(Press-News.org) May 29, 2024
Boosters that target the omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 are still providing reasonably durable protection against infection, hospitalization and death from COVID-19, according to new data from a study led by researchers at the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health.
Published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, the study found that COVID-19 boosters targeting the XBB.1.5 subvariants were most effective one month after receiving one. After four weeks, the vaccines were 52.2% effective at preventing infection and 66.8% effective at preventing hospitalization.
The vaccines were also highly effective at preventing death, but exact certainty was hard to quantify given the small number of deaths reported during the study period.
After peaking at four weeks, booster effectiveness waned over time. Effectiveness at preventing infection decreased to 32.6% after 10 weeks and 20.4% after 20 weeks, while effectiveness at preventing hospitalization decreased to 57.1% after 10 weeks.
Danyu Lin, PhD, Dennis Gillings Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biostatistics at the Gillings School, is lead author on the study. Additional co-authors include Yangjianchen Xu at the Gillings School; Yi Du, PhD, Sai Paritala, PharmD, and Matthew Donahue, MD, from the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services; and Patrick Maloney, PhD, from the University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Using data from the Nebraska Electronic Disease Surveillance System and the Nebraska State Immunization Information System, the research team studied the efficacy of vaccination before and after Oct. 25, 2023, when the JN.1 variant began to emerge.
Vaccine effectiveness was lower in the second group, suggesting that the booster was less protective against the now-dominant JN.1 strain.
“The JN.1 subvariant has been the dominant strain in the United States this year,” said Lin. “The relatively low effectiveness of the XBB.1.5 vaccines against the JN.1 subvariant, together with the waning effectiveness over time, underscores the need for new vaccines targeting the JN.1 strain.”
Lin says the Food and Drug Administration’s general strategy is to deploy new COVID-19 vaccines annually in the fall that target the circulating strains in the spring, and that the findings in this study may contribute to this decision.
“It would be worthwhile to deploy new vaccines this fall that target the JN.1. strain,” he said.
END
Study shows effectiveness of updated COVID-19 vaccines wanes moderately over time, is lower against currently circulating variants
New research shows boosters targeting omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 are still providing reasonably durable protection against infection, hospitalization and death from COVID-19, but they are less protective against the now-dominant JN.1 strain.
2024-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers expose new ‘origin’ theories, identify experimental systems for plant life
2024-05-29
STARKVILLE, Miss.—A Mississippi State faculty member’s work on plant life symbiosis—a mutually beneficial relationship between living organisms—is pushing back against the newer theory of “single-origin”—that all life stems from one point—instead suggesting “multiple-origin” theory which opens a better understanding for genetically engineering crops.
Ryan A. Folk, an assistant professor in the MSU Department of Biological Sciences and herbarium curator, is an author on a paper published this month in ...
Researchers honored for outstanding contributions to cancer care
2024-05-29
Three Huntsman Cancer Institute researchers have recently been recognized for their work as outstanding faculty members at the University of Utah (the U).
Kim Kaphingst, ScD, director of cancer communication research at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of communication at the U, and June Round, PhD, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of microbiology and immunology at the U, were both granted the 2024 Distinguished Research Award. The faculty prize is given annually to scholars who exemplify exceptional research.
Kaphingst’s group explores cancer communication, particularly how to educate patients and families who ...
A new Hungarian method may aid protein research
2024-05-29
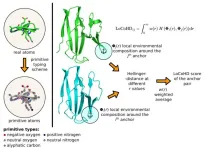
In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, the HUN-REN-ELTE Protein Modeling Research Group (Institute of Chemistry) has laid the foundations for a mathematical method, allowing the computer-assisted comparison of the three-dimensional structures of proteins. The method is unique in that while the alternatives available so far only took into account the position of the atoms, the new technique, called LoCoHD (Local Composition Hellinger Distance), also includes the chemical information of the atoms.
Proteins are molecular machines that carry out processes necessary for cells to function, acting as molecular switches, transcribing information ...
AIM algorithm enhances super-resolution microscope images in real time
2024-05-29
When trying to measure molecular structures with nanometer precision, every bit of noise shows up in the data: someone walking past the microscope, tiny vibrations in the building and even the traffic outside. A new processing technique removes noise from optical microscope data in real time, allowing scientists to track individual molecules over 10 times more precisely than was possible before.
A team of bioengineering researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has introduced an algorithm called adaptive intersection maximization, or AIM, that removes high-frequency ...
Rice researchers uncover surprising role of opioid receptors in gut development
2024-05-29
Researchers at Rice University have revealed a previously unknown function of opioid receptors in the development of the enteric nervous system (ENS), often referred to as the “brain in the gut.” This discovery challenges conventional understanding of opioid receptors, shedding new light on their significance beyond pain management and addiction.
Led by Rosa Uribe, an assistant professor of biosciences at Rice and a Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) Scholar, the research team identified the genes critical for ENS development by conducting a series of experiments using zebrafish ...
Cleveland Clinic and IBM researchers apply quantum computing methods to protein structure prediction
2024-05-29
CLEVELAND - Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and IBM recently published findings in the Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation that could lay the groundwork for applying quantum computing methods to protein structure prediction. This publication is the first peer-reviewed quantum computing paper from the Cleveland Clinic-IBM Discovery Accelerator partnership.
For decades, researchers have leveraged computational approaches to predict protein structures. A protein folds itself into a structure that determines how it functions and binds to other ...
Blood flow makes waves across the surface of the mouse brain
2024-05-29
WHAT: Researchers have, for the first time, visualized the full network of blood vessels across the cortex of awake mice, finding that blood vessels rhythmically expand and contract leading to “waves” washing across the surface of the brain. These findings, funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), improve the understanding of how the brain receives blood, though the function of the waves remains a mystery.
A network of elastic and actively pumping vessels carrying oxygenated blood span the surface of the brain before entering the cortex. There, they feed into a second network of capillaries that supply oxygen deeper into ...
More out-of-state patients seek abortions in Washington state
2024-05-29
More out-of-state women, largely from Texas and Alaska, are traveling to Washington state to obtain an abortion than was the case before the U.S. Supreme Court struck down the constitutional right to abortion, according to research published today in JAMA Network Open.
The study tracked the number of abortions performed at the Cedar River Clinics, a large network of care sites in Washington state, both before and after the 2022 Dobbs decision.
Researchers found a 50% increase in out-of-state patients (from 4% to 6%) and documented an average one-week delay in care for all patients seeking ...
Researchers take step toward development of universal COVID-19 antibodies
2024-05-29
SAN ANTONIO (May 29, 2024) – SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 disease, continues to evolve and evade current vaccine and therapeutic interventions. A consortium of scientists at Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed), the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) and Columbia University have developed a promising new human monoclonal antibody that appears a step closer to a universal antibody cocktail that works against all strains of SARS-CoV-2.
“This antibody worked against the original SARS-CoV-2 strain, Omicron and SARS-CoV, providing ...
Do epilepsy medications taken during pregnancy affect a child’s creativity?
2024-05-29
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MAY 29, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – While older drugs for epilepsy, taken while pregnant, have been shown in previous research to affect the creative thinking of children, a new study finds no effects on creativity for children born to those taking newer epilepsy drugs. This study is published in the May 29, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Overall, the study found no effects on the children’s creative abilities or their executive function, which is a person’s ability to plan, focus, and manage multiple tasks. However, when ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Study shows effectiveness of updated COVID-19 vaccines wanes moderately over time, is lower against currently circulating variantsNew research shows boosters targeting omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 are still providing reasonably durable protection against infection, hospitalization and death from COVID-19, but they are less protective against the now-dominant JN.1 strain.