(Press-News.org) An Oregon-based program that monitors social media use may have helped deter more than 150 youth suicide attempts in the five years it’s operated, reports a new study published online today in the journal Psychiatric Services.
Staff with Lines for Life, a nonprofit that operates mental health crisis support services, and researchers at Oregon Health & Science University collaborated to closely document interventions by the Safe Social Spaces program, launched in 2019 by Lines for Life.
The study’s senior author said it’s an example of meeting people where they are.
“Community engagement is critical,” said Alan Teo, M.D., M.S., associate professor of psychiatry in the OHSU School of Medicine. “Health care systems often wait for patients to come to the clinic or hospital, but if you just wait for patients to come to you, there are a lot of people in need who will be missed.”
Whatever its role in driving the mental health crisis affecting young people, the new study suggests, social media can be used as a unique tool in detecting concerning messages for those paying attention.
In this case, trained staff with the Safe Social Spaces intervention program contacted more than 3,000 young people who openly shared their experience with emotional problems on social media. The program estimates that, through supportive dialogue, 163 instances of self-harm, which can include suicide attempts, have been avoided so far.
Teo acknowledged the irony of using social media to achieve a positive mental health outcome.
“Experiences on social media can be stressful, but what I love about this program is that it illustrates a way to use forums online for a good purpose,” Teo said. “It’s obviously not as black and white as saying social media is evil or screen time is all bad. We know that youth are spending time there and, as with all technologies, the important thing is in how you use it.”
In addition to Teo, co-authors on the study included Laura Levy, a graduating M.D.-M.P.H. student in the OHSU School of Medicine and the OHSU-Portland State University School of Public Health, and Angela Nielsen of Lines for Life.
Teo serves as a staff psychiatrist in the VA Portland Health Care System and his research is supported by the Veterans Health Administration Office of Research and Development, Health Systems Research.
END
Crisis intervention program leverages social media to reduce suicide risk
Study by OHSU, Lines for Life documents innovative intervention for youth through Safe Social Spaces program
2024-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An unlikely hero in evolution: worms
2024-06-01
One of Earth’s most consequential bursts of biodiversity—a 30-million-year period of explosive evolutionary changes spawning innumerable new species—may have the most modest of creatures to thank for the vital stage in life’s history: worms.
The digging and burrowing of prehistoric worms and other invertebrates along ocean bottoms sparked a chain of events that released oxygen into the ocean and atmosphere and helped kick-start what is known as the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event, roughly 480 million years ago, according ...
Detecting machine-written content in scientific articles
2024-06-01
The recent surge in popularity of AI tools such as ChatGPT is forcing the science community to reckon with its place in scientific literature. Prestigious journals such as Science and Nature have attempted to restrict or prohibit AI use in submissions, but are finding it difficult to enforce because of how challenging it is becoming to detect machine-generated language.
Because AI is getting more advanced at mimicking human language, researchers at the University of Chicago were interested in learning ...
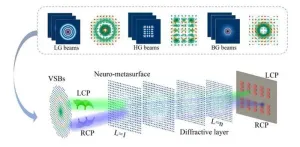
Sorting complex light beams: A breakthrough in optical physics
2024-06-01
In the dynamic realm of optical physics, researchers are continually pushing the boundaries of how light can be manipulated and harnessed for practical applications. As reported in Advanced Photonics Nexus, a groundbreaking study from the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) introduces a method for sorting and distinguishing various types of vector structured beams (VSBs), promising significant advancements in optical communication and quantum computing.
Unlike conventional light beams that propagate in simple, straight trajectories, VSBs are engineered to form complex, intricate patterns. These beams transmit ...
Supervised physical exercise improves the wellbeing of carers of the elderly
2024-06-01
Mainly older and middle-aged women, working class, with a very high prevalence of lower back pain and consequently possible psycho-affective problems and a poorer quality of life... This is the general profile of carers of the elderly. Who cares for the carer? This question or demand is not new in our society. Members of the Ageing On research group of the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) asked themselves the following question: “How can we care for the carers?”
The Ageing On group develops, ...
Polygenic risk scores give inaccurate and highly inconsistent results in embryo selection
2024-06-01
Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) are estimates of an individual’s susceptibility to a specific complex trait obtained by aggregating the effects of dozens, thousands, and potentially millions of genetic variants associated with that specific trait into a single figure. Some private companies now market PRS embryo screening to prospective parents through the use of in vitro fertilisation and pre-implantation genetic testing. While PRS has great potential for prediction in live-born (mostly adult) individuals, its accuracy ...
Molecular profiling improves diagnosis and survival for children with high risk cancers
2024-06-01
Berlin, Germany: Cancer is the leading cause of disease-related death in children in most developed countries, and at least a quarter of these patients are diagnosed with aggressive high-risk or relapsed cancers, with an expected five-year survival rate of less than 30%. Accurate diagnosis can be difficult, and survivors often suffer life-long side effects because of the toxic treatments needed to cure them. Now, researchers from Australia have shown that, by using precision medicine*, it is possible not only to obtain more accurate diagnoses, but also that using precision-guided, targeted treatments earlier improves the two year progression-free ...
New FRIB precision measurement program advances understanding of proton halos
2024-05-31
In May 2022, the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) at Michigan State University (MSU), launched its precision measurement program. Staff from FRIB’s Low Energy Beam and Ion Trap (LEBIT) facility take high-energy, rare-isotope beams generated at FRIB and cool them to a lower energy state. Afterward, the researchers measure specific particles’ masses at high precision.
The LEBIT team, led by Ryan Ringle, adjunct professor of physics at FRIB and in the MSU Department of Physics and Astronomy and senior ...
A greener, more effective way to kill termites
2024-05-31
UC Riverside scientists have discovered a highly effective, nontoxic, and less expensive way to lure hungry termites to their doom.
The method, detailed in the Journal of Economic Entomology, uses a pleasant-smelling chemical released by forest trees called pinene that reminds western drywood termites of their food. They follow the scent to a spot of insecticide injected into wood.
“We saw significant differences in the death rates using insecticide alone versus the insecticide plus pinene,” said UCR entomologist Dong-Hwan Choe, who led the discovery. “Without pinene, we got about 70% mortality. When we added it in, it was over 95%.
Native ...
Engineered circulatory systems may help fight disease
2024-05-31
The pharmaceutical drug development and approval process is a multi-step undertaking that requires a plethora of testing before reaching the market. Even then, humans respond differently to drugs depending on their individual bodies and medical needs.
Dr. Abhishek Jain, associate professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, and his lab received a grant from Texas A&M Innovation to continue developing an advanced vessel-chip deployment platform for large-scale pharmaceutical testing services that holds promise for ...
Moffitt Cancer Center and Virogen Biotechnology forge groundbreaking partnership to accelerate oncology and immunotherapy innovations
2024-05-31
TAMPA, Fla., and PLEASANTON, Calif. — Moffitt Cancer Center, a world-renowned cancer treatment and research center, and Virogen Biotechnology Inc., a clinical-stage biotechnology company, announced a groundbreaking strategic partnership today. This collaboration aims to propel the development of Virogen's cutting-edge fusion protein, VG712 (Resimmune), addressing significant unmet needs in oncology and immunotherapy.
Under this strategic alliance, Moffitt will offer Virogen priority access to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
[Press-News.org] Crisis intervention program leverages social media to reduce suicide riskStudy by OHSU, Lines for Life documents innovative intervention for youth through Safe Social Spaces program