One in four Thai concerned about colorectal cancer screening cost
To better address the global burden of CRC and reduce its impact, BGI Genomics has launched the second edition of its global CRC awareness report.
2024-05-31
(Press-News.org)
According to research led by Prof. Varut Lohsiriwat, Professor of Surgery, Division of General Surgery (Section of Colorectal Surgery) of Siriraj Hospital, at Mahidol University, CRC is the third most common cancer in Thailand, accounting for 11% of the cancer burden. It is the only malignancy with an increased incidence in both genders in the country.
By 2040, the burden of CRC is projected to increase to 3.2 million new cases and 1.6 million deaths per year representing a 66% and 71% rise in new cases and deaths respectively relative to 2020.
To better address the global burden of CRC and reduce its impact, BGI Genomics has launched the second edition of its global CRC awareness report, covering 1,938 respondents from Brazil (306), China (367), Poland (300), Saudi Arabia (300), Thailand (362), and Uruguay (303):
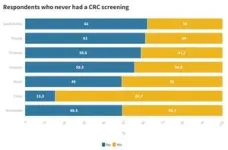
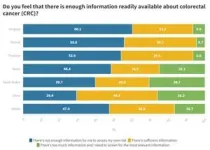
CRC Screening Gaps Vary Globally: A significant 58.8% of Thai have never had a CRC screening, higher than the global average of 49.3%. In addition, 54% of Thai point out that there is not enough information about CRC available.
Preference for Fecal Testing Over Colonoscopy: Although colonoscopies are more recognized (33.4%), fecal tests at healthcare facilities are preferred (31.8%), reflecting a trend towards non-invasive methods. Professor Varut Lohsiriwat suggest “Doctors usually will explain the pros and cons for the patient in 3 to 5 mins about different screening method. But in the end, it’s the patients that makes the decision and the best screening method is the one that accepted by the patients”.
Cost as the Determinant in Screening Choices: Cost plays a crucial role in individuals' decisions regarding CRC screening in Thailand. Thailand (24.5%) and Poland (20.6%) indicate the most concern about costs, with 88.2% of Thai preferring either moderately priced options with good accuracy or inexpensive options with average accuracy.
Medical Advice and Family History Drive CRC Screening: Given that doctor's recommendations (29.1%) are the biggest single factor that makes Thai individuals more likely to undergo screening for CRC without any symptoms. Additionally, Thai with a family history of CRC are more proactive in screening (62.8%), compared to the general population (33.4%). This points to the critical role of healthcare professionals and familial awareness in encouraging screening.
For more region-level comparisons, access the full BGI Genomics 2024 State of CRC Awareness Report.
All data involved in this report come from the results of an online survey project conducted by BGI Genomics. It only surveys awareness related to colorectal cancer and does not involve personally identifiable data.
About BGI Genomics and COLOTECT
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
COLOTECT is a non-invasive fecal DNA test developed by BGI Genomics for detecting CRC and precancerous lesions. It uses multiplex methylation-specific PCR (MSP) technology to trace abnormal DNA-methylation biomarkers in CRC from stool samples. It has 88% CRC sensitivity, and for early detection, its sensitivity for advanced adenoma is 46%, which are both superior to conventional fecal tests.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-31
Speech and music are the dominant elements of an infant’s auditory environment. While past research has shown that speech plays a critical role in children’s language development, less is known about the music that infants hear.
A new University of Washington study, published May 21 in Developmental Science, is the first to compare the amount of music and speech that children hear in infancy. Results showed that infants hear more spoken language than music, with the gap widening as the babies get older.
“We wanted to get a snapshot of what’s happening in infants’ home environments,” said corresponding author ...
2024-05-31
Research led by the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) has led to a new tool for forecasting coral disease that could help conservationists step in at the right times with key interventions. Ecological forecasts are critical tools for conserving and managing marine ecosystems, but few forecasting systems can account for the wide range of ecological complexities in near-real-time.
