DNA methylation clocks for estimating biological age in Chinese cohorts
2024-06-04
(Press-News.org)
The ovary is an essential organ for female fertility, and its age-dependent decline in function is a major cause of infertility. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying ovarian aging are still not well understood, particularly in higher vertebrates like primates. In this study, researchers used spatiotemporal transcriptomics to analyze the gene expression patterns in young and aged primate ovaries.
Key findings from the study include:
The study identified significant changes in DNA methylation associated with aging. Principal component analysis revealed a reduction in global DNA methylation levels and an increase in methylation entropy with age. Specific differential methylation positions (DMPs) were identified, with distinct patterns of hypermethylation and hypomethylation linked to gene regulation during aging.
The iCAS-DNAmAge clock was developed using 65 CpG sites, with 35 upregulated and 30 downregulated with age. This clock demonstrated high accuracy in predicting age in both the Quzhou and CAS cohorts, outperforming previous DNA methylation clocks in these populations.
The researchers created multi-modal aging clocks (compositeAge, facialAge, transAge, etc.) based on diverse biological datasets. These clocks showed strong correlations with chronological age and health status, indicating their robustness as biological age predictors.
The study validated the predictive power of the iCAS-DNAmAge clock and multi-modal clocks in different Chinese cohorts, emphasizing their potential for generalization. The clocks were highly correlated with health metrics and could predict age-related disease risks and lifestyle factors.
The study developed and validated a new DNA methylation clock (iCAS-DNAmAge) and multi-modal aging clocks specifically for Chinese cohorts. These clocks provide accurate estimates of chronological age and are associated with various health and aging-related factors. The iCAS-DNAmAge clock outperformed existing DNA methylation clocks, demonstrating high predictive accuracy and robustness. Multi-modal aging clocks, derived from a combination of biological datasets, offer comprehensive insights into the aging process. The findings enhance the understanding of DNA methylation's role in aging and present valuable tools for assessing biological age and informing aging intervention strategies. This research paves the way for further exploration of DNA methylation clocks in different ethnic populations and their application in personalized medicine and aging research. The work entitled “ DNA methylation clocks for estimating biological age in Chinese cohorts ” was published on Protein & Cell (published on Mar. 14, 2024).
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-04
Optical waves propagating through air or multi-mode fiber can be patterned or decomposed using orthogonal spatial modes, with far-ranging applications in imaging, communication, and directed energy. Yet the systems that perform these wavefront manipulations are cumbersome and large, restricting their utilization to high-end applications. The development of a Free-Standing Microscale Photonic Lantern Spatial Mode (De-)Multiplexer using 3D Nanoprinting, as revealed by a recent study, marks a significant advancement in photonic technology. This spatial multiplexer, characterized by its compactness, minimal footprint, and ability to directly print ...
2024-06-04
A comprehensive new study by Tulane University’s Newcomb Institute and the University of California San Diego School of Global Policy and Strategy has quantified the staggering economic impact of intimate partner violence in California, revealing billions in costs that deeply affect survivors, communities and taxpayers across the state.
The report, “The Costs of Intimate Partner Violence in California,” reveals a cost of $73.7 billion to the state in health care, lost productivity and income and criminal justice ...
2024-06-04
An international research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has uncovered in a recent research project that people’s beliefs in science and religion are primarily shaped by the words of others, rather than their personal experiences. The study could help enhance public understanding of people’s belief formation in important scientific issues, such as climate change and vaccination.
Conventionally, people are generally more confident about the existence of scientific phenomena, like oxygen, than religious phenomena, like God, as it is thought that people can experience oxygen, for instance, while it is harder to observe ...
2024-06-04
Researchers have discovered sustained hunting by humans prevented the woolly rhinoceros from accessing favourable habitats as Earth warmed following the Last Ice Age.
An international team of researchers, led by scientists from the University of Adelaide and University of Copenhagen, used computer modelling to make the discovery, shedding light on an aeons-old mystery.
“Using computer models, fossils and ancient DNA, we traced 52,000 years of population history of the woolly rhinoceros across Eurasia at a resolution not previously considered possible,” said lead author Associate ...
2024-06-04
Australians are no strangers to long, hot summers, but new Griffith University research has looked at the impact of hot weather on patients with pre-existing chronic diseases and how it increases their risk of being hospitalised.
The research, recently published in eBioMedicine, found the risk of hospitalisation increased with the number of pre-existing chronic diseases during hot weather.
Individuals over the age of 65 with multimorbidity, defined as having two or more chronic diseases, were most at risk during hot weather.
Dr Zhiwei Xu from Griffith’s School ...
2024-06-04
It’s often said we can’t control the weather. But what if the weather controls how and when we invest our money? More specifically, what if the skies control how much we’re willing to gamble in the stock market?
New research by the University of South Australia has found a connection between pleasant weather conditions and higher investment in lottery-like stocks.
Lottery-like stocks are cheap compared to other stocks and, like lottery tickets, they can be seen as an opportunity to make a substantial gain. However, the chance of a higher return is minimal, and it’s therefore considered a high-risk investment. A study by UniSA finance researchers ...
2024-06-04
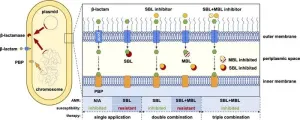
In the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance, a new study published in Engineering by Zhuoren Ling’s research team unveils a promising triple combination of antibiotics that significantly expands our arsenal against drug-resistant bacteria. Titled “The Triple Combination of Meropenem, Avibactam, and a Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitor Optimizes Antibacterial Coverage Against Different β-Lactamase Producers,” the research sheds light on a novel approach to tackle one of the most pressing global ...
2024-06-04
LA JOLLA (June 4, 2024)—Global temperatures are on the rise, with experts projecting an increase of 2.7°F by 2050. Because plants cannot regulate their own temperatures, they are especially sensitive to these temperature changes. In higher temperatures, plants instruct their root systems to grow faster, creating long roots that stretch through the soil to absorb more water and nutrients. While this response may help the plants in the short term, new research suggests it’s both unsustainable for the plants and potentially ...
2024-06-04
Researchers from The University of Texas at Arlington received 20 utility patents for their work in 2023, contributing to the University of Texas System’s overall ranking of No. 3 in the Top 100 U.S. Universities Granted U.S. Utility Patents in 2023 list.
Compiled by the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), the rankings are based on data obtained from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. The University of California system and Massachusetts Institute of Technology claimed the top ...
2024-06-04
The combination of alcohol plus cabin pressure at cruising altitude may threaten sleeping plane passengers’ heart health, particularly on long haul flights, suggests the first study of its kind, published online in the respiratory journal Thorax.
The duo lowers the amount of oxygen in the blood (SpO2) and raises the heart rate for a protracted period, even in the young and healthy, the findings indicate.
The higher the alcohol consumption, the greater these effects might be, particularly among older passengers and those with pre-existing medical conditions, say ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] DNA methylation clocks for estimating biological age in Chinese cohorts