(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — May 28, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute has created a comprehensive data analysis tool to help metropolitan areas curb urban heat islands (UHIs) and pursue mitigation methods for especially vulnerable populations. This internally funded project was a collaboration with the City of San Antonio.
UHIs occur when dense concentrations of pavement and buildings absorb heat and raise surrounding temperatures. Without green spaces to provide a cooling effect, UHI temperatures can exceed other areas by as much as 20 degrees Fahrenheit, which could be dangerous to residents during summer.
“Tackling UHIs goes beyond simply analyzing spatial temperature differences,” said SwRI Senior Environmental Engineer Justin Long. “A comprehensive analysis of UHIs must also identify vulnerable populations, as well as viable mitigation methods in the areas where they reside.”
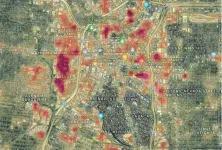
SwRI has created a data fusion tool that compiled and combined more than 230 datasets collected from several different city departments and public databases. The tool allows city leaders to analyze and explore several scenarios at once.
“Before the City of San Antonio can prioritize resources to address UHIs, it needs to identify all their characteristics, particularly zones where conditions are the most severe and that have a direct impact on the public,” Long said. “We discovered, for example, that many areas that experience extreme heat are also zones with historically high bus ridership. On hot summer days, pedestrians in these areas may be at higher risk of prolonged heat exposure and related illnesses.”
The tool could show city leaders where bus stops and high surface temperatures overlap and locations where planting trees or erecting artificial structures to mitigate the heat could be most effective.
To demonstrate how the data fusion tool could inform UHI policy making, SwRI created a hypothetical case study, merging multiple datasets from different sources for comparison. The scenario focused on locating regions with concentrated UHI effects that could pose a health hazard to bus riders and reduce the use of public transportation. Equipped with this knowledge, city officials could select locations to implement UHI mitigation strategies based on local socioeconomic, environmental and infrastructure characteristics.
“Mitigation strategies must be tailored to the specific characteristics of locations experiencing extreme heat from UHIs,” Long said. “The tool integrates data from multidisciplinary sources and enables users to rapidly identify candidate sites for mitigation strategies.”
While the tool was developed to address UHI, SwRI is working with the City of San Antonio to explore ways it can address other challenges as well. This project is one of many UHI-related studies that are part of a collaboration between SwRI, the City of San Antonio and The University of Texas at San Antonio.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/industries/fluids-engineering.
END
SwRI data fusion tool targets urban heat islands in San Antonio
Internally funded project uses more than 230 datasets to provide comprehensive view of socio-economic impacts of hot spots
2024-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does the requirement to offer retirement plans help workers save for retirement?
2024-05-28
A study published in Contemporary Economic Policy reveals significant benefits gained from the first implementation of the state-run retirement savings program in Oregon, known as OregonSaves, in 2017.
OregonSaves is available to Oregon workers whose employers do not offer a workplace retirement plan, self-employed individuals, and others. Businesses that do not offer retirement plans are required to automatically enroll employees, but workers can opt out at any time.
The analysis found that the program substantially boosted retirement savings among previously ...
Apple versus donut: How the shape of a tokamak impacts the limits of the edge of the plasma
2024-05-28
Harnessing energy from plasma requires a precise understanding of its behavior during fusion to keep it hot, dense and stable. A new theoretical model about a plasma’s edge, which can become unstable and bulge, brings the prospect of commercial fusion power closer to reality.
“The model refines the thinking on stabilizing the edge of the plasma for different tokamak shapes,” said Jason Parisi, a staff research physicist at PPPL. Parisi is the lead author of three articles describing the model that were published in the journals Nuclear Fusion and Physics of Plasma. The primary paper focuses on a part of the plasma called ...
Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, receives prestigious award from World Heart Federation
2024-05-28
The World Heart Federation (WHF) is honoring Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, President of Mount Sinai Heart and Physician-in-Chief of The Mount Sinai Hospital, with its Lifetime Achievement Award for 2024. This top honor recognizes his remarkable contributions to the WHF mission, and to the entire cardiovascular disease community for his dedication to combating this disease worldwide.
The WHF will present Dr. Fuster with this award on Saturday, May 25, during the World Heart Summit in Geneva, Switzerland.
“I am proud of this award, particularly because it represents Mount Sinai’s worldwide scientific contributions and dedication to advancements in the cardiovascular ...
Nonlinear photochromic properties in a perylene-substituted rhodamine spirolactam
2024-05-28
Photochromic compounds, which change their color when exposed to light, have been widely used as photoswitches to control different properties of materials. Nonlinear photochromic compounds, characterized by a nonlinear response to the intensity of incident light, have attracted special attention among researchers as the nonlinearity leads to enhanced contrast and improved spatial resolution in photochromic reactions. It also allows for multiple photochromic properties in a single molecule with a single light source. These qualities have made them valuable in nonlinear optical and holographic elements, super-resolution microscopy, and biomedical applications.