Using ecological and marine environmental conditions, the Multi-Factor Coral Disease Risk product predicts the risk of two diseases across reefs in the central and western Pacific and along the east coast of Australia. An article ...
2024-05-31
Tobacco-funded research is still appearing in highly-cited medical journals - despite attempts by some to cut ties altogether, finds an investigation by The Investigative Desk and The BMJ today.
Although the tobacco industry has a long history of subverting science, most leading medical journals don’t have policies which ban research wholly or partly funded by the industry.
And even when publishers, authors and universities are willing to restrict tobacco industry ties, they struggle ...
2024-05-31
Trout living in rivers polluted by metal from old mines across the British Isles are genetically “isolated” from other trout, new research shows.
Researchers analysed brown trout at 71 sites in Britain and Ireland, where many rivers contain metal washed out from disused mines.
While trout in metal-polluted rivers appear healthy, they are genetically distinct – and a lack of diversity in these populations makes them vulnerable to future threats.
By comparing the DNA of trout in rivers with and without metal pollution, the researchers found that metal-tolerant trout ...
2024-05-31
Trust is vital to the widespread acceptance of AI across industries, especially when safety is a concern. For example, people may be hesitant to ride in a self-driving car knowing that the AI running it can be hacked. One barrier to increasing trust is that the algorithms powering AI are vulnerable to such attacks.
Dr. Samson Zhou, assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Texas A&M University, and Dr. David P. Woodruff, professor in the Computer Science Department at Carnegie Mellon University, hope to strengthen algorithms used by big data AI models against attacks. Big data AI models are ...
2024-05-31
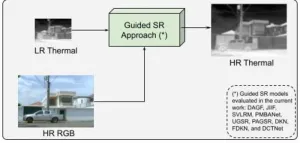
Researchers of CIDIS at ESPOL Polytechnic University have developed a new method to enhance thermal image super-resolution by employing synthetic imagery. This novel approach utilizes high-resolution images from the visible spectrum to guide the super-resolution of low-resolution thermal images, significantly improving the detail and utility of thermal imaging across various applications.
When visualizing thermal images, one typically imagines the blurry, less-detailed outputs common with standard thermal ...
2024-05-31
Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC scientists studying ultra-processed foods have created a new tool for assessing the rewarding and reinforcing properties of foods that make up 58 percent of calories consumed in the United States. The foods have been linked to a wide range of negative health outcomes.
The research, which was published in April in the journal Appetite, provides a collection of carefully curated images of minimally processed and ultra-processed foods matched on 26 characteristics, including macronutrients, sodium, dietary fiber, calories, price, and visual characteristics such as a color and portion size.
The work was based on the NOVA classification system ...
2024-05-31
New images of Jupiter's volcano-studded moon Io, taken by the Large Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham in Arizona, offer the highest resolution of Io ever achieved with an Earth-based instrument. The observations were made possible by a new high-contrast optical imaging instrument, dubbed SHARK-VIS, and the telescope's adaptive optics system, which compensates for the blurring induced by atmospheric turbulence.
The images, to be published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, reveal surface features as small as 50 miles across, ...
2024-05-30
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – May 30, 2024 – Researchers at Wake Forest University of School of Medicine have received a five-year, $1.5 million grant from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to study bone microarchitecture in patients following bariatric surgery.
With the funding support, researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine will partner with Virginia Tech to add a virtual biopsy that uses an innovative technique called high-resolution peripheral quantitative ...
2024-05-30
Urinary catheters are required for nearly every surgical procedure. However, a major challenge for the health care industry is predicting who may develop catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) and when these infections may lead to death.
Now, a study from the University of Notre Dame has identified a population that is more susceptible to developing a CAUTI.
Researchers showed that models with fibrinolytic deficiencies, or conditions that cause overactivation of the protein fibrin, had increased risk for developing severe and persistent CAUTIs. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] One in four Thai concerned about colorectal cancer screening cost
To better address the global burden of CRC and reduce its impact, BGI Genomics has launched the second edition of its global CRC awareness report.