Climate change is moving tree populations away from the soil fungi that sustain them
2024-05-27
(Press-News.org) As our planet warms, many species are shifting to different locations as their historical habitats become inhospitable. Trees are no exception – many species’ normal ranges are no longer conducive to their health, but their shift to new areas that could better sustain them has been lagging behind those of other plants and animals. Now, scientists show that the reason for this lag might be found belowground. A study published in PNAS on May X, shows that trees, especially those in the far north, may be relocating to soils that don’t have the fungal life to support them.
Most plants form belowground partnerships with mycorrhizal fungi, microscopic, filamentous fungi that grow in the soil and connect with plant roots to supply plants with critical nutrients in exchange for carbon. Most large coniferous trees in northern latitudes form relationships with a kind of mycorrhizal fungi called ectomycorrhizal fungi.
“As we examined the future for these symbiotic relationships, we found that 35% of partnerships between trees and fungi that interact with the tree roots would be negatively impacted by climate change,” says lead author Michael Van Nuland, a fungal ecologist at the Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN).
The trees most at risk of this climate mismatch in North America are those in the pine family, find the authors. Areas of particular concern are the edges of species ranges where trees often face the harshest conditions. Here, the authors discovered that trees with higher survival rate in these locations have more diverse mycorrhizal fungi, a sign that these symbioses may be critical for helping trees withstand the effects of climate change.
“Ectomycorrhizal fungi have a different relationship to climate than ectomycorrhizal trees do,” says co-author Clara Qin, a data scientist at SPUN. “We are finding evidence that the trees have to answer for these differences.”
The study sheds light on how climate change might be affecting symbioses. “While we expect climate-driven migrations to be limited by abiotic factors like the availability of space at higher latitudes and elevations, we don't usually account for biotic limitations like the availability of symbiotic partners,” says Qin.
“It’s absolutely vital that we continue to work to understand how climate change is affecting mycorrhizal symbioses,” says Van Nuland. “These relationships underpin all life on Earth – it’s critical that we understand and protect them.”
***
Download the full paper here.
This research was funded by a National Science Foundation grant awarded to Kai Zhu and Kabir Peay (NSF Awards 1926438, 2244711)
PNAS, Van Nuland et al., “Climate mismatches with ectomycorrhizal fungi contribute to migration lag in North American tree range shifts”
The Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN) is a scientific research organization with a mission to map and preserve Earth’s fungal networks. In collaboration with researchers and local communities, SPUN is accelerating efforts to protect the underground ecosystems largely absent from conservation and climate agendas. To learn more about SPUN, visit: https://spun.earth/.
Author Contacts:
Michael Van Nuland
Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN)
michael@spun.earth
Clara Qin
Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN)
clara@spun.earth
Kabir Peay
Department of Biology, Stanford University
kpeay@stanford.edu
Kai Zhu
Institute for Global Change Biology and School for Environment and Sustainability, University of Michigan
zhukai@umich.edu
Media Contact:
Kelcie Walther
Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN)
kelcie@spun.earth
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-27
Researchers have been working to track and study floating sargassum, a prolific seaweed swamping Caribbean and West African shorelines, and causing environmental and economic harm.
The stranded seaweed blocks fishing boats; threatens tourism; disrupts turtle nesting sites, reefs and mangroves, and releases toxic gas, which impacts human health and damages electrical equipment.
First reported by Christopher Columbus in the 15th century, floating mats of sargassum have long been present in the North Atlantic. However, since 2011, a floating population has established ...
2024-05-27
Of the many perils facing members of the military, injuries incurred in training or on deployment repeatedly sideline elite operators.
“It’s a pervasive problem,” says Dhruv Seshadri, an assistant professor of bioengineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science. “We’re looking at how we can integrate physiological data, biomechanical data, and subjective assessments to help reduce the risk of these injuries happening in the first place, and when they do happen, how we can use those data to accelerate the soldier’s return to operation.”
Seshadri ...
2024-05-27
No two volcanic eruptions are exactly alike, but scientists think a series of explosive eruptions at Kīlauea volcano fit into a whole new category.
