(Press-News.org) Among fathers, heart health was worse for men who became fathers under the age 25
First U.S. multiethnic longitudinal study to analyze cardiovascular health outcomes of fathers
Results differed by race and ethnicity subgroups
Age-adjusted rate of death for Black fathers was lower than for nonfathers
‘Fatherhood may be protective for Black men’
CHICAGO --- Heart disease is the leading cause of death among men, and being a father may put men at an even greater risk of poor heart health later in life, reports a new study from scientists at Northwestern University and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
The study of 2,814 men between the ages of 45 and 84 found cardiovascular health in older age was worse for fathers compared to nonfathers. Study participants’ heart health was rated based on their diet, physical activity, smoking habits, weight, blood pressure, and level of lipids and glucose in their blood.
“The changes in heart health we found suggest that the added responsibility of childcare and the stress of transitioning to fatherhood may make it difficult for men to maintain a healthy lifestyle, such as a healthy diet and exercise,” said corresponding author Dr. John James Parker, an internist, pediatrician and assistant professor of pediatrics and general internal medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
“We really need to study fathers as a unique population and track men’s health outcomes as they become fathers. Cardiovascular health is especially important since the health behaviors and factors are all modifiable.”
The study was published as a peer-reviewed preprint earlier this month in the journal AJPM Focus with a more finalized version publishing soon.
Fathers have worse heart health but lower death rates
Despite fathers in the study having worse hearth health in older age, the study found they actually have lower rates of death than nonfathers. Parker said this conflicting association could be because fathers may have a more robust social support system, and social connectedness has been linked with lower mortality.
“Fathers may also be more likely to have someone as their future caretaker (i.e., their children) to help them attend medical appointments and manage medications and treatments as they get older,” Parker said. “We also found that fathers had lower rates of depressive symptoms than nonfathers, so mental health may be contributing to the lower age-adjusted death rates in fathers.”
The study included men who self-identified as Black, Chinese, Hispanic or White, and the age-adjusted rate of death for all Black fathers was lower than for Black nonfathers, the only racial and ethnic subgroup with this association.
“Fatherhood may be protective for Black men,” Parker said. “Maybe becoming a father helps promote a healthy lifestyle for Black men. Studying this association further could have important public health implications.”
Previous studies that evaluated fatherhood, cardiovascular health, cardiovascular disease and mortality have not included racially and ethnically diverse populations and lacked comprehensive cardiovascular health evaluation. This study is novel because it included men from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).
This study also examined influence of the age men transition to fatherhood on heart health and disease outcomes. Interestingly, men who became at younger ages (25 years old and younger) — especially Black and Hispanic men — had worse heart health and high death rates and may benefit from focused clinical and public health attention.
“If you’re under 25, you may be less financially stable, your brain may be less mature, and, especially for racial and ethnic minorities, you may have lower-paying jobs with fewer benefits and limited leave policies,” Parker said. “All of this can make it harder to focus on your health. There are a lot of public health interventions for young mothers, but no one has ever really looked at young fathers in this way.”
‘A father’s health has a major influence on their family’
Since most men in the U.S. are fathers, identifying some of the explanations for the associations among health, disease and fatherhood could have important health implications for men, especially for men of color, the scientists said.
“A lot of times we focus on the health of mothers and children, and we don’t even think of fathers, but their health has a major influence on their family,” said Parker, citing previous research that found higher obesity rates among partners if their spouse was obese. “To improve the health of families, we need to consider the multi-directional relationship among mothers, fathers, other caregivers and children.”
The study also found a higher smoking rate among fathers, which Parker said is surprising because other studies have shown many fathers quit smoking when they have kids.
“This study looked at older fathers, so it’s possible men might quit smoking when they become fathers but then later, maybe they become more stressed and take up the habit again,” Parker said. “Either way, we should look at what’s happening with smoking rates because smoking is a leading cause of preventative death and if a father is smoking it will influence their families as well.”
The scientists defined study participants’ cardiovascular health using the American Heart Association Life's Essential 8 scores (excluding sleep). Men were categorized as either fathers (82% study participants) or nonfathers based on an interview in which participants were asked to list any children's ages and medical conditions. Men who did not list any children were categorized as nonfathers.
Other Northwestern study authors include Dr. Craig Garfield, Clarissa Simon, Laura Colangelo and Norrina Allen.