The simplest ...
Binge-eating disorder not as transient as previously thought
2024-05-28
BELMONT, Mass. (May 28, 2024) Binge-eating disorder is the most prevalent eating disorder in the United States, but previous studies have presented conflicting views of the disorder’s duration and the likelihood of relapse. A new five-year study led by investigators from McLean Hospital, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, showed that 61 percent and 45 percent of individuals still experienced binge-eating disorder 2.5 and 5 years after their initial diagnoses, respectively. These results contradict previous ...
Pharmacists prove effective, less costly care option for minor illnesses
2024-05-28
SPOKANE, Wash. – Greater use of pharmacists to treat minor illnesses could potentially save millions of dollars in health care costs, according to new research led by Washington State University. The findings also indicate a way to improve healthcare access by expanding availability of pharmacists’ clinical services including prescribing medications, amid an ongoing shortage of primary care providers.
The study found that care for a range of minor health issues – including urinary tract infections, shingles, animal bites and headaches – costs an average of about $278 less when treated in pharmacies compared to patients with similar ...
Inexpensive microplastic monitoring through porous materials and machine learning
2024-05-28
Optical analysis and machine learning techniques can now readily detect microplastics in marine and freshwater environments using inexpensive porous metal substrates. Details of the method, developed by researchers at Nagoya University with collaborators at the National Institute for Materials Sciences in Japan and others, are published in the journal Nature Communications.
Detecting and identifying microplastics in water samples is essential for environmental monitoring but is challenging due in part to the structural similarity of microplastics with natural organic compounds derived from biofilms, algae, and decaying organic matter. Existing detection methods ...
Mystery of ‘slow’ solar wind unveiled by Solar Orbiter mission
2024-05-28
Scientists have come a step closer to identifying the mysterious origins of the ‘slow’ solar wind, using data collected during the Solar Orbiter spacecraft’s first close journey to the Sun.
Solar wind, which can travel at hundreds of kilometres per second, has fascinated scientists for years, and new research published in Nature Astronomy, is finally shedding light on how it forms.
Solar wind describes the continuous outflow of charged plasma particles from the Sun into space – with wind travelling at over 500km ...
Study suggests ‘biodegradable’ teabags don’t readily deteriorate in the environment and can adversely affect terrestrial species
2024-05-28
Some teabags manufactured using plastic alternatives do not degrade in soil and have the potential to harm terrestrial species, a new study has shown.
The research looked at commonly available teabags made using three different compositions of polylactic acid (PLA), which is derived from sources such as corn starch or sugar cane.
The teabags were buried in soil for seven months, and a range of techniques were then used to assess whether – and to what extent – they had deteriorated.
The results showed that teabags made solely from PLA remained completely intact. However, the ...
Algorithms could help improve judicial decisions
2024-05-28
A new paper in the Quarterly Journal of Economics, published by Oxford University Press, finds that replacing certain judicial decision-making functions with algorithms could improve outcomes for defendants by eliminating some of the systemic biases of judges.
Decision makers make consequential choices based on predictions of unknown outcomes. Judges, in particular, make decisions about whether to grant bail to defendants or how to sentence those convicted. Companies now use machine learning based models increasingly in high-stakes decisions. There are various assumptions about human behavior underlying the deployment of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
Mayo Clinic installs first magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia system for cancer research in the US
Calibr-Skaggs and Kainomyx launch collaboration to pioneer novel malaria treatments
JAX-NYSCF Collaborative and GSK announce collaboration to advance translational models for neurodegenerative disease research
Classifying pediatric brain tumors by liquid biopsy using artificial intelligence
Insilico Medicine initiates AI driven collaboration with leading global cancer center to identify novel targets for gastroesophageal cancers
Immunotherapy plus chemotherapy before surgery shows promise for pancreatic cancer
A “smart fluid” you can reconfigure with temperature
New research suggests myopia is driven by how we use our eyes indoors
Scientists develop first-of-its-kind antibody to block Epstein Barr virus
With the right prompts, AI chatbots analyze big data accurately
Leisure-time physical activity and cancer mortality among cancer survivors
Chronic kidney disease severity and risk of cognitive impairment
Research highlights from the first Multidisciplinary Radiopharmaceutical Therapy Symposium
New guidelines from NCCN detail fundamental differences in cancer in children compared to adults
Four NYU faculty win Sloan Foundation research fellowships
[Press-News.org] SwRI data fusion tool targets urban heat islands in San AntonioInternally funded project uses more than 230 datasets to provide comprehensive view of socio-economic impacts of hot spots