(Press-News.org) Joint research led by Yutaro Shuto, Ryoya Nakagawa, and Osamu Nureki of the University of Tokyo determined the spatial structure of various processes of a novel gene-editing tool called “prime editor.” Functional analysis based on these structures also revealed how a “prime editor” could achieve reverse transcription, synthesizing DNA from RNA, without “cutting” both strands of the double helix. Clarifying these molecular mechanisms contributes greatly to designing gene-editing tools accurate enough for gene therapy treatments. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier for developing a groundbreaking yet simple way to edit DNA, the “blueprint” of living organisms. While their discovery opened new avenues for research, the accuracy of the method and safety concerns about “cutting” both strands of DNA limited its use for gene therapy treatments. As such, research has been underway to develop tools that do not have these drawbacks.
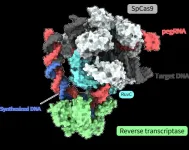
The prime editing system is one such tool, a molecule complex consisting of two components. One component is the prime editor, which combines a SpCas9 protein, used in the first CRISPR-Cas gene editing technology, and a reverse transcriptase, an enzyme that transcribes RNA into DNA. The second component is the prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA), a modified guide RNA that identifies the target sequence within the DNA and encodes the desired edit. In this complex, the prime editor works like a “word processor,” accurately replacing genomic information. The tool has already been successfully implemented in living cells of organisms such as plants, zebrafish, and mice. However, precisely how this molecule complex executes each step of the editing process has not been clear, mostly due to a lack of information on its spatial structure.
“We became curious about how the unnatural combination of proteins Cas9 and reverse transcriptase work together,” says Shuto, the first author of the paper.
The research team used cryogenic electron microscopy, an imaging technique that makes observations possible at a near-atomic scale. The method required samples to be in glassy ice to protect them from the potential damage by the electron beams, posing some additional challenges.
“We found the prime editor complex to be unstable under experimental conditions,” explains Shuto. “So, it was very challenging to optimize the conditions for the complex to stay stable. For a long time, we could only determine the structure of Cas9.”
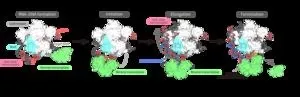
Finally overcoming the challenges, the researchers succeeded in determining the three-dimensional structure of the prime editor complex in multiple states during reverse transcription on the target DNA. The structures revealed that the reverse transcriptase bound to the RNA–DNA complex that formed along the “part” of the Cas9 protein associated with DNA cleavage, the splitting of a single strand of the double helix. While performing the reverse transcription, the reverse transcriptase maintained its position relative to the Cas9 protein. The structural and biochemical analyses also indicated that the reverse transcriptase could lead to additional, undesired insertions.
These findings have opened new avenues for both basic and applied research. So, Shuto lays out the next steps.
“Our structure determination strategy in this study can also be applied to prime editors composed of a different Cas9 protein and reverse transcriptase. We want to utilize the newly obtained structural information to lead to the development of improved prime editors.”
END
Editing without “cutting”: Molecular mechanisms of new gene-editing tool revealed
Researchers elucidate the spatial structure and molecular mechanisms of “prime editor,” a novel gene-editing tool
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Identifying the initial steps in colorectal cancer formation
2024-05-29
Research led by Weill Cornell Medicine provides new evidence that most colorectal cancers begin with the loss of intestinal stem cells, even before cancer-causing genetic alterations appear. The results, published on May 29 in Developmental Cell, overturn the prevailing theory for colorectal tumor initiation and suggest new ways to diagnose the disease before it has a chance to become established.
“Colorectal cancer is very, very heterogeneous, which has made it difficult for many years to classify these tumors in order to inform therapy,” said senior author Dr. ...
hnRNPM, a guardian of the integrity of cellular protein production
2024-05-29
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have discovered that a protein called hnRNPM helps protect the integrity of the process cells use to make proteins. hnRNPM works by preventing the cell from making mistakes while it is putting together the different components leading to newly produced proteins. In cancer cells, loss of hnRNPM triggers an interferon immune response, suggesting that this protein may hold clinical promise. The findings appeared in Molecular Cell.
“Synthesizing a protein is like putting together the different parts of a machine. If during the assembly process parts that do not belong are incorporated ...
