(Press-News.org) The burial mounds of Eberdingen-Hochdorf and Asperg-Grafenbühl, known as Fürstengräber, are among the richest burials of German prehistory, with gold finds and elaborate bronze vessels. A new genetic analysis has now revealed that the two princes, buried about 10 kilometers apart, were biologically closely related. "It has long been suspected that the two princes from the burial mounds in Eberdingen-Hochdorf and Asperg ‘Grafenbühl‘ were related," says Dirk Krausse of the State Office for the Preservation of Historical Monuments, "but only now has this assumption been confirmed by the new analyses“.
For the current analyses, teeth and skull bones of the inner ear were sampled at the MPI-EVA using the latest methods, and the remaining DNA was sequenced to reconstruct the genomes of a total of 31 individuals. The two central burials stand out from the rest of the group due to their close relationship.
Two princes closely related
After establishing a genetic relationship between the two individuals, the team looked at all possible connections, such as brothers, half-siblings, grandfather and grandson, as well as uncle and nephew. "Based on the fairly precise death dates, estimates of age at death and the genetic similarity of the two princes, only one scenario comes into question as uncle and nephew, more precisely: the sister of the Hochdorf prince was the mother of the Asperg prince," explains Stephan Schiffels from MPI-EVA.
"This result shows that political power in this society was most likely inherited through biological succession, comparable to a dynasty," says Joscha Gretzinger from MPI-EVA. This is also supported by evidence of relationships between other individuals from the two mounds, as well as from the much more distant Magdalenenberg mound, which was built about 100 years earlier. Gretzinger adds: "Overall, we seem to be dealing with a broad network among the Celts in Baden-Württemberg, in which political power was underpinned by biological kinship".
But how were the Celts related to other inhabitants of Iron Age Europe beyond Baden-Württemberg? A detailed analysis of the genetic origins of this group reveals a genetic origin most likely to be found in present-day France, but which was widespread throughout southern Germany at the time. In addition, several individuals show a genetic origin from Italy, which also fits well with the objects found in the graves, many of which show Mediterranean styles.
The study is therefore an important piece of the puzzle in our understanding of European history in the Middle and Late Iron Age, which, unlike the Roman and other Early Medieval periods, can hardly be researched from written sources.
END
Kinship and ancestry of the Celts in Baden-Württemberg, Germany
Genetic analyses of Celtic burial mounds from 500 BCE reveal close relationships and provide new insights into the power structures of early Celtic elites
2024-06-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How sharks survived a major spike in Earth’s temperature
2024-06-03
The sharks we know today as the open ocean’s top predators evolved from stubby bottom dwellers during a dramatic episode of global warming millions of years ago.
A massive outpouring of volcanic lava about 93 million years ago sent carbon dioxide levels soaring, creating a greenhouse climate that pushed ocean temperatures to their hottest. UC Riverside researchers discovered that some sharks responded to the heat with elongated pectoral fins.
This discovery is documented in a paper published today in the journal Current Biology. It was made by taking body length and fin measurements from over 500 living and fossilized shark species.
“The ...
Cacao of Excellence announces the launch of the 2025 Edition of the Cacao of Excellence Awards
2024-06-03
[Rome, 3 June 2024] – Cacao of Excellence is delighted to announce the official launch of the 2025 Edition of the Cacao of Excellence Awards. Since its inception in 2009, Cacao of Excellence has been the premier platform for cacao producers to showcase the superior quality of their cacao, celebrating the diversity of flavours of cacao produced worldwide.
Held biennially, the Cacao of Excellence Awards bring together leading sensory evaluation experts and the chocolate industry to recognise and reward cacao producers who demonstrate excellence. The Awards offer the possibility for selected producers and the origins they represent to compete ...
The unexpected connection between brewing coffee and understanding turbulence
2024-06-03
In 1883 Osborne Reynolds injected ink into water in a short, clear pipe to observe its movement. His experiments showed that as the input water velocity increased, the flow went from laminar (smooth and predictable) to turbulent (unsteady and unpredictable) through the development of localized patches of turbulence, known today as “puffs.” His work helped launch the field of fluid mechanics, but, as experiments often do, it raised more questions. For example, why do these transitions between laminar and turbulent flows occur and how can the transitions be characterized quantitatively?
