemistry. In this regard, research into photoredox catalytic reactions, which use light to initiate redox or reduction-oxidation reactions via a photoredox catalyst, has gained significant attention. This approach reduces the reliance on harsh and toxic reagents and uses visible light, a clean energy source.
A key research area has been the development of recycling methods for photocatalysts, which offer both economic and environmental benefits. Photocatalysts use light to accelerate a chemical reaction without getting consumed in the process, and photoredox ...
2024-05-24
Researchers have developed a method to make adaptive and eco-friendly sensors that can be directly and imperceptibly printed onto a wide range of biological surfaces, whether that’s a finger or a flower petal.
The method, developed by researchers from the University of Cambridge, takes its inspiration from spider silk, which can conform and stick to a range of surfaces. These ‘spider silks’ also incorporate bioelectronics, so that different sensing capabilities can be added to the ‘web’.
The fibres, at least 50 times smaller than a ...
2024-05-24
Splash a few drops of water on a hot pan and if the pan is hot enough, the water will sizzle and the droplets of water seem to roll and float, hovering above the surface.
The temperature at which this phenomenon, called the Leidenfrost effect, occurs is predictable, usually happening above 230 degrees Celsius. The team of Jiangtao Cheng, associate professor in the Virginia Tech Department of Mechanical Engineering, has discovered a method to create the aquatic levitation at a much lower temperature, and the results have been published in Nature ...
2024-05-24
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have fabricated a device no wider than a human hair that will help physicists investigate the fundamental nature of matter and light. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, could also support the development of more efficient lasers, which are used in fields ranging from medicine to manufacturing.
The device is made of a special kind of material called a photonic topological insulator. A photonic topological insulator can guide photons, the wave-like particles that make up light, ...
2024-05-24
The study, a collaboration between researchers at Imperial College London and GNS Science, suggests that reducing plastic pollution by 5% per year would stabilize the level of microplastics – plastics less than 5 mm in length – in the surface oceans.
However, the modelling shows that even reducing pollution by 20% per year would not significantly reduce existing microplastics levels, meaning they will persist in our oceans beyond 2100.
Microplastics have been found to be circulating in all of the Earth’s oceans and some of the greatest concentrations of them are thousands of miles from land. These tiny particles ...
2024-05-24
The DRIVE-RM consortium, led by Professor of Experimental Nephrology Marianne Verhaar from UMC Utrecht, has been awarded €37.5 million under the prestigious NWO SUMMIT program. The SUMMIT grant recognizes world-class collaborations, while further strengthening these partnerships. The DRIVE-RM collaboration involves UMC Utrecht, Utrecht University, Eindhoven University of Technology, Maastricht University, and the Hubrecht Institute, focusing on smart materials that assist the body in healing.
Regenerative medicine involves repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs by leveraging the body's own healing processes. DRIVE-RM ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Autophagy in pancreatitis