Children often exposed to problematic click bait during YouTube searches
2024-05-29
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – When a child peruses YouTube, the content recommended to them is not always age appropriate, a new study suggests.
Researchers mimicked search behaviors of children using popular search terms, such as memes, Minecraft and Fortnite, and captured video thumbnails recommended at the end of each video.
Among the 2,880 thumbnails analyzed, many contained problematic click bait, such as violence or frightening images, according to the Michigan Medicine led research in JAMA Network Open.
“Children spend a significant amount of time on free video sharing platforms that ...
Modular, scalable hardware architecture for a quantum computer
2024-05-29
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Quantum computers hold the promise of being able to quickly solve extremely complex problems that might take the world’s most powerful supercomputer decades to crack.
But achieving that performance involves building a system with millions of interconnected building blocks called qubits. Making and controlling so many qubits in a hardware architecture is an enormous challenge that scientists around the world are striving to meet.
Toward this goal, researchers at MIT and MITRE have demonstrated a scalable, modular hardware platform that ...
Landmark study is step towards energy-efficient quantum computing in magnets
2024-05-29
Researchers from Lancaster University and Radboud University Nijmegen have managed to generate propagating spin waves at the nanoscale and discovered a novel pathway to modulate and amplify them.
Their discovery, published in Nature, could pave the way for the development of dissipation free quantum information technologies. As the spin waves do not involve electric currents these chips will be free from associated losses of energy.
The rapidly growing popularity of artificial intelligence comes with an increasing desire for fast and energy efficient computing devices and calls for novel ...
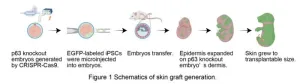
Grow the skin you’re in: in vivo generation of chimeric skin grafts
2024-05-29
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that donor keratinocytes injected into mouse embryos form sheets of epidermis that can be used as autologous skin grafts
Tokyo, Japan – Skin grafting is an essential procedure used to treat severe skin wounds. In the case of extensive wounds, however, it can be challenging to harvest enough donor skin, and generating artificial skin substitutes that include hair follicles and sweat glands and can engraft on deep wounds has not been successful. Now, researchers from Japan report a new way to “grow your own” donor skin that could help improve the success of skin graft generation.
In a study published last ...
BGU researchers and colleagues discover therapeutic potential of increasing MIF protein levels as a novel approach for treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
2024-05-29
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, May 29, 2024 – A recent collaborative research endeavor, published in the prestigious Cell Press journal Cell Reports Medicine, highlights a promising therapeutic avenue for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Led by researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in conjunction with counterparts from Germany, the USA, and Canada, the study delves into the potential of augmenting macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) protein levels as a novel approach to tackling ALS.
ALS, often referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a devastating neurodegenerative condition characterized by the progressive loss of motor neurons, leading to muscle ...
War magnifies politicians’ gendered behavior, public biases, research finds
2024-05-29
Women’s participation in politics is essential to advancing women’s rights and contributes to countries’ overall stability and economic prosperity. According to a 2023 report by UN Women and the Inter-Parliamentary Union, one-fourth of parliamentary positions worldwide are held by women. Although current representation is still far from equal, it represents a significant increase over the last 20 years.
However, a new paper from Washington University in St. Louis — published ...
International experts reach consensus on the labeling of spatial neglect
2024-05-29
East Hanover, NJ, May 29, 2024 — A consensus has been achieved by an international team of rehabilitation researchers and clinicians on the standardized labeling of spatial neglect, a common disorder following neurological injury, which is characterized by a lack of awareness or response to objects or stimuli on the side opposite a brain lesion. The panel reached a 75% consensus to adopt "spatial neglect" as the standard term for the disorder.
The consensus paper, titled “An International and ...
Gaps in transition from pediatric to adult care for individuals living with sickle cell disease associated with more hospital visits
2024-05-29
(WASHINGTON, May 29, 2024) – Individuals living with sickle cell disease (SCD) who experience a delay of more than six months in transitioning from pediatric to adult care are twice as likely to be hospitalized compared to those who transition in less than two months, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
SCD is the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States, affecting an estimated 100,000 people. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, SCD affects one out of every 365 Black or African American births and one out of every 16,300 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Editing without “cutting”: Molecular mechanisms of new gene-editing tool revealedResearchers elucidate the spatial structure and molecular mechanisms of “prime editor,” a novel gene-editing tool