(Press-News.org) Researchers have discovered sustained hunting by humans prevented the woolly rhinoceros from accessing favourable habitats as Earth warmed following the Last Ice Age.
An international team of researchers, led by scientists from the University of Adelaide and University of Copenhagen, used computer modelling to make the discovery, shedding light on an aeons-old mystery.
“Using computer models, fossils and ancient DNA, we traced 52,000 years of population history of the woolly rhinoceros across Eurasia at a resolution not previously considered possible,” said lead author Associate Professor Damien Fordham, from the University of Adelaide’s Environment Institute.
“This showed that from 30,000 years ago, a combination of cooling temperatures and low but sustained hunting by humans caused the woolly rhinoceros to contract its distribution southward, trapping it in a scattering of isolated and rapidly deteriorating habitats at the end of the Last Ice Age.
“As Earth thawed and temperatures rose, populations of woolly rhinoceros were unable to colonise important new habitats opening up in the north of Eurasia, causing them to destabilise and crash, bringing about their extinction.”
An iconic species of megafauna, the woolly rhinoceros had thick skin and long fur, and it once roamed the mammoth step of northern and central Eurasia, before its extinction around 10,000 years ago.
This recent discovery, published in PNAS, contradicts previous research that found humans had no role in the extinction of the woolly rhinoceros – despite the animal co-occurring with humans for tens of thousands of years prior to its extinction.
“The demographic responses revealed by our analysis were at a much higher resolution to those captured in previous genetic studies,” said Professor Eline Lorenzen, from the University of Copenhagen’s Globe Institute.
“This allowed us to pinpoint important interactions that woolly rhinoceroses had with humans and document how these changed through space and time. One of these largely overlooked interactions was persistent low levels of hunting by humans, probably for food.”
Humans pose a similar environmental threat today. Populations of large animals have been pushed into fragmented and suboptimal habitat ranges due to over hunting and human land-use change.
There were 61 species of large terrestrial herbivores – weighing more than one tonne – alive in the late Pleistocene, and only eight of these exist today. Five of those surviving species are rhinoceroses.
“Our findings reveal how climate change and human activities can lead to megafauna extinctions,” said Professor David Nogues-Bravo, from the University of Copenhagen, who was a co-author of this study.
“This understanding is crucial for developing conservation strategies to protect currently threatened species, like vulnerable rhinos in Africa and Asia. By studying past extinctions, we can provide valuable lessons for safeguarding Earth’s remaining large animals.”
END
Human activity contributed to woolly rhinoceros’ extinction
2024-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hot weather increases risk of emergency hospitalisations for patients with multimorbidity
2024-06-04
Australians are no strangers to long, hot summers, but new Griffith University research has looked at the impact of hot weather on patients with pre-existing chronic diseases and how it increases their risk of being hospitalised.
The research, recently published in eBioMedicine, found the risk of hospitalisation increased with the number of pre-existing chronic diseases during hot weather.
Individuals over the age of 65 with multimorbidity, defined as having two or more chronic diseases, were most at risk during hot weather.
Dr Zhiwei Xu from Griffith’s School ...
Sunshine spurs spending: Investors bet big on sunny days
2024-06-04
It’s often said we can’t control the weather. But what if the weather controls how and when we invest our money? More specifically, what if the skies control how much we’re willing to gamble in the stock market?
New research by the University of South Australia has found a connection between pleasant weather conditions and higher investment in lottery-like stocks.
Lottery-like stocks are cheap compared to other stocks and, like lottery tickets, they can be seen as an opportunity to make a substantial gain. However, the chance of a higher return is minimal, and it’s therefore considered a high-risk investment. A study by UniSA finance researchers ...
Novel triple antibiotic combination offers breakthrough in combatting antibiotic resistance
2024-06-04
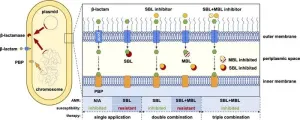
In the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance, a new study published in Engineering by Zhuoren Ling’s research team unveils a promising triple combination of antibiotics that significantly expands our arsenal against drug-resistant bacteria. Titled “The Triple Combination of Meropenem, Avibactam, and a Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitor Optimizes Antibacterial Coverage Against Different β-Lactamase Producers,” the research sheds light on a novel approach to tackle one of the most pressing global ...
Key nutrients help plants beat the heat
2024-06-04
LA JOLLA (June 4, 2024)—Global temperatures are on the rise, with experts projecting an increase of 2.7°F by 2050. Because plants cannot regulate their own temperatures, they are especially sensitive to these temperature changes. In higher temperatures, plants instruct their root systems to grow faster, creating long roots that stretch through the soil to absorb more water and nutrients. While this response may help the plants in the short term, new research suggests it’s both unsustainable for the plants and potentially ...
UTA scientists recognized nationally for inventions and innovation
2024-06-04
Researchers from The University of Texas at Arlington received 20 utility patents for their work in 2023, contributing to the University of Texas System’s overall ranking of No. 3 in the Top 100 U.S. Universities Granted U.S. Utility Patents in 2023 list.
Compiled by the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), the rankings are based on data obtained from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. The University of California system and Massachusetts Institute of Technology claimed the top ...
Inflight alcohol + cabin pressure may threaten sleeping passengers’ heart health
2024-06-04
The combination of alcohol plus cabin pressure at cruising altitude may threaten sleeping plane passengers’ heart health, particularly on long haul flights, suggests the first study of its kind, published online in the respiratory journal Thorax.
The duo lowers the amount of oxygen in the blood (SpO2) and raises the heart rate for a protracted period, even in the young and healthy, the findings indicate.
The higher the alcohol consumption, the greater these effects might be, particularly among older passengers and those with pre-existing medical conditions, say ...
High excess death rates in the West for 3 years running since start of pandemic
2024-06-04
Excess death rates have remained high in the West for three years running since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, finds a data analysis of 47 countries published in the open access journal BMJ Public Health.
This is despite the implementation of various containment measures and the availability of COVID-19 vaccines, giving rise to “serious cause for concern,” say the researchers who call on governments and policymakers to thoroughly investigate the underlying causes.
The researchers wanted to gauge the effectiveness of the response to the health crisis ...
Facial thermal imaging + AI accurately predict presence of coronary artery disease
2024-06-04
A combination of facial thermal imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) can accurately predict the presence of coronary artery disease, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Health & Care Informatics.
This non-invasive real-time approach is more effective than conventional methods and could be adopted for clinical practice to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and workflow, pending testing on larger and more ethnically diverse numbers of patients, suggest the researchers.
Current guidelines for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease rely on probability assessment of ...
New Durham University study shows selective breeding has constrained communication abilities in domestic dogs compared to wolves
2024-06-04
-With images and video-
A new study from researchers at Durham University has found that the process of domestication and selective breeding has limited the ability of domestic dogs to use facial expressions to convey affective states (emotions) as effectively as their wolf ancestors.
The research, published in Nature’s Scientific Reports, used an extended Dog Facial Action Coding System to analyse video recordings of captive wolves and domestic dogs during spontaneous social interactions and reactions to external stimuli.
The researchers identified nine distinct affective ...
Frequent mowing puts poisonous weed into survival mode
2024-06-04
By John Lovett
University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture
Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — A study of the effects of mowing on a common weed has found that what doesn’t kill you can make you stronger.
A study published in Nature’s Scientific Reports has found that frequent mowing of Solanum elaeagnifolium may help create a “superweed.”
Solanum elaeagnifolium — also known as silverleaf nightshade — can be found from south Texas to South Africa and Greece, infesting fields and soaking up valuable nutrients intended for cash crops. The weed with purple flowers – sometimes white and light ...