Although ...
Researchers call for return of Sumas Lake following devastating 2021 floods
2024-06-03
A new proposal has emerged in response to the November 2021 floods that swept Sumas Prairie in the Fraser Valley, British Columbia, causing mass evacuations and millions in damages.
Instead of rebuilding the dykes to manage water flows and prevent future floods, scientists at UBC, along with members of the Sumas First Nation and other research partners, suggest an alternative: let Sumas Lake, which was drained in the early 1920s and converted into the farmland known as Sumas Prairie, return to its natural state.
This ...
Transition-metal-free zeolite catalyst for direct conversion of methane to methanol
2024-06-03
In light of the waste-to-wealth movement, technology for converting greenhouse gases into value-added materials has gained significant attention in recent years. One such technology is the catalytic conversion of methane into methanol, a widely used industrial solvent and raw material for chemical synthesis. The industrial process for conversion of methane to methanol is extremely energy and resource-intensive. In the past decade, scientists have developed several catalyst systems that can enable direct oxidation of methane to methanol. However, most of them are based on ...
Retrospective study based on electronic health records finds popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs associated with reduction in incidence and recurrence of alcohol-use disorder by at least half
2024-06-03
CLEVELAND—A new study by researchers at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine reveals that the popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs Wegovy and Ozempic are linked to reduced incidence and recurrence of alcohol abuse or dependence.
The team’s findings, recently published in the journal Nature Communications, may suggest a possible new treatment for excessive alcohol use—including alcohol-use disorder (AUD), a health condition that causes about 178,000 deaths in the United States each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
To date, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ...
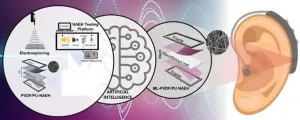
Enhancing nanofibrous acoustic energy harvesters with artificial intelligence
2024-06-03
(LOS ANGELES) June 3, 2024 – Scientists at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), have employed artificial intelligence techniques to improve the design and production of nanofibers used in wearable nanofiber acoustic energy harvesters (NAEH). These acoustic devices capture sound energy from the environment and convert it into electrical energy, which can then be applied in useful devices, such as hearing aids.
Many efforts have been made to capture naturally occurring and abundant energy sources ...
Research pioneer and paradigm-shifting thought leader for breast cancer precision medicine to receive the 2024 Szent-Györgyi Prize for Progress in Cancer Research
2024-06-03
June 3, 2024 (Rockville, MD)
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) is announcing that the blue-ribbon selection committee, composed of world-renowned research leaders and visionaries, has awarded the 2024 Szent-Györgyi Prize for Progress in Cancer Research to Dennis J. Slamon, M.D., Ph. D. from UCLA Health for his groundbreaking research discoveries that helped to shape the field of precision medicine for breast cancer patients.
The cancer research community will celebrate Dr. ...
Assessing the environmental and downstream human health impacts of decentralizing cancer care
2024-06-03
About The Study: This cohort study found that using decentralization through telemedicine and local care may substantially reduce cancer care’s greenhouse gas emissions; this corresponds to small reductions in human mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Gregory A. Abel, M.D., M.P.H., email gregory_abel@dfci.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2744)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Telehealth can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with cancer care, study finds
2024-06-03
BOSTON – Telemedicine visits for cancer care may not only be more convenient and easier to schedule than in-person appointments, they're also better for the planet, new research by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists shows.
Based on an analysis of data from a regional cancer center, the researchers calculate that, nationwide, cancer care that utilizes telehealth and local care would generate 33.1% less greenhouse gas emissions than the traditional model of in-person care, primarily because of reduced travel to medical appointments. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
[Press-News.org] Kinship and ancestry of the Celts in Baden-Württemberg, GermanyGenetic analyses of Celtic burial mounds from 500 BCE reveal close relationships and provide new insights into the power structures of early Celtic elites