(Press-News.org) BOSTON—Stress during childhood is associated with earlier substance use in male and female adolescents, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. Traumatic events may increase substance use risk for males, while environmental stress and early puberty may increase the risk for females, the researchers found.
Early life stress is children’s experiences of abuse, neglect and conflict. Approximately 20% of adolescents in the United States have experienced early life stress at some point, and these experiences influence adolescent and adult health behavior outcomes.
“Starting substance use at an earlier age is associated with more severe substance use disorder in adulthood,” said lead researcher Alexandra Donovan, Ph.D., of Charles R. Drew University of Medicine and Science in Los Angeles, Calif. “Early life stress and early puberty have both been associated with early substance use, but it wasn’t clear whether these connections are the same across boys and girls.”
Donovan and colleagues evaluated sex differences in the impact of puberty and stress on alcohol, nicotine and cannabis use by the age of 13. They analyzed data from 8,608 male and female participants in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study, who were 9 or 10 years old when the study began. The study included data from the first three years of the ABCD study.
The researchers looked at the effects of early life stress and found it increased the likelihood of earlier use of alcohol, nicotine or cannabis use across both males and females.
Early life stress increased the likelihood of earlier substance use for males by 9-18% and for females by 13-20%. Environmental stress increased the likelihood of early use of nicotine and cannabis in females by 15-24%. Traumatic event stress increased the likelihood in males by 15-16%. Higher pubertal development scores increased the likelihood of earlier nicotine use for females while decreasing the likelihood for males.
“Our study supports the link between early life stress and teen substance use, extending our understanding of how this connection can differ across sex,” Donovan said. “These findings may be used to refine prevention programs in schools, encouraging a more individualized approach.”
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Childhood stress linked with earlier substance use in male and female teens
2024-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Childhood sedentariness may cause premature liver damage in young adulthood
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Children who are sedentary for more than six waking hours a day have a significantly increased risk of severe fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis by young adulthood, a new study finds. The research findings will be presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass and published in Nature’s npj Gut and Liver.
“We found that this relationship between sedentariness and liver damage is likely causal,” said lead researcher Prof. Andrew Agbaje, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., of the University of Eastern Finland ...
Experimental therapy shows promise in pancreatic cancer clinical trial
2024-06-01
WASHINGTON --- Clinicians at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center reported promising preliminary findings based on outcomes in the first six patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer enrolled in a phase 2 clinical trial of the experimental drug BXCL701 in combination with the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab (Keytruda). Immunotherapy drugs alone have not shown to be responsive to pancreatic cancer.
The findings were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2024 annual meeting in Chicago on June 1, 2024 (LBA4132).
BXCL701, made by BioXcel Therapeutics, is ...
Clinical trials show promise in treating central nervous system lymphoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma
2024-06-01
Boston – Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers are leading 3 separate studies with encouraging results in treating patients with central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma. The studies support future research in these potential breakthroughs where treatment options may be limited. The research teams will present their findings at the 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in Chicago, May 31-June 4, 2024. ASCO is the world’s largest clinical cancer research meeting, attracting more than 30,000 global oncology professionals.
These findings are among more than 80 studies presented at ASCO that ...
Crisis intervention program leverages social media to reduce suicide risk
2024-06-01
An Oregon-based program that monitors social media use may have helped deter more than 150 youth suicide attempts in the five years it’s operated, reports a new study published online today in the journal Psychiatric Services.
Staff with Lines for Life, a nonprofit that operates mental health crisis support services, and researchers at Oregon Health & Science University collaborated to closely document interventions by the Safe Social Spaces program, launched in 2019 by Lines for Life.
The study’s senior author said it’s an example of meeting people where they are.
“Community engagement is critical,” said Alan Teo, M.D., M.S., associate professor of ...
An unlikely hero in evolution: worms
2024-06-01
One of Earth’s most consequential bursts of biodiversity—a 30-million-year period of explosive evolutionary changes spawning innumerable new species—may have the most modest of creatures to thank for the vital stage in life’s history: worms.
The digging and burrowing of prehistoric worms and other invertebrates along ocean bottoms sparked a chain of events that released oxygen into the ocean and atmosphere and helped kick-start what is known as the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event, roughly 480 million years ago, according ...
Detecting machine-written content in scientific articles
2024-06-01
The recent surge in popularity of AI tools such as ChatGPT is forcing the science community to reckon with its place in scientific literature. Prestigious journals such as Science and Nature have attempted to restrict or prohibit AI use in submissions, but are finding it difficult to enforce because of how challenging it is becoming to detect machine-generated language.
Because AI is getting more advanced at mimicking human language, researchers at the University of Chicago were interested in learning ...
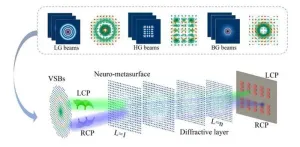
Sorting complex light beams: A breakthrough in optical physics
2024-06-01
In the dynamic realm of optical physics, researchers are continually pushing the boundaries of how light can be manipulated and harnessed for practical applications. As reported in Advanced Photonics Nexus, a groundbreaking study from the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) introduces a method for sorting and distinguishing various types of vector structured beams (VSBs), promising significant advancements in optical communication and quantum computing.
Unlike conventional light beams that propagate in simple, straight trajectories, VSBs are engineered to form complex, intricate patterns. These beams transmit ...
Supervised physical exercise improves the wellbeing of carers of the elderly
2024-06-01
Mainly older and middle-aged women, working class, with a very high prevalence of lower back pain and consequently possible psycho-affective problems and a poorer quality of life... This is the general profile of carers of the elderly. Who cares for the carer? This question or demand is not new in our society. Members of the Ageing On research group of the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) asked themselves the following question: “How can we care for the carers?”
The Ageing On group develops, ...
Polygenic risk scores give inaccurate and highly inconsistent results in embryo selection
2024-06-01
Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) are estimates of an individual’s susceptibility to a specific complex trait obtained by aggregating the effects of dozens, thousands, and potentially millions of genetic variants associated with that specific trait into a single figure. Some private companies now market PRS embryo screening to prospective parents through the use of in vitro fertilisation and pre-implantation genetic testing. While PRS has great potential for prediction in live-born (mostly adult) individuals, its accuracy ...
Molecular profiling improves diagnosis and survival for children with high risk cancers
2024-06-01
Berlin, Germany: Cancer is the leading cause of disease-related death in children in most developed countries, and at least a quarter of these patients are diagnosed with aggressive high-risk or relapsed cancers, with an expected five-year survival rate of less than 30%. Accurate diagnosis can be difficult, and survivors often suffer life-long side effects because of the toxic treatments needed to cure them. Now, researchers from Australia have shown that, by using precision medicine*, it is possible not only to obtain more accurate diagnoses, but also that using precision-guided, targeted treatments earlier improves the two year progression-free ...