By analyzing the dynamics of 12 back-to-back explosions that happened in 2018, researchers describe a new type of volcanic eruption mechanism. The explosions were driven by sudden pressure increases as the ground collapsed, which blasted plumes of rock fragments and hot gas into the air, much like a classic stomp-rocket toy.
Researchers from the University of Oregon, United States Geological Survey and China’s Sichuan University report their findings in a paper published May 27 in Nature Geoscience.
The ...
2024-05-27
While recent reports have stated that more than half the world’s largest lakes, including lakes in the Tibetan plateau, are drying up, a paper in Nature Geoscience today (27/5/24 DOI 10.1038/s41561-024-01446-w ) suggests that, by the end of this century, land-locked lakes on the Tibetan Plateau are set to increase exponentially, resulting in major land loss and related economic, environmental and climatic impacts.
Climate and weather predictions suggest that increased rainfall due to climate change will enlarge these lakes, and see water levels rise by up to 10 metres.
The volume of water caught in these land-locked lakes is estimated to ...
2024-05-27
Feeding children peanuts regularly from infancy to age five reduced the rate of peanut allergy in adolescence by 71%, even after many years when the children ate or avoided peanut as desired.
The new findings provide conclusive evidence that introducing peanuts into babies’ diets early will achieve long-term prevention of peanut allergy.
Lead investigator Professor Gideon Lack from King’s College London said: “Decades of advice to avoid peanuts has made parents fearful of introducing peanuts at an early age. The evidence is clear that early introduction of peanut in infancy ...
2024-05-27
Why do people in Paris like seaweed and tofu salad? Will Italians be tempted to try a beetle skewer? How many young Polish consumers are "food innovators", eager to eat chickpea pâté? In an international project, researchers from SWPS University analysed European consumers' attitudes towards alternative protein food products.
In the face of the fight against climate change, more and more people are modifying their diets, giving up or limiting conventional sources of protein (e.g., beef, pork, poultry, and animal dairy) in favour of those with a lower environmental impact. These are the so-called alternative protein food (APF) products, which may be based on ...
2024-05-27
ETRI research team has won a main prize at the German International Design Competition, one of the top three design award competitions in the world. This signifies global recognition of our research team’s technology.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that its Teach Pendant software for the autonomous mobile collaborative robot (MOBY1)) won the main prize in the User Experience (UX2)) category at the ‘iF Design Award 20243)’, an international design competition in Germany.
1) MOBY: Equipped with the AI-based vision solution ‘IndyEye’ and the ...
2024-05-27
Reducing carbon emissions from small-scale combustion systems, such as boilers and other industrial equipment, is a key step towards building a more sustainable, carbon-neutral future. Boilers are widely used across various industries for essential processes like heating, steam generation, and power production, making them significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions.
Boilers are generally quite efficient. As a result, it is difficult to reduce CO2 emissions simply by improving the combustion efficiency. Therefore, researchers are exploring alternative approaches to mitigating the environmental ...
2024-05-27
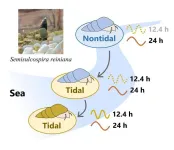
Organisms, including humans, follow a schedule that coordinates important bodily functions such as sleep-wake cycles, metabolism, hormone production, cognitive function, and feeding habits to environmental cycles. While most organisms possess circadian rhythms synchronized with the 24-hour day-night cycle, they have also developed other internal clocks to suit their local environments. Marine animals have evolved circatidal rhythms, aligning activities with the 12.4-hour tidal cycle, complementing circadian rhythms.
Researchers from Chiba University have discovered that snails living in downstream tidal areas have biological ...
2024-05-27
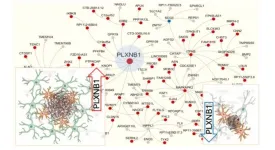
New York City, [May 27, 2024] – Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have made a significant breakthrough in Alzheimer’s disease research by identifying a novel way to potentially slow down or even halt disease progression. The study, which focuses on the role of reactive astrocytes and the plexin-B1 protein in Alzheimer's pathophysiology, provides crucial insights into brain cell communication and opens the door to innovative treatment strategies. It was published in Nature Neuroscience (DOI 10.1038/s41593-024-01664-w) on May 27.
This groundbreaking work is centered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Climate change is moving tree populations away from the soil fungi that sustain them