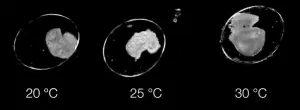
(Press-News.org) Research led by the University of Plymouth has shown that a new deep learning AI model can identify what happens and when during embryonic development, from video.
Published today (Wednesday 29 May) in the Journal of Experimental Biology, the study highlights how the model, known as Dev-ResNet, can identify the occurrence of key functional developmental events in pond snails, including heart function, crawling, hatching and even death.
A key innovation in this study is the use of a 3D model that uses changes occurring between frames of the video, and enables the AI to learn from these features, as opposed to the more traditional use of still images.
The use of video means features ranging from the first heartbeat, or crawling behaviour, through to shell formation or hatching are reliably detected by Dev-ResNet, and has revealed sensitivities of different features to temperature not previously known.
While used in pond snail embryos for this study, the authors say the model has broad applicability across all species, and they provide comprehensive scripts and documentation for applying Dev-ResNet in different biological systems.
In future, the technique could be used to help accelerate understanding on how climate change, and other external factors, affect humans and animals.
The work was led by PhD candidate, Ziad Ibbini, who studied BSc Conservation Biology at the University, before taking a year out to upskill himself in software development, then beginning his PhD. He designed, trained and tested Dev-ResNet himself.
He said: “Delineating developmental events – or working out what happens when in an animal’s early development – is so challenging, but incredibly important as it helps us to understand changes in event timing between species and environments.
“Dev-ResNet is a small and efficient 3D convolutional neural network capable of detecting developmental events using videos, and can be trained relatively easily on consumer hardware.
“The only real limitations are in creating the data to train the deep learning model – we know it works, you just need to give it the right training data.
“We want to equip the wider scientific community with the tools that will enable them to better understand how a species’ development is affected by different factors, and thus identifying how we can protect them. We think that Dev-ResNet is a significant step in that direction.”
Dr Oli Tills, the paper’s senior author and a UKRI Future Leaders Research Fellow, added: “This research is important on a technological level, but it is also significant for advancing how we perceive organismal development – something that the University of Plymouth, within the Ecophysiology and Development research Group, has more than 20 years’ history of researching.
“This milestone would not have been possible without deep learning, and it is exciting to think of where this new capability will lead us in the study of animals during their most dynamic period of life.”
The full paper, entitled Dev-ResNet: Automated developmental event detection using deep learning, is now available to view in the Journal of Experimental Biology (doi: 10.1242/jeb.247046).
END
New deep learning model is ‘game changer’ for measuring embryo development
A new deep learning model performs a task that biologists have struggled with for centuries – how to measure the incredibly complex process of embryonic development
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smarter foragers do not forage smarter
2024-05-29
Primates, including humans, have larger brains than most other mammals, but why? Scientists searching for the answer have long followed a trail pointing to diet—specifically fruit—as the reason for why primates evolved larger brains. A team from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and the Smithsonian Institute of Tropical Research tested this idea for the first time—finding that the fruit-diet theory might be out of juice. The researchers used drone imaging, GPS tracking, and fine-scale behavioral analyses to test how four species of fruit-eating mammals solved the same natural foraging puzzle in a Panamanian rainforest. They ...
A unified account of Darwinism’s varieties
2024-05-29
A new paper published in The Quarterly Review of Biology examines the question of what Darwinism is and how its nonscientific uses relate to the scientific theory of evolution.
Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species in 1859 as a work in biology. However, in the past century and a half, Darwin’s ideas have impacted a broad range of domains and stimulated scientists and scholars to advance "evolutionary approaches" in domains as diverse as economics, engineering, psychology, and history. The ideas have been used (and abused) to undermine religiously inspired ideas about the origin of humans and their status concerning other species, ...
Marketers can manage 'feature creep'
2024-05-29
AUSTIN, Texas — Wifi-enabled washing machines. Voice-controlled microwaves. App-enabled TVs, vacuum cleaners, and even window blinds you can control from the comfort of your couch.
Many of the technological features now included in everyday products are useful and accessible. But research has shown that having too many can overwhelm potential buyers, making them less likely to make a purchase.