END
“This consideration could be the starting point to study whether Silibinin could contrast tumor progression, aging and inflammaging through molecular and cellular mechanisms [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 28, 2024 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 23, 2024, entitled, “The importance of integrated therapies on cancer: Silibinin, an old and new molecule.”
In this new review, researchers Elisa Roca, Giuseppe Colloca, Fiorella Lombardo, Andrea Bellieni, Alessandra Cucinella, Giorgio Madonia, Licia Martinelli, Maria Elisa Damiani, Ilaria Zampieri, and ...
A pioneering study has used extensive global datasets and machine learning to map the activities of seafloor invertebrate animals, including worms, clams and shrimps, across the entire ocean, revealing for the first time critical factors that support and maintain the health of marine ecosystems.
The international team, led by Texas A&M University and including investigators from Yale University and the University of Southampton, specifically focused on the unsung yet vital role burrowing animals play as "ecosystem engineers" in shaping nutrient ...
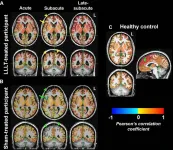
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Low-level light therapy appears to affect healing in the brains of people who suffered significant brain injuries, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Lights of different wavelengths have been studied for years for their wound-healing properties. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) conducted low-level light therapy on 38 patients who had suffered moderate traumatic brain injury, an injury to the head serious enough to alter cognition and/or be visible on a brain scan. Patients received ...
Background and Goal: Team-based care is considered the gold standard in delivery models. It uses integrated clinical teams with diverse skills and perspectives to provide efficient, high-quality health care services. Within these teams, individuals from minoritized racial-ethnic groups, often referred to as persons of color (POC), typically occupy roles with less authority (e.g., medical assistants), while white individuals more frequently hold positions of greater power (e.g., physicians). Few studies have explored the viewpoints of staff members in lower-power roles, who are disproportionately POC and constitute the majority of a health care team. This study aims to ...
NRG Oncology (NRG), a National Cancer Institute (NCI) National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) group focused on improving outcomes for adults with cancer through multi-center clinical research, recently announced two new Vice-Chairs to co-lead the NRG Patient Advocate Committee (PAC) alongside the current PAC Committee Chair, Dorothy Erlanger.
Marlyn Molero, was appointed as Vice-Chair of the NRG PAC. Marlyn is a clinical researcher in the oncology area with Commonspirit Research Institute as well as a Spanish interpreter at Vituity. Marlyn brings a unique perspective to the NRG PAC leadership ...
The toe tapping behavior of various amphibians has long attracted attention from researchers and pet owners. Despite being widely documented, the underlying functional role is poorly understood. In a new paper, researchers demonstrate that Dyeing poison frogs modulate their taps based on specific stimuli.
Dyeing poison frogs, Dendrobates tinctorius, have been shown to tap their posterior toes in response to a range of prey sizes, from small fruit flies to large crickets. In the present study, ...
Irvine, Calif., May 28, 2024 — A multidisciplinary research team at the University of California, Irvine has revealed that the circadian clock – the biological pacemaker that governs daily rhythms in physiological processes, including immune functions – can be leveraged to enhance the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy. Checkpoint inhibitors block different proteins from binding to tumor cells, allowing the immune system’s T cells to kill the tumor.
The study, published online ...
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 27, 2024) As gene sequencing technologies become more powerful, our understanding of cellular diversity has grown in parallel. This led scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital to create a tool to improve the ease and accuracy with which investigators can study specific subpopulations of cells. The tool, named Conditional Viral Expression by Ribozyme Guided Degradation (ConVERGD), allows researchers to specifically access these subgroups of cells and precisely manipulate ...
Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have updated their guidelines on when to neuter 40 popular dog varieties by breed and sex. Their recent paper in Frontiers in Veterinary Science adds five breeds to a line of research that began in 2013 with a study that suggested that early neutering of golden retrievers puts them at increased risk of joint diseases and certain cancers.
That initial study set off a flurry of debate about the best age to neuter other popular breeds. Professors Lynette and Benjamin Hart of the School of Veterinary Medicine, the study’s lead authors, set out to add more breed studies by examining more than a decade ...
Music and speech are among the most frequent types of sounds we hear. But how do we identify what we think are differences between the two?
An international team of researchers mapped out this process through a series of experiments—yielding insights that offer a potential means to optimize therapeutic programs that use music to regain the ability to speak in addressing aphasia. This language disorder afflicts more than 1 in 300 Americans each year, including Wendy Williams and Bruce Willis.
“Although music and speech are different in many ways, ranging from pitch to timbre to sound texture, ...