In new research, Wayne Hoyer, marketing professor and James L. Bayless/William S. Farrish Fund Chair for Free Enterprise at Texas McCombs, digs into the phenomenon of “feature creep” and its impact on consumer sentiment. ...
Intermittent fasting shows promise in improving gut health, weight management
2024-05-29
A new study by researchers from Arizona State University and their colleagues highlights a dietary strategy for significant health improvement and weight management.
Participants following an intermittent fasting and protein-pacing regimen, which involves evenly spaced protein intake throughout the day, saw better gut health, weight loss and metabolic responses. These benefits were notably greater than those seen with simple calorie restriction.
The findings, reported today in the journal Nature ...
Scientists identify gene that could lead to resilient ‘pixie’ corn
2024-05-29
AMES, Iowa – A widely found gene in plants has been newly identified as a key transporter of a hormone that influences the size of corn. The discovery offers plant breeders a new tool to develop desirable dwarf varieties that could enhance the crop’s resilience and profitability.
A team of scientists led by Iowa State University spent years working to pinpoint the functions of the gene ZmPILS6. Now, they have been able to characterize it as an important driver of plant size and architecture, a carrier for an auxin hormone that helps govern growth in roots below ground and shoots, or stalks, above ground. Their findings were published in the Proceedings ...
Utilizing medical assistants to manage patient portal messages shown to support practice and physician efficiency
2024-05-28
Many primary care clinicians directly receive messages from patients via electronic health records’ portal inboxes. The COVID-19 pandemic saw a rapid uptick in this trend. Data suggests that this additional work is linked to clinician burnout. Penn Family Care, a primary care group at Penn Medicine, instead routed incoming messages to certified medical assistants who had been taught how to distribute each message to the most appropriate physician. There was a 40% decrease in the number of messages going directly to primary care physicians, and both practice and clinician efficiency showed improvement after adopting this team-based care model.
Utilizing Medical Assistants ...
Study shows clinic continuity associated with reduced hospital and emergency visits
2024-05-28
Background and Goal: Relational continuity, the ongoing relationship between a patient and a family physician, is linked to better patient care, fewer unnecessary procedures, hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and lower costs, along with higher patient satisfaction. With the rise of part-time practices, patients often see multiple family physicians within the same clinic. This study aimed to explore how continuity in a primary care clinic—separate from individual physician continuity—affects patient ...
Recognizing the range of experiences among individuals of Latino, Hispanic, and/or Spanish origin is an essential step toward health equity
2024-05-28
Background: Currently, people of Latiné/e/x/o/a, Hispanic, and/or Spanish (LHS) origin make up 19.1% of the population of the U.S. There is great variation in the personal experiences and family backgrounds of LHS individuals, including differences in country of origin, time in the U.S., colonization histories and immigration experiences.
Key Argument: This essay considers the importance of recognizing the heterogeneity of lived experiences among LHS populations in the U.S. in a health care context.
Why ...
study reveals decline in reported medicare outpatient procedures by family physicians amid an aging population
2024-05-28
Background and Goal: Family physicians perform a wide range of procedures outside the hospital and tend to be office based. Examples may include surgical procedures such as excisions, suturing, and joint injections. Since the training can vary substantially, the Council of Academic Family Medicine (CAFM) issued a statement on which procedures they recommend physicians be able to perform competently upon completion of a family medicine residency. The aim of this study was to determine the extent to which family physicians perform CAFM-recommended procedures for Medicare Part B, the outpatient portion ...
COVID-19 pandemic leads to drop in breast cancer screenings, especially among older and racial minority women
2024-05-28
Background and Goal: Breast cancer is the second most common cancer among women in the U.S. Early detection of the disease through screening can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment and is an essential preventive service in primary care. The COVID-19 pandemic interrupted breast cancer screening as many screening programs were temporarily suspended due to personal concerns about exposure to the virus and the burden on the health care system. The goal of this study was to use real-world electronic health records (EHR) across the U.S. to examine the changes in breast cancer screening utilization since the COVID-19 pandemic and how the follow-up screening rates were impacted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] New deep learning model is ‘game changer’ for measuring embryo developmentA new deep learning model performs a task that biologists have struggled with for centuries – how to measure the incredibly complex process of embryonic development